Dark Data – Unveiling the Darkness
1. Have you heard of Data that is “Dark”?
Imagine a photography-lover meticulously capturing every sunrise, interesting street corner, and delicious meal he encounters. His camera roll overflows with thousands of images, but most remain unedited, unorganized, and unseen. Buried within this digital archive of moments could be stunning portfolio pieces or heartwarming memories, but the photographer is overwhelmed by the sheer volume. This scenario exemplifies the phenomenon of “picture hoarding”.
Imagine you meticulously track your expenses using a budgeting app, but never analyze your years of old receipts tucked away in a drawer. Buried within those forgotten purchases could be hidden patterns – a tendency to overspend at certain restaurants, a category consistently exceeding your budget. This untapped trove of information is a personal example of “data hoarding”.
Those hoarding actions can be significant contributors to the term “dark data”.
Dark data also lurks within organizations, stemming from a vast collection of information gathered during regular business activities but left unused. Businesses typically collect dark data alongside data of more current value to a company. Sometimes the company collects specific data thinking it will use it in the future but actually does not. Sometimes data is collected just because it can be collected, even though there’s no real use for it.
Dark data may be any or all of the following: Older, Incomplete, Incompatible, Redundant, Irrelevant. To most companies, dark data has little or no perceived value. In many instances, the company doesn’t even know it exists . It’s a hidden potential for improved operations, product development, and customer satisfaction, waiting to be unlocked.
What is Dark Data?
Gartner defines dark data as information assets collected, processed, and stored during regular activities but not used for further analysis . Think of it as digital clutter accumulating in the background, hindering your ability to see the bigger picture.
While the term “dark data” might sound ominous, it’s simply information waiting to be harnessed. Just like a cluttered attic might hold forgotten treasures, dark data can hold valuable insights. Dark Data is a friend, not a foe. Furthermore, dark data is a common occurrence in our information age – the sheer volume of data we generate daily, coupled with the lack of robust data management strategies, almost guarantees its existence.
A staggering amount of data qualifies as dark data. Research suggests over half, and potentially up to 75% or more , of a company’s information remains unused. That’s a significant portion of valuable insights gathering dust!
The dark data brief view
Examples of Dark Data
If it’s dark, it’s not that easily discovered. So where to look for dark data? What are the tell-tale signs? We can look at some examples below:
- Structured data:
- Sensor data: Manufacturing plants and logistics companies use an array of sensors to monitor everything from temperature fluctuations to machine performance. This data, while neatly organized, remains dark if not analyzed to identify potential equipment failures or optimize production processes.
- Server log files: Every click, search, and page view on your company website is recorded in server logs. Without analyzing these patterns, you can miss opportunities to optimize user experience.
- Others: electronic bank statements, medical records…
- Semi-structured data:
- Customer surveys: Businesses conduct customer surveys to gather feedback. These surveys often remain semi-structured data if not properly categorized and analyzed using sentiment analysis tools.
- Customer service call transcripts: Call center holds a wealth of semi-structured information. Customer frustrations, product feedback, and feature requests are embedded within call transcripts.
- Others: HTML code, invoices, graphs, tables and XML documents…
- Unstructured data:
- Machine log files: Complex machinery generates vast amounts of log data. Without proper tools to parse and analyze this unstructured data, it remains a cryptic record of machine activity, offering no insights into potential maintenance issues or areas for performance improvement.
- Social media mentions: Brand mentions, customer reviews, and competitor analysis can be gleaned from social media platforms. This unstructured data requires sentiment analysis tools to transform it into actionable insights.
- Others: Email correspondences, PDFs, text documents, call center recordings, chat logs and surveillance video footage…
While the sheer volume of untapped potential within dark data is evident, its existence isn’t a recent discovery. To understand how we arrived at this point, let’s look at the timeline below.
Dark Data: A Timeline of Discovery
- 2012: “Dark data” emerges, highlighting the challenge of stored data with unknown value.
- 2013: Gartner refines the concept and explores analysis methods.
- 2015: IBM reveals the dark side of unused sensor data in the age of IoT.
- 2016: A study shows a vast amount of data remains hidden from key decision-makers.
- 2017: Major acquisitions signal efforts to unlock dark data’s potential.
- 2018: The definition expands to encompass hidden data beyond traditional sources.
