DeepSeek and the Dangers No One Tells You About
In a world where technology is rapidly advancing, companies are increasingly adopting new advancements to support their work. One of these technological breakthroughs is artificial intelligence (AI), with many large companies investing in, building, and developing it, such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google DeepMind’s Gemini, GitHub Copilot… A recently emerging AI that is making waves globally comes from China and is called DeepSeek. It brings many exciting new technologies, using open source and consuming fewer resources. However, researchers have recently discovered security and user data issues in the DeepSeek app on iOS, affecting information safety.
Threats from DeepSeek iOS
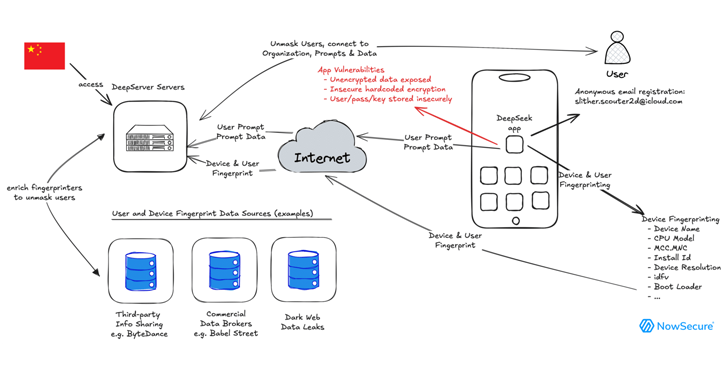
Researchers from NowSecure conducted an analysis of the DeepSeek iOS mobile app and discovered several vulnerabilities that put individuals, businesses, and government employees at risk of leaking sensitive information. The risks identified by NowSecure include:
- Unencrypted Data Transmission
- Weak and Hardcoded Encryption Keys
- Insecure Data Storage
- Extensive Data Collection and Fingerprinting
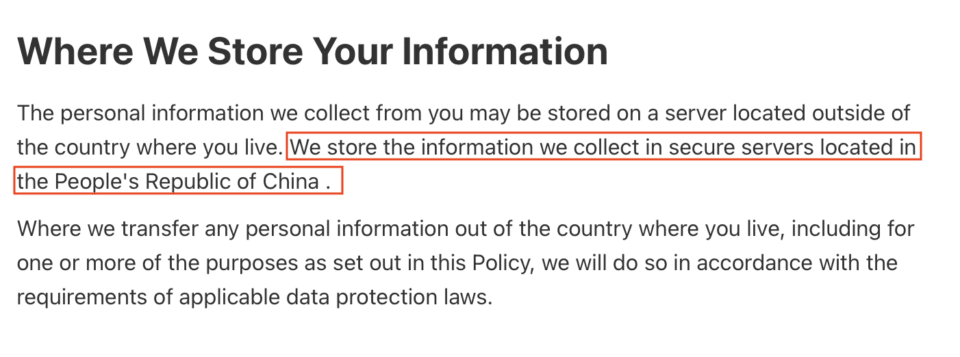
- Data Sent to China and Governed by PRC (People’s Republic of China) Laws
Data is not encrypted and can be modified over the network.
The DeepSeek iOS app sends registration information and device data over the Internet without encryption. This is very dangerous, as it allows attackers to monitor the network traffic and obtain important information related to DeepSeek app users. Although Apple has built-in platform protections to prevent developers from encountering this vulnerability, this function has been globally disabled for the DeepSeek iOS app.
Attackers can use Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) techniques to intercept and modify data, compromising the application’s integrity and data safety. At the end of 2024, an attack on Internet service providers in the US was carried out by a group of hackers from China called Salt Typhoon. This hacker group is linked to the Chinese government and poses a significant threat if they conduct eavesdropping on the DeepSeek iOS app’s data transmission.
