Applying technology to digitizing cultural heritage
Cultural heritage and antiquities offer invaluable insights into humanity’s history, the development of civilizations, and the natural laws that govern our world. Cultural heritages themselves not only carry thousands of years of knowledge, identity, history, and human values but are also beautiful works of art that captivate and inspire.
Today, as science and technology continue to advance, new technologies are making it easier for people to accomplish extraordinary things like space travel, weather forecasting with supercomputers, artificial intelligence (AI), and, most notably, imaging technologies like multi-dimensional digitization and robotic automation. These technologies also help create digital versions of objects with the highest possible visualization such as virtualization, 3D technology, virtual reality (VR), etc., allowing people to “touch” antiquities in a vivid and engaging way even though they are not physically present. Modern technologies provide optimal solutions for preserving, promoting, and utilizing valuable digital resources. This approach aids in disseminating the profound human values left by our ancestors, helping people understand their origins and the world around them.
1. In Vietnam
Vietnam, with its long-standing and diverse culture, boasts countless tangible and intangible cultural heritages tied to the history of its 54 ethnic groups. These cultural and artistic heritages are treasures of Vietnam, many of which are recognized by UNESCO as part of the heritage of humanity and hold significant economic potential. Efficient exploitation of these resources is necessary to facilitate the sustainable development of the country. However, over time, heritages are increasingly at risk of being lost and damaged, which makes digitizing and preserving these heritages crucial and urgent.
| Thánh địa Mỹ Sơn | My Son Sanctuary |
| Thắng cảnh Vịnh Hạ Long | Hạ Long Bay |
| Quần thể di tích cố đô Huế | The Complex of Hue Monuments |
Although Vietnam’s heritage digitization was first started 20 years ago, the process has not yet been widely and simultaneously implemented. The government has thus far decided to implement a specialized heritage digitization program for the years 2021-2030; however, the goal is to digitize all of the tangible and intangible cultural heritages, museums and documentary heritages represent a challenge that calls for community participation.
A few of the standards that must be followed in order to create digital heritages are those related to format, metadata, storage, and preservation. Several international large and prestigious organizations have conducted research and published these standards. These digital heritages are being created not only for inspiration and preservation but also for extensive application across multiple scientific and research domains. In order to make cultural heritage digitization deeply applicable in several fields, three fundamental principles must be followed:
- Empirical provenance: digital surrogates are easily used in science and cultural heritage studies. Transparent qualitative evaluation of their authenticity and reliability is essential.
- Perpetual digital conservation: digital heritage can be used, stored and preserved with scientific methods that will guarantee their availability for future generations. The conservation plan must include capacity for contribution and stewardship from organizations and institutions worldwide.
- Democratization of technology: digitization of heritage must allow those who study and care for our past to have easy and simple access to digital heritage along with related data.
Recent research breakthroughs in computer graphics, robotics, and machine vision have converged to make a new generation of robust digital tools for construction of digital surrogates possible, ensuring the above-mentioned principles.
It is evident that digitization for archiving digital cultural heritage is increasingly recognized as a crucial method of heritage preservation in today’s digital society. This approach significantly contributes to the management and dissemination of information, providing a foundation for academic research in historical studies. Moreover, it grants people from every corner of the country the opportunity to access heritage as if they were visiting it directly. The digitization of cultural heritage, furthermore, has been generating digital content that qualify as works of art in their own right. The visual richness, spatial depth, dynamic movement, and contextual immersion of digital surrogates are capable of captivating the viewer’s senses. Hence, beyond its role in preserving and promoting the value of digital heritage, archive digitization also plays a pivotal role in safeguarding works of art for future generations.
Digital Heritage
Digital heritage is a new concept, referring to cultural heritages stored and preserved in digital form. These heritage items can be documents, artwork, architecture, or anything that has cultural value and can be stored digitally.
Static digital heritage
- Includes digital documents such as 3D models, images, text documents, audio and video files stored on computers, cloud servers or other storage devices.
- Dynamic digital heritage
- Includes websites, applications, and other online platforms used to create and share digital content.
- Digital heritage or heritage digitization is the most suitable solution to preserve natural, cultural, historical, tangible and intangible cultural heritage within a budget and plan.