2. The cost of Darkness
In today’s data-driven world, failing to utilize all available information can be a significant disadvantage. Dark data, the vast amount of unanalyzed information collected by organizations, presents a hidden cost with untapped potential. Here’s why you should be concerned about dark data:
Financial Burden
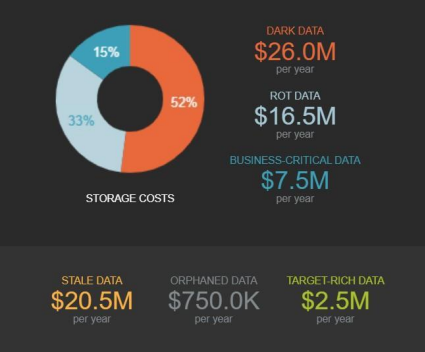
- Storage Costs: Storing unused data requires physical or digital infrastructure, leading to increased expenses as data volume grows. A Veritas study reveals that 52% of the average company’s data storage budget is spent on dark data. This translates to millions of dollars wasted on storing information with no current value. Your company is probably devoting half of your budget to store data you don’t use.
Veritas Study
- Regulatory Compliance: Data privacy laws apply to all data, even dark data, leading to potential fines for non-compliance.
- Inefficiencies: Managing large data sets, including dark data, slows down retrieval and analysis, reducing productivity and increasing labor costs.
- Security Risks: Dark data can be a security liability, increasing the risk of breaches and data loss.
A 2019 study revealed companies like Netflix spend millions storing data on AWS, a significant portion of which might be dark data. Similarly, data breaches involving dark data can incur hefty fines, as seen in the Equifax case (Settlement: $1.38 billion) .
Missed Opportunities
- Limited Data Analysis: Analytics tools produce the highest quality of data analysis when they have access to complete data. The lack of access to dark data limits the pool of analyzable information. A 2015 IBM report highlights that 60% of dark data loses value rapidly after generation .
- Unexploited Potential: Untapped dark data holds valuable customer, business, and operational insights. This data can reveal crucial information on customer behavior, network security patterns, and investment trends. Competitors leveraging dark data can gain an edge, leading to lost revenue or market share for those who don’t.
Security Concerns
Unsecured dark data can be exploited by attackers seeking operational insights or document structures within an organization. This can lead to data leaks or regulatory fines if proper data inventory and access controls are not implemented. Information integrity is vital, and businesses must ensure the source and quality of data used for analysis.
Fortunately, advancements in technologies and analytics offer solutions for handling dark data. These techniques allow for large-scale, cost-effective, and automated analysis, minimizing the resources needed to unlock the value of dark data. Also, by employing the right strategies, organizations can transform dark data from a hidden cost into a competitive advantage. The next section of this paper talks about how we can harness the power of dark data.
3. Harness the power of Dark data
Between 2022 and 2023 alone, the data lake market witnessed a surge, with its value projected to reach over $34 billion by 2030 . However, the initial promise of data lakes – that simply having all your data in one place would unlock insights – hasn’t always materialized. Much of this data remains unstructured and unused, transforming the data lake into a dark data swamp. Organizations are recognizing the need for a more sophisticated approach to data management. The following three-step roadmap is a proposed solution to tackle this challenge – to shed light on Dark Data.
Step 1: Laying the Foundation
Our journey begins with establishing a solid foundation. This first part focuses on two key areas:
- Data Assessment: Here, we move beyond the data lake by conducting a thorough data assessment. Look beyond traditional sources like ERP and Point-of-Sale (POS) systems. Server logs, social media interactions, sensor data – all these can be potential goldmines of dark data. As the saying goes, “All dark data should be traceable to a source” Data audits play a crucial role, revealing sources like customer transactions, system logs, or even data streams from Internet of Things (IoT) devices .
- Data Governance: The first step is to build a strong data culture within your organization is start building proper governance. This involves setting clear ownership and access control protocols, defining data retention policies based on compliance and value, and fostering a strong data culture within your organization. Tools like IBM Watson Knowledge Catalog is one prominent candidate to execute large-scale data governance for a corporation.