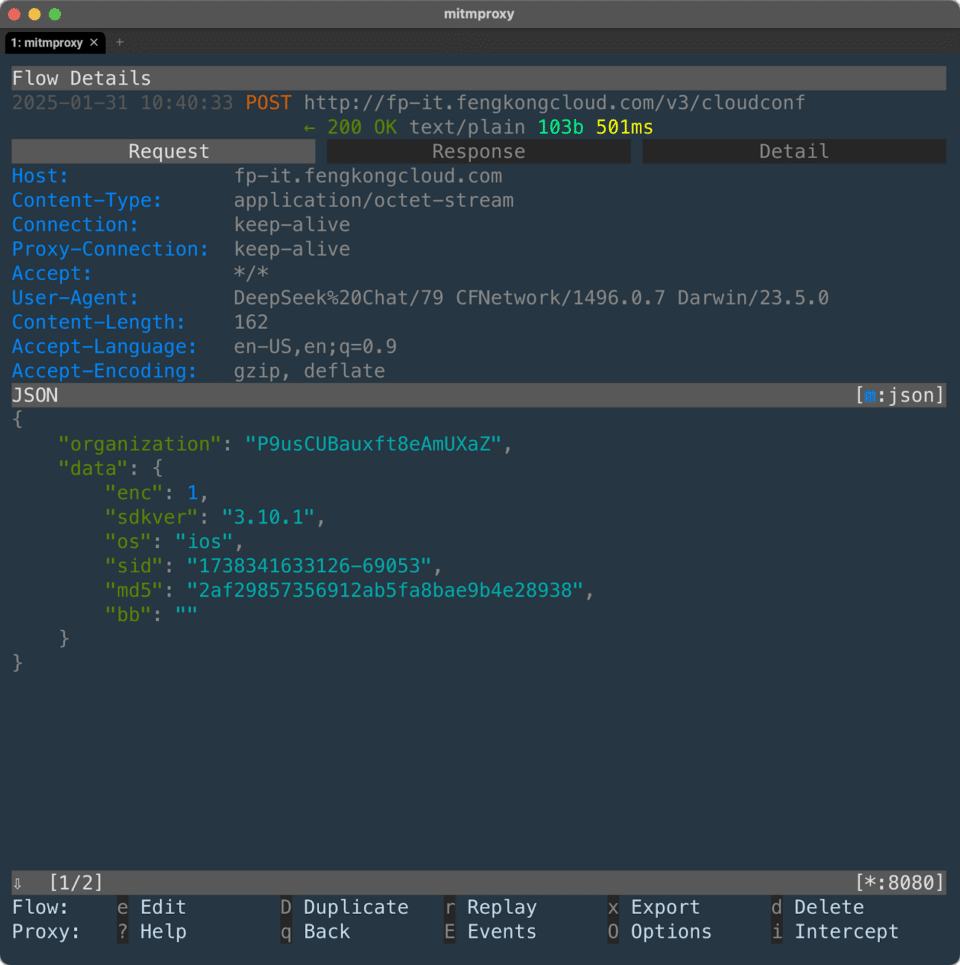
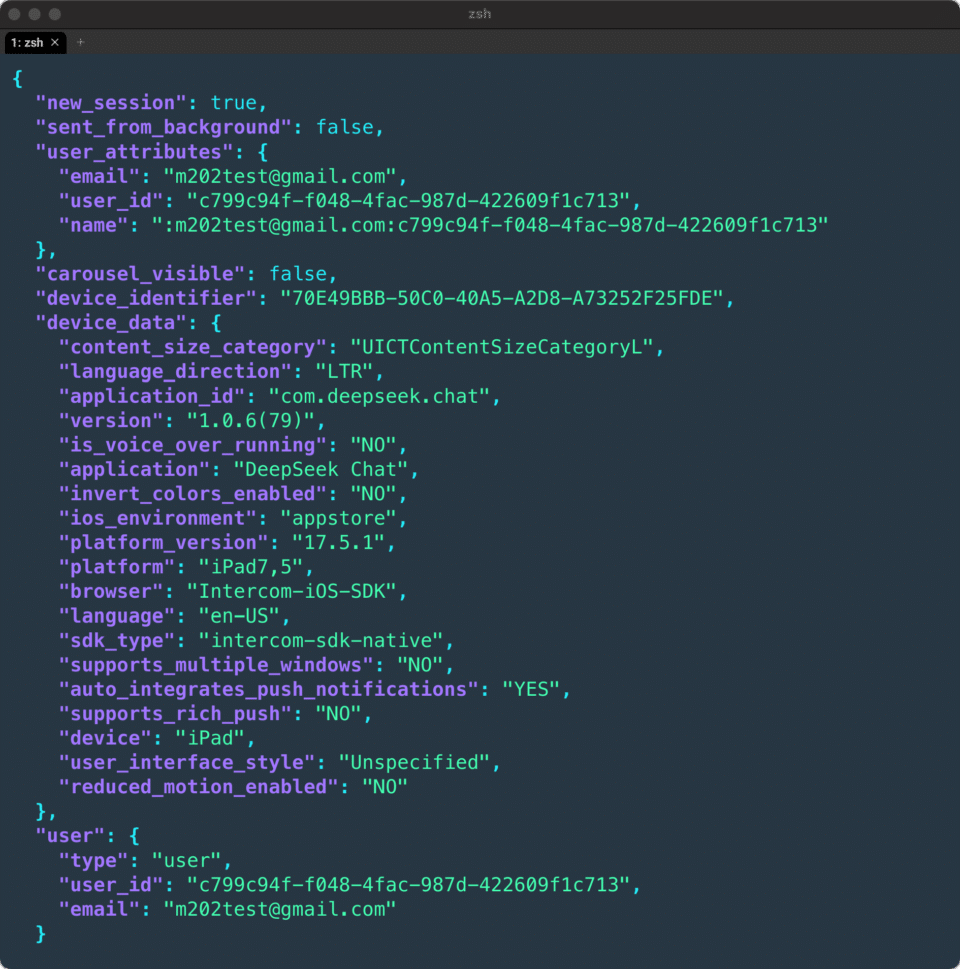
When users first run the app, it connects to DeepSeek’s backend to configure, register, and set up the device profile. Below is an example of an unencrypted request:
As you can see, the data is transmitted insecurely, with the language set for the device, user agent, organization ID information, and basic device information clearly shown in the request to the server. Although individual data points are not highly risky, compiling large amounts of data over time can identify individuals, similar to the data breach of Gravy Analytics, which exposed 30 million customer location data points.
