Health Equity: Opportunities and Challenges for Digital Transformation in Healthcare
The world has just been hit by the Covid-19 pandemic, provoking a health crisis for many countries. The pandemic exposes a reality that no country, no matter how powerful, is ready and capable of ensuring healthcare and medical treatment for a large number of patients. All medical systems, from the mighty America to ancient Europe, from vast China, populous India to average countries like Vietnam, are overloaded. Access to health equity is a pain point that need to be resolved as quickly as possible.
The health sector in many countries has been undergoing major changes, boosted by people’s heavier demands on medical examination and treatment in healthcare systems and facilities, creating great opportunities and challenges for Digital Health. In particular, Health Equity is a pain point that needs to be addressed. Technology companies can participate to solve this pain with digital transformation in healthcare.
1. World Health Overview
Global statistics from diverse sources show that ensuring health equity with technology is of great concern.
Equalizing access to healthcare services not only improves wellbeing at the individual and community levels but also positively impacts the economy: Good health, timely and effective treatment bring a better life to people and enable them to work more efficiently. A report by Mckinsey mentioned that, improvements in global health have contributed to about one third of the total economic growth of major economies.
Some leading countries in Digital Health in the world:
- Denmark, Netherlands: Advanced digital health systems which connect and share information between hospitals, doctors and people
- USA: Electronic health records (EHR) are used in numerous healthcare facilities.
- Singapore: Electronic Medical Record (EMR) system and personal health books are being heavily invested
- Estonia: The country is famous for its Digital Health and e-Government services
- Korea: Well known for mobile applications in community health management
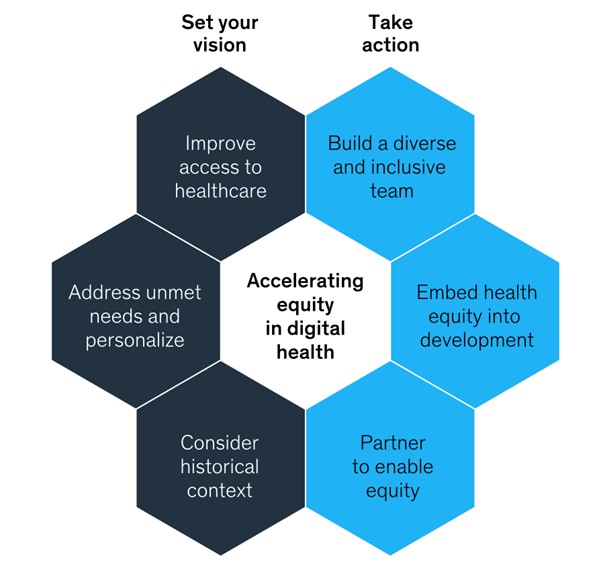
Technology companies create tools and focus on the following aspects: Improve access to medical services; address people’s unmet needs; personalize healthcare based on historical data about the patient’s health. For example: The Covid-19 pandemic has rapidly promoted Telemedicine, enhancing healthcare access for people in remote areas. London-based Babylon company cooperated with the Rwandan government to develop a telemedicine platform that has 2.6 million users.
While geographical barriers are overcome through technology (Telehealth, mHealth), the quality of medical treatment is limited due to lack of knowledge and incomplete information. Through PHR (Personal Health Record), London-based Mendelian company has offered solutions to shorten diagnosis time for more than 100 rare diseases, as well as connect patients with the right medical facilities.
Improvement of health equity is a tough task for not only countries with underdeveloped healthcare systems but also advanced countries. This great, long-term challenge opens up opportunities for technology companies to apply various new and advanced technologies to solve the “pain”.
2. Healthcare in Vietnam
Despite enormous efforts made to tackle problems in medical examination and treatment in Vietnam’s health sector over the years, the results yielded are limited and do not met expectations. The limitations include congestion and overload at higher level hospitals; health data are not shared between medical facilities; doctors have limited data about the patient’s health leading to the possibility of medical errors; patients are required to re-do paraclinical tests every time they switch healthcare facilities for medical examination or treatment; shortage of drugs, chemicals, medical supplies, equipment; long patient waiting time wasting social resources; medical managers are under pressure while health care practitioners are tired out; people buy drugs spontaneously and without prescription at pharmacies which heavily outnumber medical examination and treatment facilities leading to antibiotic resistance; lack of health data connection and sharing caused by data being fragmented and ineffectively exploited.
In recent years, these existing problems of Vietnam’s health sector have been partly addressed through IT and digital transformation solutions developed by a number of Vietnamese technology companies. Nevertheless, the application of these solutions are stuck at an extremely low speed and considerably small scale due to inadequate funding and the absence of legal frameworks.
3. Opportunities and Challenges
Vietnam issued a new Law on Medical Examination and Treatment (Law 15/2023/QH15). The Decree providing guidance on this law was also quickly completed and issued, effective December 31, 2023, creating plenty of opportunities for Digital Health and solving numerous long-standing bottlenecks.