Step 2: Adopting Tools for Transformation
Once you’ve identified your dark data and established good governance practices, it’s time to equip yourself with the right tools. Here, there are three key areas for transformation:
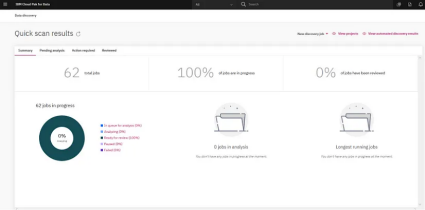
- Data Classification: You can classify data based on business needs and compliance requirements, prioritizing the most valuable information for further exploration. Tools like IBM Watson Knowledge Catalog with its Automated Discovery (AD) and Quick Scan (QS) functionalities can help you understand the purpose and potential usefulness of your dark data. Quick Scan is extremely fast and built for a shallow analysis of millions of data elements.
For some use cases, there is a need for a very deep investigation of a more limited number of data elements that an enterprise would define as critical to their business. Automated Discovery offers the features needed for a deep analysis and investigation of critical data elements within an enterprise.
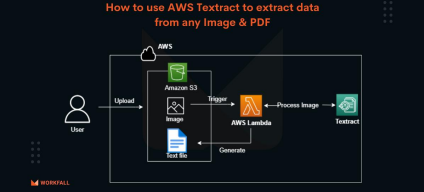
- Data Extraction: Unlocking the secrets within your dark data requires specialized tools. Here are a few options to consider: DeepDive (open source developed by Standford University), Amazon Textract from Amazon Web Services (AWS), or Dark Vision ( technology demonstrator that uses IBM Watson services to extract dark data from videos). These tools can extract valuable information from various formats like text, images, and even video data.
How to use Amazon Textract to extract data from any Image & PDF
How Dark Vision processes videos to discover what’s inside of them
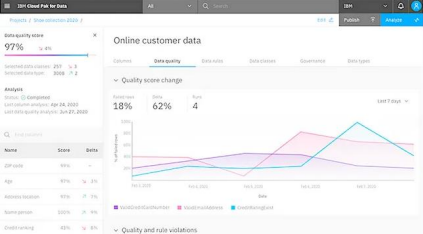
- Data Visualization: Implement tools that allow you to see the bigger picture by bringing data from all sources, including dark data, onto a single platform. This helps identify trends and insights hidden within the data that might not be readily apparent in its raw form.
Step 3: Embracing the Future
The final part of the journey focuses on long-term strategies for maximizing the value of your dark data:
- Cloud Storage: Consider migrating data storage to the cloud for improved accessibility, scalability, and real-time data processing. Cloud platforms like Google Cloud Platform (GCP) with its suite of tools (Cloud Vision API, Document AI, AutoML, Natural Language Processing (NLP) API) offer functionalities specifically designed to handle dark data.
- AI and Machine Learning Adoption: Invest in AI and Machine Learning tools like Snorkel (open source developed by Stanford University) and Azure Cognitive Services from Microsoft (with functionalities like Computer Vision, Form Recognizer, Text Analytics). These tools can process, analyze, and secure your dark data at scale, identifying patterns, exceptions, and potential business insights within the data. Additionally, Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) solutions that combine Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and AI can be instrumental in extracting valuable information from various document formats.
Some additional considerations
- Security: Ensure all data, including dark data, is properly secured to mitigate cyber security risks. Apply strong encryption standards to your data, including in-house server data and that which is in cloud storage.
- Compliance: Stay updated on data privacy regulations and ensure your dark data management practices are compliant. The recent implementation of Vietnam’s Decree 13 on Personal Data Protection (effective July 2023) adds another layer of urgency to investigating dark data. This regulation empowers individuals with the right to access and erase their personal information. Fulfilling these rights effectively may require organizations to delve into their dark data repositories to identify and manage this personal data. Failure to do so could lead to non-compliance with Decree 13, potentially resulting in fines or reputational damage. This highlights the growing importance of proactively classifying and understanding dark data to ensure adherence to evolving data privacy regulations like Decree 13.
Like dark matter in physics, dark data represents a vast amount of unseen information with hidden potential. By understanding what dark data is and how it accumulates, businesses can take steps to manage it more effectively. This can involve implementing data governance strategies, cleaning up and organizing information, and investing in tools to analyze different data formats. Shedding light on dark data can unlock valuable insights and empower businesses to make better decisions, improve customer experiences, and optimize operations.
| Exclusive article by FPT IS Expert
Author Tran Minh Chau – Data Scientist Lead, FPT IS |