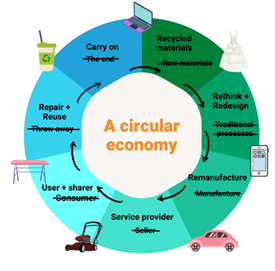
Carbon Credits: An Emerging Market and Promising Outlook in Vietnam
Over the past two decades, Vietnam’s rapid economic growth has lifted millions out of poverty and established the country as a key global manufacturing hub. Alongside these achievements, however, come increasing environmental challenges: rising greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, soaring energy demand, and mounting pressure from international trade partners to meet strict climate commitments. In response, the Government of Vietnam has pledged to achieve net–zero emissions by 2050 – aligned with the Paris Agreement and essential for maintaining global competitiveness.
Vietnam has pledged to achieve Net Zero by 2025 (Source: Internet)
One of the most critical tools to realize this ambition is the carbon credit market. More than just a financial mechanism, carbon credits serve as a bridge between economic development needs and long-term climate responsibility. Understanding how carbon credits work and unlocking their potential in Vietnam will open up significant opportunities for sustainable growth and deeper global integration.
Why We Need Carbon Credits and How They Work
A carbon credit represents the reduction, avoidance, or removal of one metric ton of CO₂ from the atmosphere. It is a highly flexible instrument that addresses multiple objectives simultaneously:
- Flexible compliance: While many companies cannot immediately overhaul their operations to fully eliminate emissions, carbon credits allow them to offset unavoidable emissions, buying time to transition to cleaner technologies. This ensures market stability and optimizes mitigation costs.
- Driving effective investment: Capital from credit trading is channeled into green projects such as renewable energy, afforestation, and ecosystem restoration-areas that achieve emission reductions at lower costs but with large, lasting impacts. This enables businesses to meet climate goals while strategically managing expenses.
- Facilitating global trade integration: More markets now require evidence of carbon reduction across supply chains. Access to carbon credits helps Vietnamese enterprises not only meet compliance requirements but also strengthen their “green” brand image and enhance credibility in international commerce.
Low-emission projects, once validated under recognized international standards, receive credits that can be sold to buyers seeking offsets. Today, two primary mechanisms exist: the compliance market and the voluntary market, which operate in parallel and complement each other.
The Benefits of Carbon Credits in Vietnam
For Vietnam, carbon credits are not merely a compliance tool but a strategic driver interlinking three pillars: economy, trade, and environment.
- Economic impact: The market opens doors to green investment for renewable energy, wind and solar power, and mangrove restoration projects. International capital not only improves infrastructure but also facilitates the adoption of advanced clean technologies that are otherwise difficult to access domestically.
- Trade competitiveness: With the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) and similar rules emerging in other markets, high-emission goods risk facing border taxes. Vietnam’s key export industries-steel, cement, textiles, and agriculture-are directly exposed. A domestic carbon credit market provides businesses with a practical solution to offset emissions, maintain price competitiveness, and preserve trade relationships.
- Environmental and social co-benefits: Carbon credit projects are often tied to mangrove restoration, reforestation, and ecosystem protection. These initiatives not only boost biodiversity and improve environmental quality but also create sustainable livelihoods for rural communities through eco-tourism and aquaculture. In this way, carbon credits become a tool that simultaneously promotes economic growth, advances social development, and enhances climate resilience.
The Potential of Vietnam’s Carbon Credit Market
Vietnam’s natural conditions, combined with clear policy direction, create strong prospects for carbon credit market growth:
- Natural capacity: Extensive forests, fertile land, and a long coastline position Vietnam to generate tens of millions of credits annually from carbon absorption and storage activities.
- Energy transition momentum: Rapid deployment of solar and wind power reduces reliance on fossil fuels and generates a substantial supply of credits once certified.
- Policy framework: The government is steadily developing monitoring, reporting, and verification systems to align with international standards. Vietnam’s domestic carbon trading exchange is expected to be fully operational by 2028, laying the groundwork for a transparent and effective market.
- Rising global demand: The voluntary carbon market is projected to exceed USD 50 billion by 2030. Multinational corporations are actively seeking high-quality credits from emerging economies-an opportunity for Vietnam to position itself as a competitive supplier.
Within this context, project developers, investors, and technology providers are the pioneers who can seize advantages before market demand far outpaces supply.
Carbon credits are not a “silver bullet” for climate change, but they are an indispensable tool on the path to a low-carbon economy. By attaching tangible market value to every ton of CO₂ reduced or removed, carbon credits mobilize green finance, support export industries, and deliver clear environmental benefits.
For Vietnam, active participation in the carbon credit market is more than a compliance measure-it is a strategic opportunity to lead in the green economy, attract international capital, safeguard ecosystems, and secure sustainable long-term growth.
References
Voluntary & Compliance Carbon Market: the difference | Regreener. (2025, March 25). https://www.regreener.earth/blog/voluntary-and-compliance-carbon-markets/
Can carbon offsets play a role in India’s compliance carbon market? (2025, March 7). 15 CEEW. https://www.ceew.in/blogs/how-can-carbon-offsets-programs-play-a-role-in-carbon-credit-market-compliance-in-india/
Castellanos, J. (2024b, August 2). Investing in carbon Credits: Navigating the emissions market. Wealth Formula. https://www.wealthformula.com/blog/investing-in-carbon-credits-emissions-market/
Capital, O. (2025, August 15). How to Invest in Carbon Credits: A Strategic Framework. Offset8 Capital. https://offset8capital.com/articles/how-to-invest-in-carbon-credits-a-strategic-framework/
| Exclusive article
by Members of the VertZéro Greenhouse Gas Inventory solution |