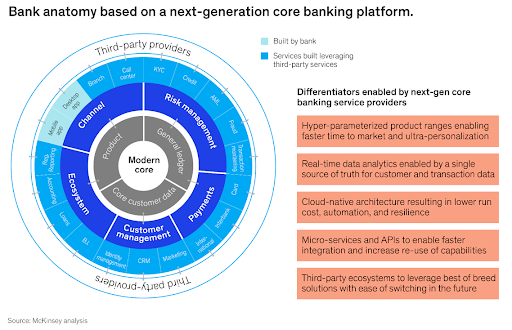
Next-generation core banking platforms
Competition in the banking industry is increasingly intense. Neo-banks are gaining market share and serving customers at about one-third the cost of traditional banks while Fintech is targeting profitable niches in the value chain. Big technology companies (BigTech) with a large customer base have become real threats to banks. More banks are investing heavily in innovation, leaving the others with conservative pace of change fall behind.
Pioneering organizations are growing their businesses and attracting customers with the help of modern core technology architecture, which enables them to innovate faster and operate more efficiently. Unsurprisingly, incumbent banks are increasingly concerned about the limitations of their own core architectures and their relatively slow pace of change. As a result, some 70 percent of banks are reviewing their core banking platforms, according to a McKinsey survey of 37 banking executives.
-
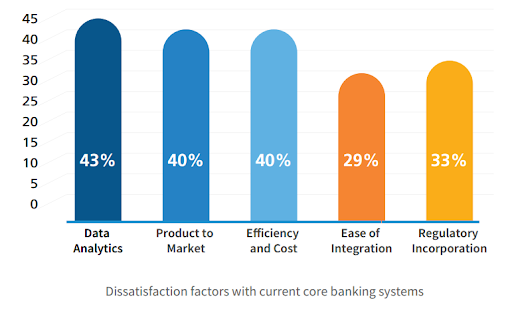
Bank’s dissatisfaction with current core systems’ capabilities
1.1. Product and channel growth
According to the market survey and various research published, banks are dissatisfied with existing monolithic and complex core banking systems in terms of the following factors:
- Data analysis 43%
- Product to market 40%
- Efficiency and cost 40%
- Ease of integration 29%
- Regulatory incorporation 33%
1.2. Other dissatisfaction factors
- Unable to support complex products
- Limited integration with new platforms like data warehouse and CRM applications
- Minimal flexibility to improve development as per market needs
- Unable to accommodate new risk management frameworks
- Incapable of providing a customer 360-degree view
- Limitations in providing more efficient and effective delivery capabilities
- High customization capabilities increase system complexity
2. The Evolution of Core Banking Systems
Core banking systems, once hailed for their reliability and efficiency, now face significant challenges stemming from their inherent inflexibility and inability to seamlessly integrate with modern digital technologies. As highlighted by a Deloitte study, over 70% of bank executives worldwide recognize the urgency of modernizing core systems to meet customer expectations and maintain competitiveness.
The current market trends show that the core banking software market was worth USD 14.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at about 12.2% each year from 2024 to 2032. With the core banking software market projected to grow to USD 41.3 billion by 2032, it’s clear that banks are recognizing the necessity of embracing technological advancements to stay relevant.
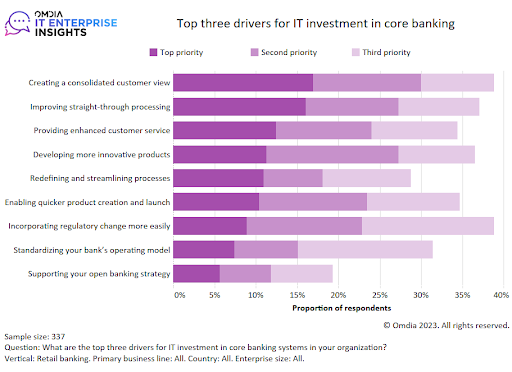
According to Omdia’s Retail Banking Survey, more than 64% of banks’ global technology budget is spent on maintaining existing legacy technology and just 36% is allocated to either growing or transforming their technology. In the same survey, banks indicated they are most worried about ‘customer management’, with 45% listing it as one of their top three business concerns.
However, there is a desire among banks to invest in core banking infrastructure, with 38% of respondents indicating that the leading factor in their decision to upgrade their core banking system is to ‘create a consolidated customer view – Customer360’.
