10 Trends will reshape the technology landscape of Vietnamese banks in the next 5 years.
In 2018, FPT introduced the applying of banking 3.0 and emerged technology such as AI, Big Data and Analytics, RPA, eKYC … to banks in Vietnam though a series of C-level roadshows. After the past five years, these technologies have been widely applied to use by most banks in Vietnam. Now, at the end of year 2023, we should look ahead and predict which technology trends will significantly impact to the operations of fintech and banking industry in the next five years. This article is built upon experience and understanding of Vietnamese BFS market, combined with references from reliable technology sources and market surveys … to provide a fresh, comprehensive perspective on the technological landscape in the financial and banking sectors. From this, we could formulate strategic directions for investing in technology, developing new products for banking and fintech.
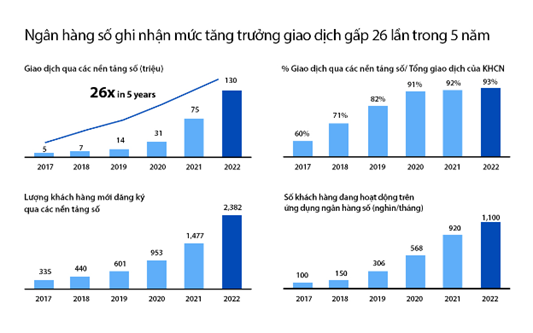
1. Digital transactions will extremely increase, posing the biggest competitive challenge to traditional card transactions.
The digital banking systems are being widely developed and adopted by banks. The bank’s policies of offering the free of charge for transfer and payment transactions on digital channel have encouraged customers to extensively use these services for consumer payments. This range of using from tiny groceries/ stores to huge shopping centers, from daily manual buying and selling transactions to transactions on e-commerce platforms. With advantages in convenience, low cost, and coverage reaching the majority of customers, especially considering the low credit card ownership rates in Vietnam, digital channel payment transactions, such as Account to Account (A2A) transfers, payments through e-wallets, QR code or the use of electronic cards (eCards), are gradually replacing traditional physical card transactions. In the near future, eCards may replace regular physical cards in normal and middle levels segments. The physical credit cards made by high-end, environment friendly materials will still used in priority or higher segments. With the increasing number of daily payment and transfer transactions at a very high level, the payment and settlement systems at banks and national level need to be upgraded to meet performance requirements. Along with that, Vietnamese banks will continue to deploy and modernize core application systems such as core banking, transaction banking, treasury, risk management system to meet processing performance as well as the ability to develop new products and compliance requirements.
Source: VIB
2. Enhancing the Data Management and Governance Platforms.
Vietnamese banks are increasingly recognizing that data is a valuable asset for their daily operational activities. Data generated from operational systems as well as data collected from external sources need to be stored, managed and utilized efficiently. Customer related data must be stored and exploited in compliance with increasingly stringent regulations from authorities, such as the Decree 13/2023/ND-CP of Vietnamese Government on the protection of personal data. Banks will need to invest in enhancing data management platforms, refining policies and technology systems for Data governance. There are essentials for effectively implementing of data analytic use cases related to customer engagements and cultivation, for developing new data driven products and services, training AI models, supporting internal management, risk management and compliance.
3. Improving of Cybersecurity.
Cybersecurity is critically important for banks in the digital age. With transactions on digital channels increasing dramatically dozens of times compared to the pre-Covid period, cybersecurity is integral to overall health and stability of banks. It not only protects sensitive data and financial transactions but also ensures regulatory compliance, maintains customer trust, and preserves the operational continuity of banking services. In the coming time, Vietnamese banks will continue to improve and strengthen their cybersecurity posture. In the coming time, Vietnamese banks will continue to improve and strengthen their cybersecurity posture by implementing the combination of strategies such as:
- Conduct regular risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats.
- Implement continuous monitoring systems to detect and respond to security incidents in real-time. Using automated threat detection tools can help identify anomalies and potential security breaches promptly.
- Invest in cybersecurity training programs for bank employees to increase awareness about security best practices and the latest threats.
- Enforce multi-factor authentication for all user accounts, especially those with access to sensitive information or critical systems.
- Strengthen endpoint security by using advanced antivirus software, endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, and regular patch management. Ensure that all devices connected to the bank’s network comply with security policies.
- Incorporate secure coding practices into the software development lifecycle. Conduct regular code reviews, static and dynamic code analysis, and ensure that developers are trained in secure coding principles.
- Develop and regularly test an incident response plan to ensure a swift and effective response to security incidents.
