“Citizen Engagement” – An inevitable trend in digital transformation
1. The digital transformation aims at citizens in certain regions of the world
Global digital transformation is taking place rapidly, giving nations more opportunities to boost productivity, promote innovation and improve national competitiveness. In particular, citizens are the most important subjects of digital transformation
In Indonesia, the World Bank supports the government in enhancing the education system in remote villages through the KIAT Guru project. This project empowers people in remote areas to require teachers to come up with methods to assess students’ abilities by making learning outcomes more accessible to the people. After one year of participating in the KIAT Guru program, students’ learning results improved from a baseline of 37% to 49% in math and from 37% to 50% in language.
The Implementation of Social Accountability framework (ISAF) program in Cambodia aims to establish collaborations between civil society organizations and the government to improve service delivery quality and accountability in 605 health centers, 1,404 primary schools, and 757 commune councils, which collectively cover 75% of the country’s districts, 62% of its provinces, and 56% of its communes. According to the impact evaluation, the program has improved the availability of budget and performance statistics along with information about the services provided, resulting in a considerable increase in service provider transparency. Additional improvements included higher use of health centers, shorter wait times for services, and more polite staff.
In the city of Nantes, France, three major public debates were held on topics of primary concern to citizens, such as the energy transition or the elderly’s important role in society. From ideas to debates, the city has become the European Capital of Innovation, with the goal of engaging as many individuals, organizations, and businesses as possible in an inclusive debate to create and test new ideas. Each solution resulted in a series of citizen recommendations that were presented for the city to consider. For example, an ‘Earth office’ will fund 500 projects by 2025, or recommend that residents walk no more than 300 meters to the closest green space, which could include public gardens, parks, forests, water sources, etc. Nature in the city needs to be given high priority.
Many cities like Madrid are implementing measures to ensure that the city government, citizens, civil society, and other local players collaborate on public policy. Locals can decide how their city is shaped thanks to the Madrid Online Decision Portal, which has inspired creative solutions for green lighting, such as repurposing plastic waste as new asphalt for city roads, installing photovoltaic panels on public buildings to lower energy costs and reduce fossil fuel consumption, and making space for bicycles outside of schools.
Each country has different digital transformation projects aimed at comprehensive development, and Vietnam may learn valuable experiences from them to formulate the best course of action for its own digital transformation.
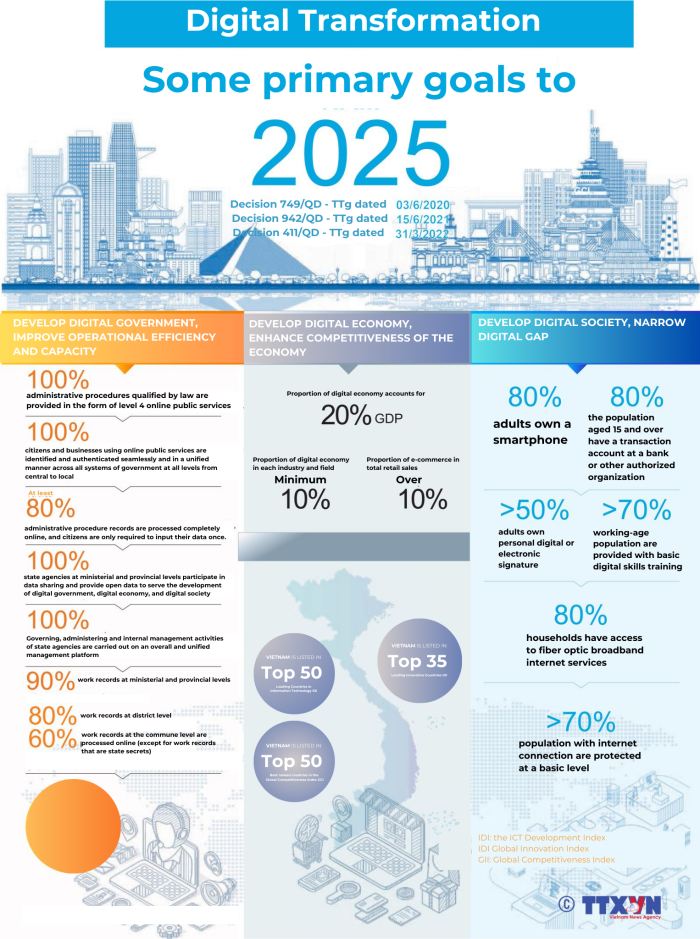
Vietnam has officially launched the VNeID application, created by the National Population Data Center of the Ministry of Public Security of Vietnam, for use by all citizens on July 18, 2022, as part of its digital transformation. This software, which is based on a database of identification, population, and electronic authentication, was created with the intention of replacing traditional documents on mobile devices, such as phones, tablets, etc. Moving forward, all Vietnamese citizens will simply need to bring their VNeID; no additional documentation is required. VneID is one of the avenues for pursuing the national digital transformation goals associated with the three pillars of digital transformation: Digital government, digital economy and digital society. Digital transformation is an important tool in building an independent and self-reliant economy, associated with proactive, extensive, substantive and effective international integration.
