Proactive cyber defense: dealing with Stealer malware for individuals and enterprises
In the digital era, cybersecurity has become a top concern for both individuals and enterprises. Stealer malware is one of the dangerous threats that silently steals sensitive information, causing enormous damage. The second article in the series “Proactive defense against stealer malware” will provide information on how different types of stealer malware work and solutions for proactive defense strategies against stealer malware for individuals and enterprises.
Learn more about “What is stealer malware?” and “Common types of stealer malware” in part 1: “Proactive cyber defense: understanding Stealer malware”.
1. How Stealer works
There are diverse reasons why users’ devices become infected with malware in general or Stealer in particular. Below are the most common paths:
- PhishingThe most common method is through phishing emails designed to target users with malicious content or attachments. Opening these emails or downloading the attachments will cause the users’ computers to be infected.
- Downloading from unsafe websites:Stealer infection can be triggered by downloading software from websites that are untrusted or contain malicious files. These files may be disguised as useful software but are actually malware.
- Attachments in chats and shared documents:Online messaging and document sharing platforms could also be paths for the spread of Stealer. Attachments or links in chats can contain malware that infectscause users’ devices when they click on or download them.
- Security vulnerabilities in software and operating systems:Some Stealers can exploit security vulnerabilities in software or operating systems to penetrate the system without direct user intervention. This can happen when users do not update their system or software with the latest security patches.
- Malicious advertising and websites:Online advertisements may contain links to malicious websites or direct malicious file downloads when clicked by the user. Visiting these unsafe websites can lead to unwanted Stealer infections.
- Applications and add-ons:Web browser add-ons and extensions can be exploited to spread Stealer. When installed from unsafe sources, these features may include malware to perform data theft.
- USB connection and peripherals:Storage devices such as USBs and external hard drives can be infected with Stealer when users connect them to computers without appropriate protection software to scan and prevent malware.
- Remote management and supporting software:Remote management and supporting software can be attacked and exploited to infect the user’s system with Stealer. Vulnerabilities in these software can be used for attacks and intrusions.
Stealer malware works by infiltrating the victim’s system and quietly collecting sensitive information that the user enters or stores on the computer. Here is how stealer generally works:
- Infiltrating and infecting:Stealer is often spread through the paths mentioned above. When the victim downloads and executes the malicious file, Stealer stealthily infects his system.
- Gathering information: After infecting the system, Stealer begins to collect sensitive data such as passwords, bank account information, credit card details, login credentials to online services, browsing history, and other personal data.
- Communicating with command and control servers: The information gathered by the Stealer is then compressed and sent over the internet to the command and control (C&C) servers controlled by the attacker. These communications are often encrypted to protect against detection by security tools.
- Maintaining anonymity and access:Stealers often use obfuscation and anti-analysis techniques to avoid detection by security software. These malware can automatically update or download new versions to maintain long-term operability on the victim’s system.
- Serving attack purposes:Information stolen by Stealer is often used to conduct other attacks such as fraud, bank account robbery, or sold on the black market for profit.
Below are typical infection chains of some popular Stealer families:
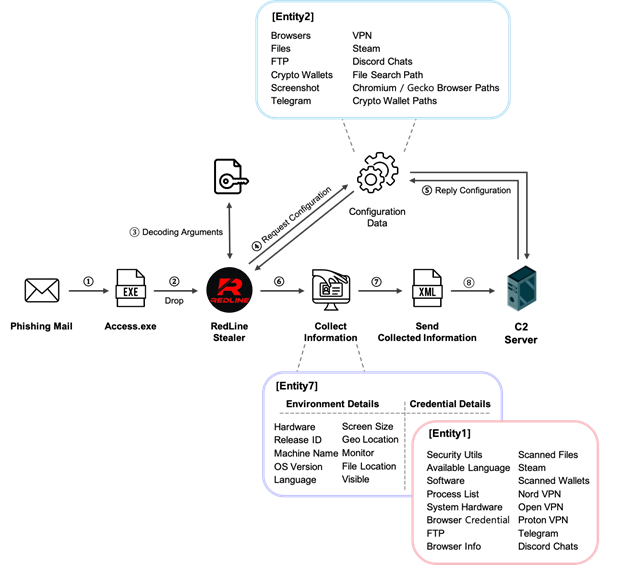
- RedLine Stealer malware:
Source: https://medium.com/s2wblog
- Raccoon Stealer malware:
Source: malware.news
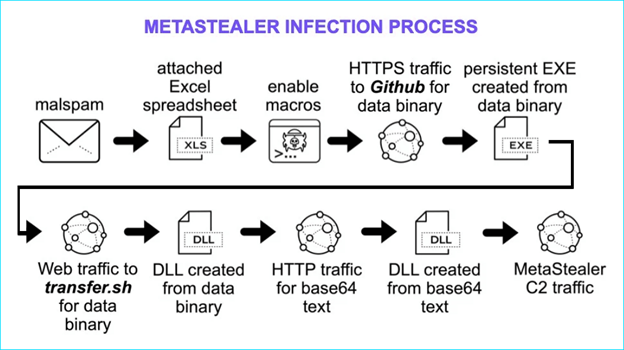
- Meta Stealer malware:
Source: gridinsoft.com
2. Risks and impacts of Stealers
Being infected with Stealer malware poses numerous risks and serious impacts on both individuals and businesses. Below are some risks and levels of impact for each subject.
For individuals:
- Financial loss
- Credit card and bank account information: Stealer malware can steal credit card and bank account details, causing direct financial loss due to invalid transactions.
- Cryptocurrency wallets: Cryptocurrency wallets can also be stolen, causing substantial losses of digital assets.