- Foster collaboration with other financial institutions, industry partners, and law enforcement agencies to share threat intelligence and best practices.
- Implement end-to-end encryption for sensitive data both in transit and at rest. This safeguards information from being intercepted or accessed by unauthorized entities.
- Regularly assess the cybersecurity practices of third-party vendors and service providers. Ensure that they adhere to industry-standard security measures and comply with the bank’s cybersecurity requirements.
- Leverage advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to enhance threat detection capabilities. These technologies can analyze large datasets to identify patterns indicative of potential security incidents.
- Stay abreast of evolving cybersecurity regulations and compliance standards relevant to the banking industry. Ensure that the bank’s cybersecurity practices align with these requirements to avoid legal consequences.
4. Banking Process Automation leveraging by BPM, RPA and Hyper Automation.
With an extremely large number of transactions being processed daily and predicted to increase continuously, Vietnamese banks are facing challenges in improving processing speed, accuracy and reliability of transaction in order to attract customers, create a competitive advantage over competitors, but they must still meet the strict compliance requirements of SBV. To solve these challenges, banks have applied automated business processes to their operations. Banking process automation involves the use of technology such as BPM, RPA and so on to streamline and optimize various operational tasks and workflows within a bank. The goal is to enhance efficiency, reduce manual errors, improve customer experiences, and ultimately achieve cost savings. However, currently the number of banks using RPA in business processes is not many although it has proven to be very effective at banks that are applying it such as BIDV, TPBank … It is predicted that in the near future, banks will more widely use RPA and other automation technologies in various business processes. The next step forward will be the combination of RPA with AI to create super automation, creating an alliance between humans and AI in business processes.
5. The enhancements of Risk and Compliance system.
Enhancing risk management and compliance systems is crucial for banks in the digital age due to several factors associated with the digital transformation of the financial industry, especially after when serious risk incidents have occurred in the Vietnamese financial system in recent times. The State Bank of Vietnam has been tightening regulations on risk management and compliance reporting for the banking system. The regulatory landscape is evolving rapidly, with new regulations and updates to existing ones. Banks must enhance their compliance systems to navigate the complex regulatory environment effectively. Failure to comply with regulations can result in financial penalties and reputational damage. The digital age brings a heightened risk of cyber threats, including data breaches, phishing attacks, and ransomware. Banks must strengthen their risk management systems to protect customer data, financial transactions, and sensitive information from evolving cyber threats. With the increasing use of digital channels and the collection of vast amounts of customer data, banks face greater scrutiny regarding data privacy. Compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, is essential to avoid legal and reputational risks associated with privacy breaches. The rise of digital payments and transactions introduces new risks related to fraud, money laundering, and other financial crimes. Banks need robust risk management systems to detect and prevent fraudulent activities while ensuring compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations. Banks increasingly collaborate with fintech companies and other third-party providers to offer innovative digital services. Managing the associated risks, including operational, reputational, and cybersecurity risks, requires effective risk assessment and due diligence processes. Rapid technological advancements, including artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain, introduce new risks and challenges. Banks need to assess the risks associated with adopting new technologies, implement effective controls, and ensure compliance with regulations governing emerging technologies. Digital systems are susceptible to disruptions, whether due to cyber incidents, technical failures, or natural disasters. Banks must enhance their risk management practices to ensure operational resilience, minimize service disruptions, and recover quickly from incidents. Digital technologies enable banks to gather vast amounts of data. Proactive risk identification through advanced analytics and machine learning helps banks detect emerging risks, trends, and anomalies early, allowing for timely mitigation measures. Reputational risk is heightened in the digital age, where news and information spread quickly through social media and online platforms. Effective risk management and compliance practices help banks mitigate reputational risks associated with incidents such as data breaches, fraud, or non-compliance. In the digital age, customers expect secure and transparent financial services. Enhancing risk management and compliance systems helps build and maintain customer trust by ensuring the security of digital transactions and protecting customer information.
Enhancing risk management and compliance systems is essential to navigate these challenges, protect against threats, and ensure the integrity, security, and compliance of digital financial services. It also contributes to maintaining the trust of customers, regulators, and other stakeholders in the digital age.