Additionally, the app also disables App Transport Security (ATS), which is a protection measure on iOS that prevents sensitive data from being sent through unencrypted channels.
Symmetric Encryption is not secure with Hardcoded Keys
To protect the confidentiality and integrity of data, applications should use data encryption, and these encryption measures need to be properly implemented. NowSecure identified several weaknesses in encryption, including:
- Using the insecure symmetric encryption algorithm (3DES). This encryption algorithm is no longer considered secure for ensuring data confidentiality.
- Hardcoded encryption key
- Using NIL for the Initialization Vector (IV)
- Reusing Initialization Vector (IV)
When conducting a deep analysis of the application, NowSecure researchers discovered that the algorithm used has a hardcoded key and an Initialization Vector (IV) with all bits set to 0. This poses a high security risk and is not recommended when developing applications.
Username, password, and encryption keys are stored insecurely.
Sensitive information like usernames and passwords is stored in the device’s cached database. In some cases, especially with physical access to an unlocked device, this sensitive information can be retrieved and used by an attacker.
Data collection and Fingerprinting
Researchers found that some information is being collected and transmitted by the DeepSeek iOS app. Nowadays, many applications also collect user data, but it is very important for us to understand the issues related to privacy.
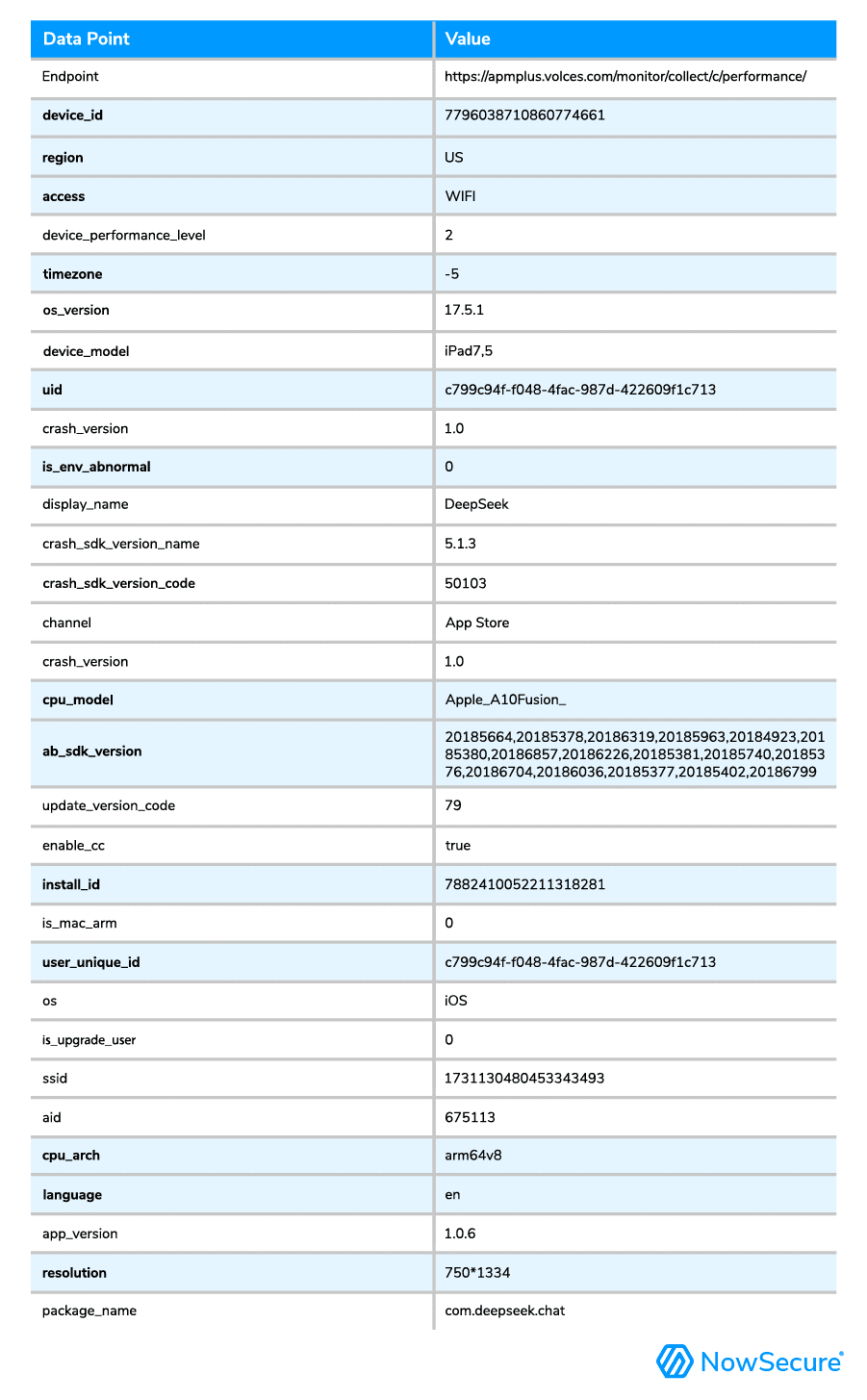
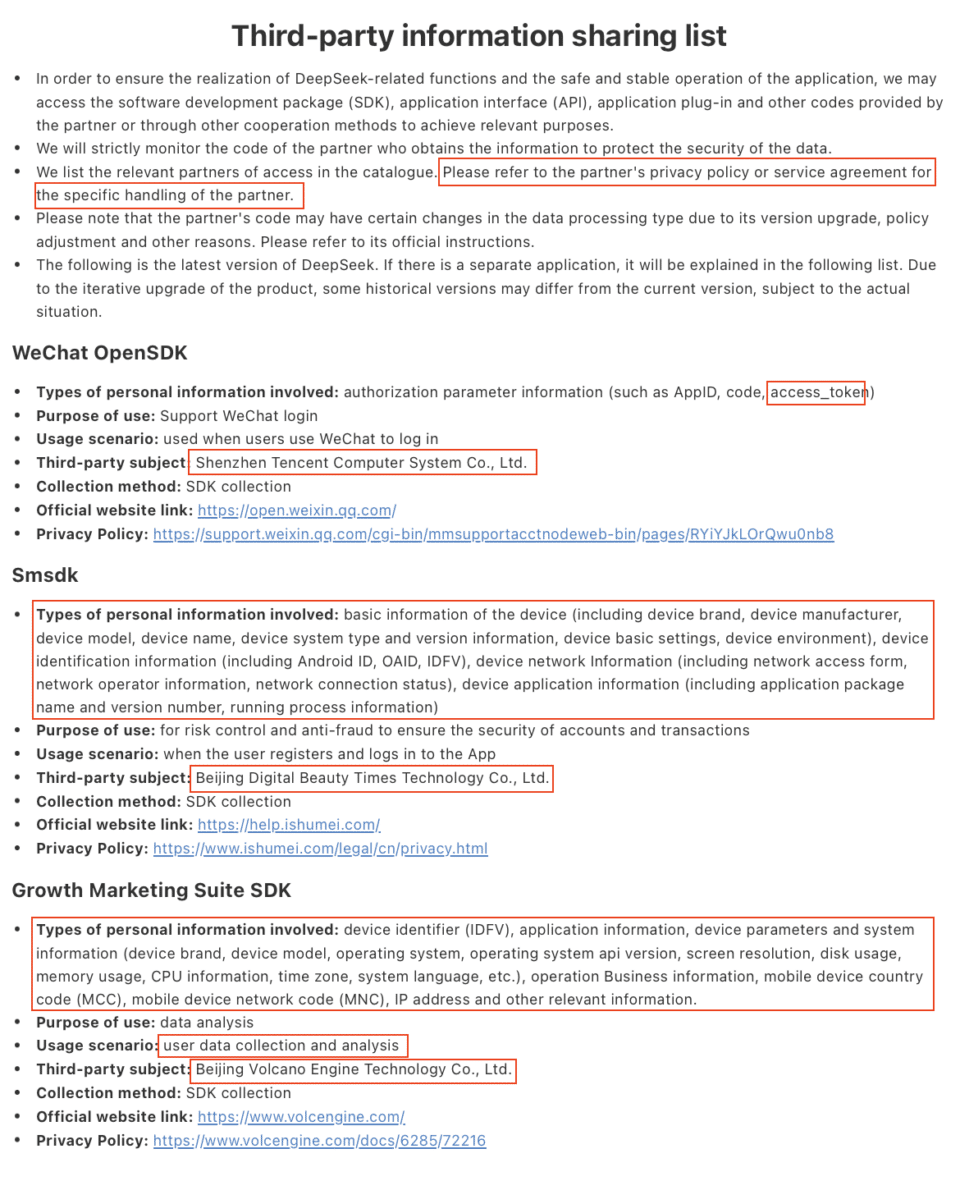
Data is sent to Volcengine, a cloud service platform launched by Bytedance in 2021 to support businesses in digital transformation and has connections to China. Sensitive information and data for tracking and monitoring purposes are highlighted as shown in the table below:
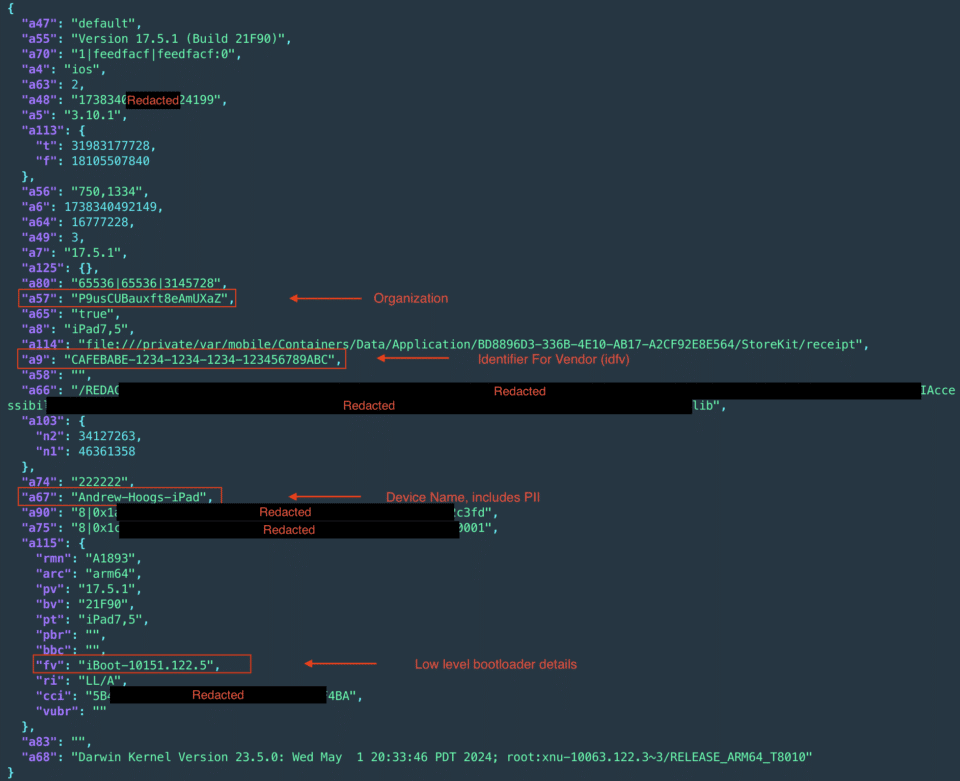
Below is an image related to the tracking data processed by the application, where the field a67 is the device name, and on most iOS devices, it is the customer’s name followed by the iOS device.