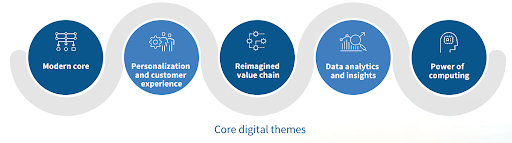
3. Core digital themes
3.1. Modern core
Banks are undergoing comprehensive digital transformations to enhance their operational efficiency, customer experience, and innovation capabilities. Modern core systems are thin, modular, composable, and resilient, which enables easy integration with external systems and quicker market launch of new product offerings.
3.2. Personalization and customer experience
Banks are striving to deliver highly personalized experiences to their customers. By leveraging data analytics, AI, and digital channels, banks can offer tailored product recommendations, personalized financial advice, and proactive alerts to meet individual customer needs and enhance their overall banking experience.
3.3. Reimagined value chain
To reimagine critical business value chains by leveraging emerging technology, banks are utilizing AI and ML technologies to improve customer service, enhance fraud detection and prevention, automate processes, and provide personalized recommendations. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are becoming common in customer support, offering quick and customized assistance to customers.
3.4. Data analytics and insights
Data analytics is helping banks gain valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and risk profiles. Advanced analytics techniques, such as predictive analytics and real-time data processing, drive personalized product recommendations, identification of cross-selling opportunities, effective management of risks, and fraud prevention activities.
3.5. Harnessing the power of computing
Cloud computing is revolutionizing the core banking industry by providing scalable infrastructure, enabling rapid deployment of new banking services, and facilitating cost-effective operations. With this flexible and secure architecture, cloud computing allows banks to leverage advanced technologies, such as AI and big data analytics, to deliver personalized and innovative financial solutions to customers.
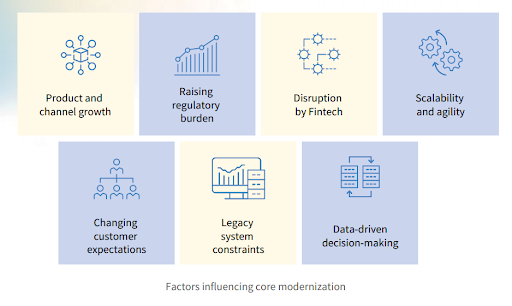
4. Factors influencing core modernization
4.1. Product and channel growth
Product and channel growth are driving the evolution of modern core banking systems by demanding flexible infrastructure that can support a wide range of products and services across multiple channels. These include online banking, mobile applications, and other digital platforms, enabling banks to effectively meet the changing needs and performances of their customers.
4.2. Raising regulatory burden
The regulatory landscape for banking institutions continues to evolve, with new compliance requirements and reporting standards being introduced. Core banking modernization helps banks adapt to regulatory changes more efficiently, ensuring compliance with Anti-Money Laundering (AML), Know Your Customer (KYC), data privacy, and other regulations.
4.3. Legacy system constraints
Many banks still operate on outdated legacy core banking systems that are inflexible, costly to maintain, and lack interoperability. A modernized core banking system, built on new technologies, enables flexible real-time processes and simplifies APIs for integration with third-party applications. It also helps address the limitations of legacy systems and enables banks to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve integration with other systems and channels.
4.4. Disruption by Fintech
Fintech start-ups, challenger banks, and non-banking players are disrupting the traditional banking landscape. To stay competitive, banks must modernize their core banking systems to offer innovative products, services, and customer experiences that differentiate them in the market.
4.5. Data-driven decision-making
Core banking modernization facilitates better data management and analytics capabilities. Banks can leverage data from various sources, including transactions, customer behavior, and external vendors. This helps gain actionable insights, identify patterns, and make informed decisions to drive business growth, risk management, and fraud detection.
4.6. Scalability and agility
Traditional core banking systems often need help to handle increasing transaction volumes, accommodate new products and services, or adapt to changing business requirements.
Modernizing core banking infrastructure enables banks to achieve greater scalability, flexibility, and agility to respond quickly to market demands and scale their operations efficiently.
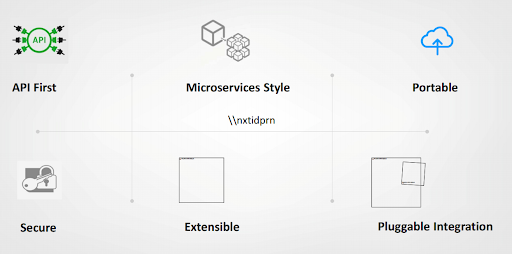
5. Features of new age core banking systems
Low maintenance cloud-native architecture: With cloud-native architecture, core banking systems offer Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)-based implementation, which improves resilience and cost-effectiveness while reducing maintenance needs.
Open APIs for easy integration: API-enabled new-age core systems are easy to integrate with third-party systems.