6. Hyper Personalized banking
Competitive pressure is increasing, requiring Vietnamese banks to improve products and services to attract and retain customers, especially customers of the Gen Z and 2K generations… The adoption of hyper-personalized banking is driven by the need to meet customer expectations, gain a competitive edge, enhance customer loyalty and satisfaction, and leverage data for more effective decision-making. As the financial industry continues to evolve, banks that prioritize personalization are better positioned to succeed in a rapidly changing landscape. Hyper-personalized banking involves tailoring financial services and interactions to meet the unique needs and preferences of individual customers. To implement hyper-personalized banking, financial institutions can leverage advanced technologies and data analytics. To apply hyper personalized banking, banks will have tp deploy processes and technologies such as:
- Collect and Analyze Data:
Gather comprehensive data on customer behaviors, transactions, preferences, and demographics.
Utilize advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to gain insights from the collected data.
- Customer Segmentation:
Identify different customer segments based on their financial needs, preferences, and behaviors.
Create personalized profiles for each segment to better understand their requirements.
- Personalized Product and Service Recommendations:
Use customer data to recommend tailored financial products and services.
Leverage machine learning algorithms to predict customer needs and suggest relevant offerings.
- Customized Communication:
Personalize communication channels such as emails, mobile apps, and websites to deliver targeted messages.
Use customer data to send personalized promotions, updates, and alerts.
- AI-Powered Chatbots and Virtual Assistants:
Implement AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants to provide real-time, personalized support and use natural language processing to understand customer queries and offer customized solutions.
- Personal Financial Management (PFM) Tools:
Provide customers with PFM tools that offer insights into their spending habits, budgeting, and financial goals.
Use AI to analyze transactions and suggest ways to save or invest based on individual financial situations.
- Biometric Authentication:
Enhance security and convenience by implementing biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint or facial recognition.
Ensure a seamless and secure user experience for customers.
- Predictive Analytics for Risk Management:
Employ predictive analytics to assess and manage financial risks associated with individual customers.
Identify potential issues before they escalate and offer proactive solutions.
- Real-time Transaction Monitoring:
Implement real-time transaction monitoring to detect unusual or suspicious activities.
Use AI to analyze patterns and flag potential fraudulent transactions promptly.
- Continuous Improvement:
Regularly update and refine personalized banking strategies based on evolving customer needs and technological advancements.
Collect feedback from customers to understand their experiences and make necessary adjustments.
- Compliance and Data Security:
Prioritize compliance with relevant regulations to ensure the security and privacy of customer data and implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect against data breaches and unauthorized access.
7. The widely development of Banking as a Service (BaaS) model
The widely development of Banking as a Service (BaaS) model where traditional banking services are offered as a set of digital services or APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), allowing third-party companies to integrate these financial services into their own applications and platforms. BaaS is reshaping the financial services landscape in Vietnam by promoting collaboration between traditional banks and emerging fintech players. BaaS enables non-banking entities, such as fintech startups, technology companies, or other financial institutions, to leverage the infrastructure and capabilities of traditional banks without having to build and maintain a full banking system. BIDV is a pioneer bank by successfully deploying the Open APIs system and they are providing connections to partner companies in the common ecosystem to provide financial services to consumer clients. Other banks are also interested in researching and implementing Open banking services. In the near future, ecosystems will soon appear in providing financial services to individuals, SME and enterprise businesses with traditional banks at the center, connecting with other service providers, e-commerce, insurance, and more …
8. The applying of the Generative AI (Gen-AI).
Generative AI is making great strides in technology. Chat GPT in particular has been a phenomenon with many different sectors experimenting with and speculating around potential uses cases. Soon, Vietnamese banks will apply the generative AI in their operation. Generative AI can be applied in various ways within the banking industry to enhance efficiency, customer experience, and decision-making processes. Here are several ways in which generative AI can be used in banks:
- Customer Services Chatbots, banks are using AI-powered chatbots for customer services but they will soon upgrade to generative AI-powered chatbots. These chatbots can simulate natural language interactions, improving the overall customer experience.
- Credit scoring and Risk Assessment, bank could use generative AI to analyze a wide range of data, including non-traditional data sources, to assess creditworthiness and manage risks more effectively. Generative models can identify relevant patterns and make predictions based on the available information.
- Automated Report Generation, Generative AI can automate the generation of reports and documents, saving time for bank employees. This can include regulatory compliance reports, financial statements, and other documentation that requires data synthesis.
- Fraud Detection and Prevention, Generative AI models can analyze patterns in transaction data to identify anomalies and potential instances of fraud. They can learn from historical data to detect new and evolving fraud patterns, providing an additional layer of security.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Compliance, Banks could use generative AI to enhance AML compliance efforts by analyzing vast amounts of transaction data and identifying suspicious patterns. These models can adapt to changing money laundering techniques and improve the accuracy of detection.