For the first time, information technology is added to the cost that is used to set the price for medical examination and treatment services (Article 110, Law on Medical Examination and Treatment 15/2023/QH15), stimulating medical facilities’ investment in information technology. Consequently, a mountainous wave of adoption of Health IT in healthcare is expected to arrive in the near future.
Article 80 of the Law on Medical Examination and Treatment 15/2023/QH 15 also clearly clarifies Telemedicine, forming a solid legal framework for the rapid development of Telemedicine in the near future.
Article 112 stipulates regulations on Information Systems in medical examination and treatment management, opening up various possibilities and creating the premise for the establishment of output and data standards required for data connection and sharing among information systems.
In addition, the Law on Medical Examination and Treatment recognizes that electronic and paper medical records have the same legal effect. This provision marks a significant change that enormously hastens the digitalization process and the implementation of electronic medical records nationwide.
Along with the Law on Medical Examination and Treatment, specialized agencies under the Vietnamese Ministry of Health are in a great rush for the issuance of Decrees and Circulars that provide guidance on Health Data Management. This unveils the importance and urgency in the formation, management, exploitation and sharing of national, regional and provincial health databases.
Currently, the National Population Database stores more than 80 million records, enabling the creation of personal National IDs for Vietnamese citizens, tabling the resolution for various problems in the Heath sector.
Provisions stated in the new law, decrees, and circulars will set a solid legal framework as well as mechanisms and policies for the development of Health IT, accelerating rapid and dramatic digital transformation in the Health industry, improving access to health equity for all Vietnamese people, from big cities to remote areas and islands.
Opportunities:
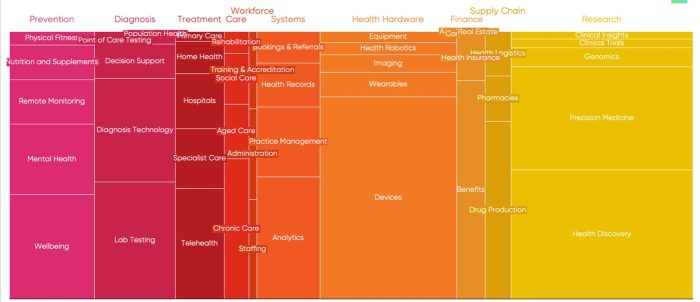
Numerous opportunities are given to technology companies to shape a national digital health platform:
- National Database on Health, Equipment, Human Resources, Pharmaceuticals, etc.
- Personal Health Records (PHR)
- Electronic Medical Records (EMR)
- Electronic Health Records (EHR)
- National Database on Insurance
- TeleHealth
- Home Care
- Digitization of Paper Medical Records
- Information security
- Cloud computing
- Big Data and AI are adopted to automate medical records, lightening the burden on medical staff; AI assists in clinical decisions by analyzing data for the best treatment recommendations; using big data to forecast epidemic trends and manage health resources in emergency situations
Challenges:
Major challenges can be listed as follows:
- Security and safety of information and data: Medical data is private and sensitive information. Developing a system that ensures information security and safety in the context of the poor attention devoted to this by applications in Vietnam poses a tough challenge.
- Information infrastructure limitations: EMR, PHR, EHR, Big Data, and AI require a powerful, smooth and secure IT infrastructure, which creates an obstacle for technology companies.
- Training and mindset change: This big hurdle requires medical staff to be trained to adapt to new technologies and managers in the health sector to quickly shift their mindsets regarding technologies.
- Investment costs: Although the mechanism to include IT in service prices has been established, there are certain constraints that need to be resolved.
- Digital transformation policies in Healthcare: Concerns may be caused by the overlaps in the basic legal framework formed.
Conclusion
The 5Ps in Health include: People, Provider, Payer, Policy, and Precision.
Lawmakers and Governments have made strong moves to promote Digital Health worldwide and in Vietnam after the pandemic.
Insurance companies are raising their investment in preventive medicine and paying more attention to people’s lifestyle to minimize the risks of sudden increase in medical compensation.
People expect better health care and more effective disease treatment.
Hospitals and clinics plan for the extensive application of technology to boost productivity, create competitive advantages, improve medical examination and treatment capacity, and fulfill peoples’ expectations.
Precision is considered essential in healthcare, and can be improved through the use of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data analysis.
The author believes that realizing digital transformation in healthcare to broaden people’s access to health equity is a great challenge. This process can be dramatically accelerated by the participation of technology companies with their appropriate strategies, capacity, intelligence and potential. The efforts made will help bring more happiness and prosperity to people and the country, respectively.
Reference:
- Law 15/2023/QH15 on Medical Examination and Treatment
- Draft Circular providing guidance on the Law on Medical Examination and Treatment
- Draft Decree on Health Data Management
- Discussion with a number of experts
- Mc Kinsey, holonIQ, Healthedge
Exclusive article by FPT IS Technology Expert
Mr. Nguyen Duy Hien
Deputy Director of Local Government Sector
FPT Information System Company