- Privacy violation
- Personal information: Sensitive information such as names, addresses, phone numbers, and other personal data can be stolen and used for malicious purposes, such as identity fraud or blackmail.
- Browsing history and login credentials: Browsing history and login information for online accounts can be exposed, leading to unauthorized access to personal accounts.
- Loss of important data
- Personal documents and files: Important documents, images, and files can be stolen and used illegally by Stealer malware.
- Damage to reputation
- Identity abuse: Personal identity can be exploited to commit illegal acts, damaging personal reputation and image. For example, social network accounts and personal email accounts.
- The possibility of being tracked and monitored
- Keylogging: Some Stealers equip with a keylogging function which enables attackers to collect detailed information about the victim’s online activities, including passwords and other sensitive information.
- Screen capture: A number of Stealers are capable of taking screenshots, which allows hackers to monitor victims’ activities and steal sensitive information.
For enterprises:
- Serious financial loss
- Financial and transaction information: Stealer malware can steal business financial information, causing direct damage due to invalid transactions or loss of assets.
- Remediation and security costs: Businesses will have to bear large costs for remediation and security enhancement measures.
- Loss of sensitive information
- Customer Data: Stolen customer information can lead to loss of trust from customers and business partners, affecting a business’s reputation.
- Intellectual property: Information related to products, technology, and business secrets may be leaked, negatively affecting competitiveness.
- Business interruption
- Denial of service attack: Stealer can be combined with other malware to perform denial-of-service attacks, disrupting business operations.
- Decrease in productivity: Malware remediation is time- and resource-consuming, which affects the performance and daily operations of the enterprises.
- Reputation damage and legality
- Violations of regulations: Businesses can face legal issues due to violations of data security regulations, especially in industries that require high security standards such as finance and healthcare.
- Loss of trust from customers and partners: Security incidents may weaken customer and partner trust, negatively affecting a company’s reputation and business relationships.
- Supply chain attacks
- Spread through partners and customers: Stealer malware can spread through a company’s business partners or customers, increasing the risk of infection and expanding the scope of the attack.
- Taking advantage of software and services: Stealers can attack the software and services used by enterprises, causing supply chain attacks and consequently leading to business disruption.
3. Prevention measures against Stealer malware attacks
3.1. For individuals
– Use anti-malware
- Install and maintain anti-malware: Make sure your anti-malware is kept up to date to protect against the latest threats.
- Perform periodic scan: Scan the system regularly to detect and remove malware.
– Be wary when opening emails and downloading attachments
- Check email origin: Do not open emails or download files from untrusted or unknown sources.
- Avoid strange links: Do not click on unknown links in emails or messages.
– Use strong passwords and perform password management
- Manage passwords: Use password managers to securely store and manage passwords.
- Use complex passwords: Create strong passwords, including upper and lower case letters, numbers, and special characters. It’s highly recommended to use passwords generated from password managers.
– Update software and operating systems
- Security patches: Make sure the operating system and all software are updated with the latest security patches.
- Automatic update: Enable automatic updates for applications and operating systems.
– Enable two-factor authentication (2FA)
- Online accounts: Enable 2FA for online accounts, important accounts, bank transaction accounts, and so on, to strengthen security.
– Restrict access right and use add-ons
- Secure add-ons: Only install add-ons from trusted sources and restrict their access.
– Use a virtual private network (VPN)
- Protect connection: Use a VPN to protect your Internet connection, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks.
- Hide IP address: VPN helps hide IP address and protect personal information from attackers.
3.2. For enterprises
– Implement and maintain comprehensive security solutions
- Anti-malware and firewalls: Leverage advanced anti-malware and firewall solutions to protect the enterprise’s network.
- Intrusion Detection System/Intrusion Prevention System (IDS/IPS): Implement IDS/IPS systems to detect and prevent cyber attacks.
- Endpoint detection and response/extended detection and response (EDR/XDR) systems: Implement EDR/XDR solutions to promptly detect abnormal behavior in the system.
– Conduct training and provide guidance to raise employees’ awareness
- Training programs: Organize regular training courses on security awareness for employees.
- Fraud prevention: Instruct employees to recognize and prevent phishing emails and other social engineering techniques.
- Phishing simulation: Periodically carry out phishing simulation on users, groups of employees who are in frequent contact with customers, and groups of users at high risk of cyber attacks.
– Adopt strong security policies and access control procedures
- Security policies: Develop and implement clear and strict security policies.
- Access control procedures: Ensure only authorized employees have access to important information and systems.
– Perform software updates and patch management
- Patch management: Implement a patch management process to ensure all software and operating systems are updated with the latest security patches.
- Vulnerability monitoring and assessment: Regularly check and evaluate systems to detect and fix security vulnerabilities.
– Back up data and develop a disaster recovery plan
- Periodic backup: Carry out regular data backups and store backup copies in multiple secure locations.
- Disaster recovery plan: Formulate and test a disaster recovery plan to ensure proper data and system recovery after an incident.
– Adopt two-factor authentication (2FA) and encrypt data
- Two-factor authentication: Apply 2FA for all critical accounts and systems.
- Data encryption: Employ encryption measures to protect sensitive data at rest and in transit.
– Monitor and check security regularly
- Security monitoring: Adopt security monitoring tools to track and detect unusual activities.
- Security checking and assessment: Perform periodic security checks and assessments to identify and remediate weaknesses in the system.
– Proactively hunt for threats
- Carry out threat hunting, proactively searching for leaked information and stolen accounts that are sold on public or private information channels to promptly respond to data exfiltration incidents.
| Exclusive article by FPT IS technology experts
Author Le Hong Hai – Information Technology Security Engineer at FPT IS |