2. Definition and importance of Citizen Engagement
A city can only be improved through collaboration and synergy between city officials and its citizens. In recent years, the government has successfully improved citizen participation in the nation-building process and established avenues for citizens to voice their opinions. By creating cultural change in administrative districts, cities can develop into smart and livable cities.
The recent COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of increasing citizen participation in coordination and dissemination of information. Decisions are made quickly and effectively based on rapid citizen feedback and behavioral changes. From there, a new concept “Citizen Engagement” was formed.
2.1. Citizen Engagement concept and service platform
Citizen Engagement means interaction between citizens and government in a proactive, positive and transparent manner. This kind of engagement can take place at any point throughout a government’s development, during the execution of policies, or during the delivery of public services.
Citizen Engagement is an important part of the decision-making process in the government’s development process. Two-way interaction between communities and local governments has created opportunities for citizens to voice their opinions and actively engage in the decision-making process on matters impacting the areas they live in. By providing a platform for residents to express their opinions, share their difficulties and suggest ideas, cities can achieve better governance and implement improvements that will be truly beneficial for all stakeholders. This platform can be called a “Citizen Engagement Hub”.
Citizen Engagement Hubs play an important role in modern society because they provide democratic participation, facilitate citizen participation in decision-making processes, and foster openness and transparency in interaction between the community and management organizations. Citizen Engagement Hubs are digital platforms, frequently in the form of web or mobile applications, that offer online spaces for citizens to discuss, share opinions, participate in voting, and interact with community decisions.
In short, Citizen Engagement helps improve the quality of democracy and helps governments find better solutions to current challenges. Citizen Engagement Hub serves as a platform and tool for people to share and participate in decision-making related to building a better society.
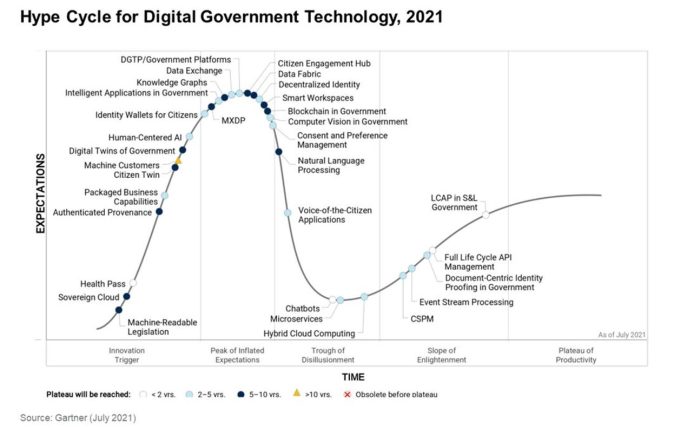
Gartner report on the importance of Citizen Engagement Hub in digital government
2.2. Interpretation of Citizen Engagement
a. Encouraging democratic engagement:
Create opportunities to participate: Through the Citizen Engagement Hub, citizens can take part in high-level decision-making processes, such as policy proposal and community project evaluation.
Create openness: These platforms expand democratic engagement by granting people the responsibility as well as the right to take part in the decision-making process.
b. Broaden your perspectives and horizons:
Gather viewpoints from a variety of sources: Citizen Engagement Hub collects input from a diverse range of sources, helping to better understand the needs and desires of the community.
Facilitate interaction between parties: To open up discussions and negotiations between the community and decision-makers.
c. Transparency and responsibility:
Enhance transparency: Citizen Engagement Hub helps improve transparency in governance, from decision-making to the utilization of public resources.
Create community responsibility: People become proactive in managing and making decisions that affect the community.
d. Facilitate changes:
Encourage creativity and innovation: Citizen Engagement Hub promotes creativity and innovation in addressing community problems.