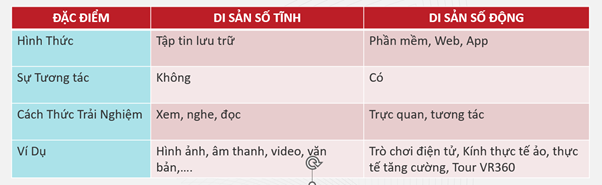
| Characteristic | Static digital heritage | Dynamic digital heritage |
| Format | Archive file | Software, Web, App |
| Interaction | No | Yes |
| Way to experience | Watch, listen, read | Intuitive, interactive |
| Example | Images, audio, video, text, etc. | Video games, virtual reality glasses, augmented reality, Tour VR360 |
- Digital heritage brings many benefits to preserving, utilizing and promoting cultural heritage, including:
- Helping store and preserve heritage effectively. Digital heritage can be stored and preserved in digital format, helping to protect from the impacts of time and environment.
- Enhancing heritage utilization and access. People can access cultural heritage no matter where they are thanks to the remote access and utilization of digital heritage.
- Raising awareness of the heritage value. Digital heritage helps users better understand cultural heritage, which increases public awareness of its value.
2. Current popular digital heritage solutions
Virtual tour
- VR360 Virtual Tour or VR360 Tour is created by linking 360-degree images together, which may be 3D design or real-world images.
- VR360 is the simplest and most widely used method for storing and recreating historical relics, museums, memorial sites, etc. in a form of a website that allows visitors to take tours from anywhere using only their phone.
- High-quality 360-degree photos, made possible by modern digital cameras and scanners, allow localities convey history, culture, and tourist attractions to visitors in a clear and vivid way, improving customer experience and enhancing the locality’s image.
| Cách tạo ra một tác phẩm ảnh 360 | How to create a 360° image |
| Ứng dụng | Application |
| Bảo tàng lịch sử TP HCM | The History Museum of Ho Chi Minh City |
| Khu di tích 915 | Historical Site 915 |
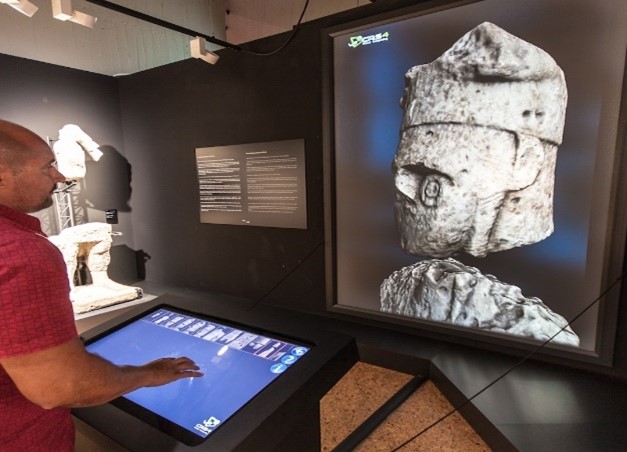
Artifact modeling – Intangible heritage
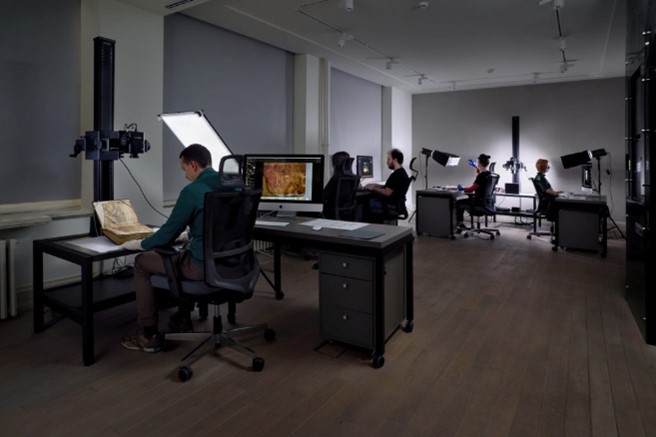
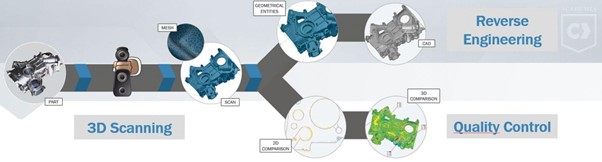
- 3D scanning is the process of analyzing a real-world object or environment to collect three dimensional data of its shape and possibly its appearance (e.g. color, size, detail, etc.). The collected data can then be used to construct digital 3D models for archiving, preservation, or the creation of new prints.
- The gathered 3D data is highly beneficial for a wide range of applications. Augmented reality (AR), motion capture, gesture recognition, robotic mapping, industrial design, orthopedics and rehabilitation, reverse engineering and prototyping, quality testing, and digital heritage are some other common applications for this technology.
| Exclusive article by FPT IS technology experts
Co-author: Ha Thi Hanh – Solution architect and Tran Nguyen Minh Nhut – Head of akaVerse solution consulting department, Ho Chi Minh City |