The app also integrates with the Intercom iOS SDK, and data is exchanged between the two platforms. As seen in the image below, this information can lead to user identification.
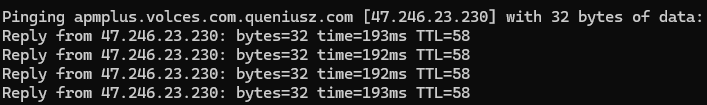
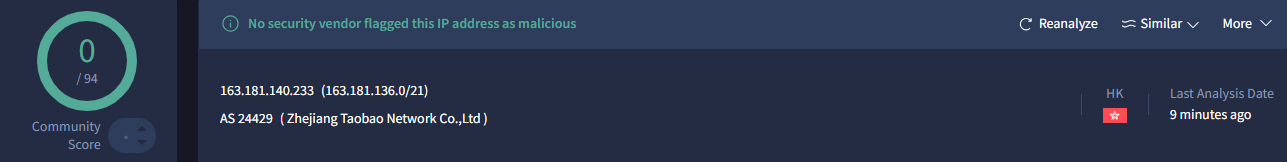
Many companies send data to servers in current countries to improve processing efficiency and address legal issues. Even if an IP address is located in the US, data may still be transferred, processed, and accessed from China, as is the case with Bytedance. In the case of the DeepSeek iOS app, if a user is in the US, when data is sent to volces.com, it resolves to an IP address:
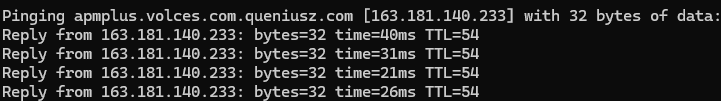
Or if the user is in Vietnam:
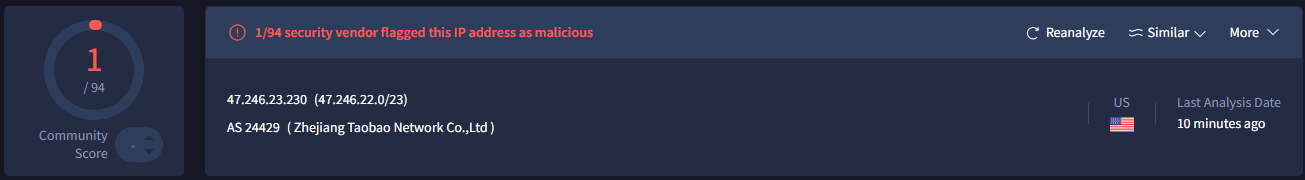
As mentioned earlier, Volcengine is a cloud platform developed by Bytedance, the company behind the TikTok app, which has faced controversies related to user data issues. It can be seen that the IP addresses 47.246.23.230 (for users in the US) and 163.181.199.245 (for users in Vietnam) both belong to Zhejiang Taobao Network Co., Ltd, part of the Alibaba Group.
Privacy Policy and Terms of Service
In the app’s privacy policy and terms of service, it can be seen that the collected data will be sent to China and how it is managed.
Recommendation
Researchers from NowSecure recommend:
- Do not use the DeepSeek iOS app until the security and privacy issues are resolved, especially on enterprise devices or for work related to government, finance, and business.
- Identify the collected data, privacy issues, and terms of service that put the organization at risk of information security breaches.
- Explore and research alternative AI solutions that offer better security.
Several countries have moved to ban the use of DeepSeek on government devices, including Australia, the Netherlands, Taiwan, South Korea, India, and the United States. Additionally, cybercriminals are actively exploiting DeepSeek to set up similar websites to distribute malware, phishing, and cryptocurrency fraud. Therefore, users need to be aware of these threats.
Reference
- NowSecure Uncovers Multiple Security and Privacy Flaws in DeepSeek iOS Mobile App – NowSecure
- DeepSeek App Transmits Sensitive User and Device Data Without Encryption
- DeepSeek Sending Unprotected Sensitive User Data To TikTok’s Parent ByteDance
|
Exclusive article by FPT IS expert: Vu Nhat Lam – FPT Information System Security Center |