Composable Microservices architecture: Modern core banking systems leverage composable microservice-based architecture which is easy to integrate with third-party systems.
Powerful parameterization: A set of fundamental components for financial products can be configured and re-configured.
Real-time transaction processing: Core banking systems use advanced technologies such as in-memory databases and event-driven architectures. These systems enable immediate and seamless processing of transactions, providing customers with online updates on their account balances and transaction history.
Quick go-to-market: New-age core banking systems empower banks to rapidly introduce new products and services in new markets and segments by providing flexible and modular architecture, streamlined integration capabilities, and efficient deployment processes.
Secure by design: New-age core systems are secure by design through a combination of robust encryption, multifactor authentication, strict access controls, continuous monitoring, and regular security updates to mitigate vulnerabilities and protect customer data.
6. Business realization with modern core
Modern core banking systems offer numerous benefits and can lead to significant business realizations. Here are some key points to consider:
6.1. Time to revenue
New products/quick to market: To expedite time to market through the modernization of core banking systems, banks can consider leveraging preconfigured solutions and templates offered by modern systems, streamlining data migration and integration processes, implementing efficient training and change management programs, and developing a comprehensive go-to-market strategy aligned with the capabilities of a new system. These steps help banks to accelerate their implementation timelines and quickly launch new products and services to generate revenue.
Target market (customer segment): With the advancement of data analytics in new core banking systems, banks can discover new customer segmentation and offer tailor-made services to specific market targeting groups. By understanding the unique needs, preferences, and behaviors of different customer segments, banks can design personalized products, enhance customer experiences, and effectively target their marketing and communication strategies.
The customer-centric approach fosters customer loyalty, attracts new customers, and drives revenue growth, ultimately maximizing the benefits of Core Banking System Modernization.
6.2. Banking experience
Composable Banking: Facilitated by the modernization of core banking systems, it allows banks to create a modular architecture where various banking services and functions can be independently developed, deployed, and scaled. This approach enables faster innovation, easier integration with external partners and fintech providers, and the ability to adapt to changing market demands quickly. Composable banking empowers banks to offer a wide range of personalized services and drive business growth in a rapidly evolving financial landscape.
Blending of industries (Ecosystem): New age core banking systems are providing advantages through the blending of industries by enabling seamless integration of financial services with other sectors. By leveraging open APIs and partnerships, these systems facilitate collaborations between banks and industries like retail, e-commerce, and fintech, allowing for innovative product offerings and enhanced customer experiences. The blending of industries also promotes financial inclusion by bringing banking services to underserved sectors, such as rural areas or emerging markets. Moreover, integrating data from different industries enables banks to gain valuable insights and develop personalized financial solutions tailored to specific customer needs.
6.3. Cost reductions
Running costs: While an initial investment is involved in implementing and migrating to a new system, modern core banking systems can lead to long-term cost saving. By streamlining operations, automating processes, reducing manual errors, and eliminating the need for multiple legacy systems, banks can achieve greater operational efficiency, reduce maintenance expenses, and scale their operations more effectively, resulting in overall cost optimization.
Change Cost: The costs associated with modernizing core banking systems can impact banks in the short term. These costs include system implementation, data migration, training, and change management expenses. However, the long-term benefits of modernization, such as improved operational efficiency, enhanced customer experience, and increased agility, can outweigh the initial change costs, leading to greater cost savings and improved profitability for the bank over time. Effective planning, budgeting, and execution of the change process can help mitigate the impact of change costs and maximize the overall return on investment.
7. Conclusion
Core banking modernization is a critical initiative for financial institutions to transform their operations, enhance customer experience, and drive growth in the digital era.
While it presents challenges and requires significant investments, the benefits of improved efficiency, agility, and customer centricity make it a worthwhile endeavor for forward-thinking organizations.
Reference sources:
https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/financial-services/our-insights/banking-matters/how-asset-managers-can-create-strategic-distance-with-technology
https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/pages/consulting/articles/core-banking-digital-transformation-strategy.html
A Transformation Approach to Smarter Core Banking (ibm.com)
https://isg-one.com/articles/the-new-future-for-core-banking-a-short–medium–and-long-term-view
https://www.scribd.com/document/519436730/Thought-Machine-IDC-Whitepaper-Truly-Digital-Core-Banking#
https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/tech-forward/how-banks-can-use-sevenlevers-to-modernize-their-core-systems
https://ibsintelligence.com/ibsi-news/3-challenges-faced-by-banks-in-modernizing-their-core-banking-systems/
| Exclusively written by the FPT IS experts
Tran Dac Thang – Banking Solutions Consulting – Finance and Banking Division FPT Information System Company |