Facilitate sustainable development: Community participation and contribution can create solutions for sustainable development and environmental adaptability.
3. Difficulties and challenges to enhance Citizen Engagement
3.1. Trust and relationships
Trust is an important aspect and serves as a basis for encouraging citizen participation in public affairs. Lack of trust can stem from previous negative experiences, dishonesty, or lack of transparency when it comes to seeking public opinions without being recognized. This leads to public indifference to important national issues such as policy development, process improvement, changes in laws, etc.
3.2. Communication between citizens and government
A lack of effective communication can seriously impede attempts to gather public opinion since it is essential to promoting public participation. There may be a loss of connection if communication channels or tools are inaccessible to or irrelevant for the target audience. Or information and messages conveyed unclearly or even inconsistently can create feelings of confusion, frustration, and distrust among the public.
3.3. Lack of awareness or understanding
Lack of awareness of available opportunities or the importance of participation is the main barrier in building community participation. This can stem from a lack of information, unclear communication, or lack of outreach efforts. Due to limited access to information, many young people might not be aware of their chances to engage fully in citizenship rights. Even when citizens are aware, some may not see the value in being involved, which might cause resistance or indifference.
3.4. Limited resources
Limited resources, whether financial, human, or physical, can impede community engagement efforts. For example, organizing events or creating platforms for citizen engagement requires a lot of costs on a large scale. Insufficient human resources could restrict outreach initiatives, which would lower citizen participation.
3.5. Cultural and language differences
Cultural and language differences can cause misunderstandings, discomfort, or exclusion. For example, if cultural norms are not acknowledged and respected, parts of the community may become hostile toward the organization or stop accepting information. Language barriers are also a major problem in promoting public participation, particularly in ethnic communities. People might find it challenging to participate if they cannot get information in a language they can comprehend.
3.6. Socioeconomic factors
Diverse socioeconomic backgrounds can result in varying needs, interests, and abilities to participate. Citizens with limited financial resources may lack access to technology or transportation, which would limit their participation. Diverse needs and interests in society may give rise to additional wants and interests, hence increasing the complexity of strategies for engaging citizens.
4. SuperApp dCitizen – Digital Citizen Super App to enhance citizen engagement
Realizing the importance of public engagement and participation in the process of administrative reform in general and digital transformation of e-government in particular, the Digital Citizen platform, including the special Digital Citizen super app, provides a number of solutions and tools to help local governments quickly access and operate more easily to facilitate greater citizen engagement.
4.1. The rationale behind creating developing SuperApp – Digital Citizen Super App
a. What is SuperApp?
SuperApp is an application that provides end users (customers, partners) with a core set of features along with access to individually developed small applications (miniapps). SuperApp was built as a platform to provide an ecosystem of miniapps that users can choose to enable for a consistent and personalized app experience.
With many tools that users can use and remove as needed, SuperApp functions similarly to a multipurpose knife. SuperApp is becoming a trend because users, especially the younger generation born in the smartphone era, demand a powerful and easy-to-use mobile-based experience. SuperApp has started gaining traction because users, particularly the younger generation born in the smartphone era, demand a powerful and easy-to-use mobile-based experience. SuperApp will grow to incorporate chatbots, IoT (Internet of Things) technology, and other immersive experiences like virtual worlds.
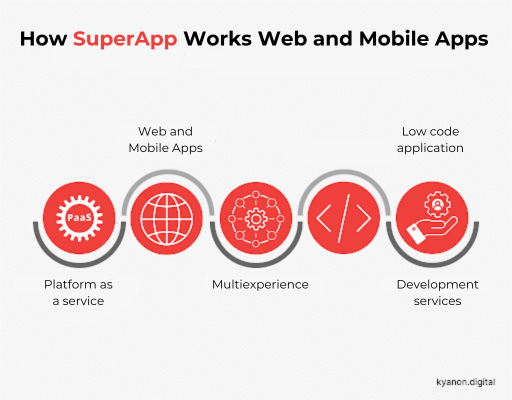
b. How does SuperApp work?
Users access a range of individual services through an ecosystem in which internal development teams and external partners build and deploy modular microapps for SuperApp. This ecosystem adds value to SuperApp by making access to a range of other services within the app seamless.