- Natural Language Processing for Contracts: Apply generative models with natural language processing capabilities to review and analyze legal contracts. This can streamline contract management processes, identify potential risks, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Customer Interaction and Engagement: Implement generative AI for creating personalized marketing content and communication. This can enhance customer engagement by tailoring messages based on individual preferences, transaction history, and other relevant data.
- Cybersecurity: Generative AI can play a role in cybersecurity by identifying and responding to potential security threats. This includes the use of generative models for anomaly detection, predicting potential vulnerabilities, and improving overall system security.
- Voice and Speech Recognition for Authentication: Use generative AI for voice and speech recognition to enhance authentication processes. This can provide an additional layer of security for accessing accounts and conducting transactions.
- Predictive Analytics for Financial Markets: Apply generative AI models to analyze market trends and make predictions regarding investment opportunities. These models can process large datasets and identify patterns that may be challenging for traditional analytical methods.
9. Transitioning technology infrastructure to hybrid clouds.
Vietnamese banks are continually considering the transition their technology infrastructure to cloud. In recent times, some banks such as TCB, VIB… have moved their infrastructure to a number of public cloud platforms. However, public cloud platforms have also revealed a number of limitations such as high costs, performance affected by unstable internet connections, suppliers do not have data centers in Vietnam as well as data security and confidential regulations of government and SBV. Undoubtedly, the benefits that cloud computing brings to banks and financial institutions such as it allows banks to scale their IT infrastructure up or down based on demand. This flexibility is crucial for handling fluctuations in transaction volumes, supporting new services, and adapting to changing market conditions. Cloud computing facilitates faster deployment of new technologies and services. Banks can leverage the innovation and agility provided by the cloud to quickly roll out new features, products, or services without the delays associated with traditional infrastructure deployment. Vietnamese banks will increasingly consider the transition to a hybrid cloud infrastructure for several compelling reasons, balancing the advantages of cloud computing with the unique requirements and concerns of the financial industry. Hybrid cloud solutions offer cost savings through the ability to use public cloud resources for non-sensitive workloads, avoiding the need to invest in and maintain on-premises hardware for peak loads. It enables banks to optimize costs by utilizing a mix of public and private cloud resources based on their specific needs. Hybrid cloud models allow banks to keep sensitive data and critical applications within a private cloud or on-premises environment, addressing security and compliance concerns. This is particularly important in the financial industry, where data protection and regulatory compliance are top priorities. Hybrid cloud provides banks with robust disaster recovery and business continuity capabilities. By maintaining critical systems on-premises or in a private cloud and utilizing the redundancy and resilience of the public cloud, banks can ensure the availability of services in the event of disruptions. Hybrid cloud solutions often provide centralized management tools, allowing banks to oversee and manage their entire IT infrastructure more efficiently. This centralized approach simplifies administration and enhances overall operational efficiency.
By adopting a hybrid cloud model, banks can harness the benefits of cloud computing while addressing the unique challenges and requirements of the financial industry, including security, compliance, and data control. This approach positions banks to be more agile, innovative, and responsive to the dynamic landscape of the financial services sector.
10. Branches Digitization
Vietnamese banks will continue to promote the digitalization of branches and transaction offices to enhance the image of modern, friendly banking, attract customers and increase competitiveness. Banks are increasingly digitizing their branches to adapt to changing customer preferences, enhance operational efficiency, and remain competitive in the rapidly evolving financial industry. Digitalization at bank branches will follow the application of digital technologies to simplify customer journeys at the counter, increasing self-service customer services based on kiosk banking, CDM, and STM devices… Instead of focusing on routine transactions, branches can become centers for advisory services, relationship-building, and more complex financial discussions, leveraging digital tools for efficiency in routine tasks. Applying automated processes at the counter with the support of AI/OCR, RPA/BPM will help tellers increase service productivity, reduce waiting time, and increase customers satisfaction. Reality has proven that, banks that embrace branches digital transformation gain a competitive edge in the market, such as Live-bank of TPBank, CDMS of VPBank. By offering innovative digital services, they can attract tech-savvy customers and differentiate themselves from competitors that may be slower to adopt digital solutions. In summary, the digitization of bank branches is driven by the desire to enhance customer experiences, reduce costs, and stay competitive in an industry undergoing significant technological transformation. By leveraging digital channels and technologies, banks can create a more efficient, customer-centric, and adaptable banking environment.
Exclusive article by FPT IS Technology Expert
Vu Minh Tuan
Deputy Director of Technology Consulting Center – Finance and Banking Division
FPT Information System Company.