This ecosystem adds value to SuperApp by facilitating easy access to a variety of additional services within the app. For example:
- Platform-as-a-service (PaaS) providers offer cloud platform solutions
- Front-end frameworks enable deployment of miniapps in web and mobile applications
- Multiexperience development platforms (MX)
- Low-code application platforms (LCAPs)
- Development service providers.
Users can choose which miniapps to use when needed, giving them a flexible way to interact with their SuperApp. The key thing to remember is that user authentication and data exchange can be done simply, such as by using single sign-on (SSO) and tracking user preferences or application usage.
c. Develop Digital Citizen application as a SuperApp
Based on forecasts from Gartner.com: “By 2027, more than 50% of the global population will be daily active users of multiple superapps”
The Digital Citizen application plays a huge role in the digital transformation, which also serves as an effective tool to foster citizen engagement with the government, and promote public participation in administrative reform and digital transformation.
When developing a Digital Citizen application as a SuperApp, many features can be consolidated into one mobile application, saving development time and offering various competitive benefits over other development methods. Through SuperApp, people may connect more simply and quickly with the government and interact more easily in all areas of life.
4.2. Some useful solutions on the application
a. Notices from the government
Official notices are sent on mobile phone applications, which are easier and faster to distribute than traditional means such as public loudspeakers, documents, and neighborhood meetings. Editing notices can be done quickly on computers and mobile devices instead of printing paper notifications and relying on human communication. It takes far less time to issue and send notifications when this information is sent straight after compilation to the Digital Citizen app on every citizen’s smartphone rather than through door-to-door communication.
b. Local socioeconomic news
As opposed to traditional media like newspapers, radio, and television, people may read and update daily news and disseminate information faster thanks to the updating of local socioeconomic news, information on development policies, and new regulations. Additionally, users can listen directly on the app without having to read the news because it can be read aloud automatically.
c. Residential bulletin boards
With the help of the daily bulletin board on the Digital Citizen app, local authorities can stay closer to each residential group or neighborhood. For instance, the leader of the residential group or neighborhood quickly gathers or updates information directly from the ward/commune People’s Committee on the Digital Citizen management system or smartphone and promptly distributes it to citizens in the area. Regarding the citizens, their residential group or neighborhood will provide them with specific information directly through the Digital Citizen application.
d. Complaints and feedback
On the Digital Citizen app, people can freely share information, voice opinions or desires, and suggest solutions on matters pertaining to the management of rules, regulations, laws, policies, or challenges they face in their communities. Agencies, organizations, units, and individuals have the authority to handle, resolve, and respond to people through the Digital Citizen application.
e. Survey
Instead of using current manual survey forms that require printing on paper and visiting each home to get opinions, agencies and organizations can design surveys to post on the Digital Citizen application. Survey results will be automatically recorded and statistical reports can be quickly exported. People freely access the Digital Citizen application and conduct surveys without having to fill out traditional paperwork.
f. Suggestion – evaluation – sharing
People are free to comment on how to make the application better and add features that are more in line with essential everyday needs. In addition, people can also freely rate and comment on locations, information and share information on the application so that more people can access the application.
5. Conclusion
As information technology advances, particularly with regard to the current trend of artificial intelligence (AI), it will become increasingly vital to support digital transformation in order to address the key challenge of e-Government in the future. Identifying people as the center of digital transformation and the importance of citizen participation will help the Government save a great deal of time and quickly achieve the desired outcomes.
6. References
– Citizen Engagement in Public Service Delivery The Critical Role of Public Officials – UNDP Global Centre for Public Service Excellence – https://www.undp.org/sites/g/files/zskgke326/files/publications/GCPSE_CitizenEngagement_Summary_2016.pdf
– Citizen Engagement – World Bank – Apr 10, 2023 – https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/citizen-engagement#1
– Five principles for citizen engagement – Euro Cities – 9 July 2020 – https://eurocities.eu/latest/five-principles-for-citizen-engagement/
– Eurocities principles on citizen engagement – https://citizens.eurocities.eu/
– Citizen Engagement in British Columbia – https://www2.gov.bc.ca/gov/content/governments/services-for-government/service-experience-digital-delivery/citizen-engagement
– Citizen engagement as a learning experience – https://www.researchgate.net/publication/270848629_Citizen_Engagement_as_a_Learning_Experience
—————————————————————————
Exclusive Article by FPT IS Technology Expert
Pham Ngoc Khoa
Product Director
FPT IS Company Limited