The Power of the Twin Transition: How Going Green and Digital Builds a Better Future
Businesses face the increasing pressure to balance environmental responsibility with economic growth. Traditional models are being challenged by climate concerns, evolving regulations, and shifting consumer demands. The Green and Digital Transition presents a powerful strategy for businesses to meet these challenges head-on, ensuring both future viability and positive environmental impact. In the blog post, “The Power of the Twin Transition: How Going Green and Digital Builds a Better Future”, we explore how these interconnected forces offer solutions for challenges such as reduced resource efficiency, vulnerability to supply chain risks, and the need for innovation in a rapidly changing world.
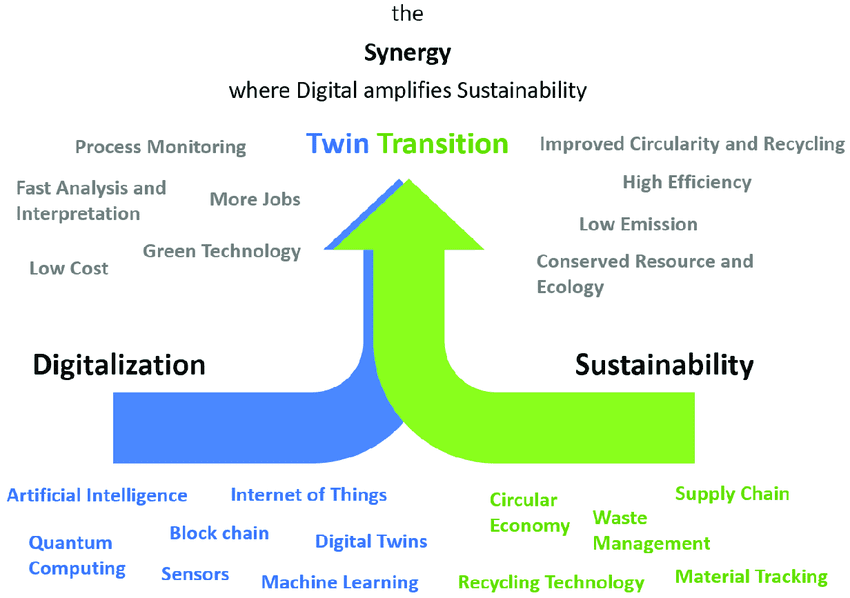
1. The Future is Digital and Green
The rising stars of sustainability, Green Transformation and Digital Transformation, are two sides of the same coin. Green Transformation focuses on shifting business practices and lifestyles towards environmental responsibility. This means reducing carbon footprints, promoting renewable energy, and adopting practices that minimize waste and pollution. Digital Transformation, on the other hand, is the integration of digital technologies across all aspects of a business. This can include areas like data analysis, artificial intelligence, automation, and cloud computing.
The intertwined concepts of green and digital transformation are reshaping the path towards sustainable business practices. Research highlights how digitalization drives green innovation, influencing areas like financing (Xue et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2023), supply chain efficiency (Minh et al., 2023; Lerman et al., 2022), and corporate environmental initiatives (Cheng et al., 2022; Sun & Guo, 2022; Sun & He, 2023; Li et al., 2022). These findings underscore the significance of the twin transition in securing both environmental progress and long-term business competitiveness.
2. Understanding the Green and Digital Transition
To navigate the complex landscape of sustainability and innovation, it’s vital to grasp the defining characteristics of both the Green Transformation and the Digital Transformation. These two movements, while distinct, have become increasingly intertwined as businesses recognize their potential as mutually reinforcing forces.
2.1. The Green Transformation: A Shift in Focus
The Green Transformation represents a fundamental shift in business goals and practices towards environmentally sustainable models. Key aspects include:
- Carbon Neutrality: Achieving a net-zero carbon footprint by minimizing greenhouse gas emissions and offsetting any remaining emissions.
- Circular Economy: Transitioning away from linear “take-make-dispose” models to systems where resources are used, reused, and recycled to minimize waste.
Green Transformation Examples:
- Renewable Energy: Shifting to sources like solar, wind, and geothermal power to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Efficiency: Optimizing processes and technologies to reduce energy consumption and resource waste.
- Sustainable Product Design: Creating products built for durability, repairability, and recyclability to reduce their environmental footprint.
2.2. The Digital Transformation: Harnessing Technology’s Power
The Digital Transformation involves the widespread adoption of digital technologies across all aspects of business operations. This entails:
Technologies:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Enabling intelligent automation, data analysis, and predictive insights.
- Cloud Computing: Shifting data storage and processing to scalable, accessible cloud-based platforms.
- Automation: Implementing robotic and software-based systems to enhance efficiency and streamline tasks.
Digital Transformation Examples:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Enabling intelligent automation, data analysis, and predictive insights (e.g., predictive maintenance, optimized energy management ).
- Cloud Computing: Shifting data storage and processing to scalable, accessible cloud-based platforms (e.g., facilitating remote work, supply chain tracking).
- Automation: Implementing robotic and software-based systems to enhance efficiency and streamline tasks (e.g., precision agriculture, paperless operations).
3. How the Twin Transitions Intersect
The Green Transformation, with its focus on sustainability, and the Digital Transformation, driven by technological innovation, are becoming inextricably linked. Understanding their intersection is crucial for businesses seeking to future-proof their operations and gain a competitive edge.
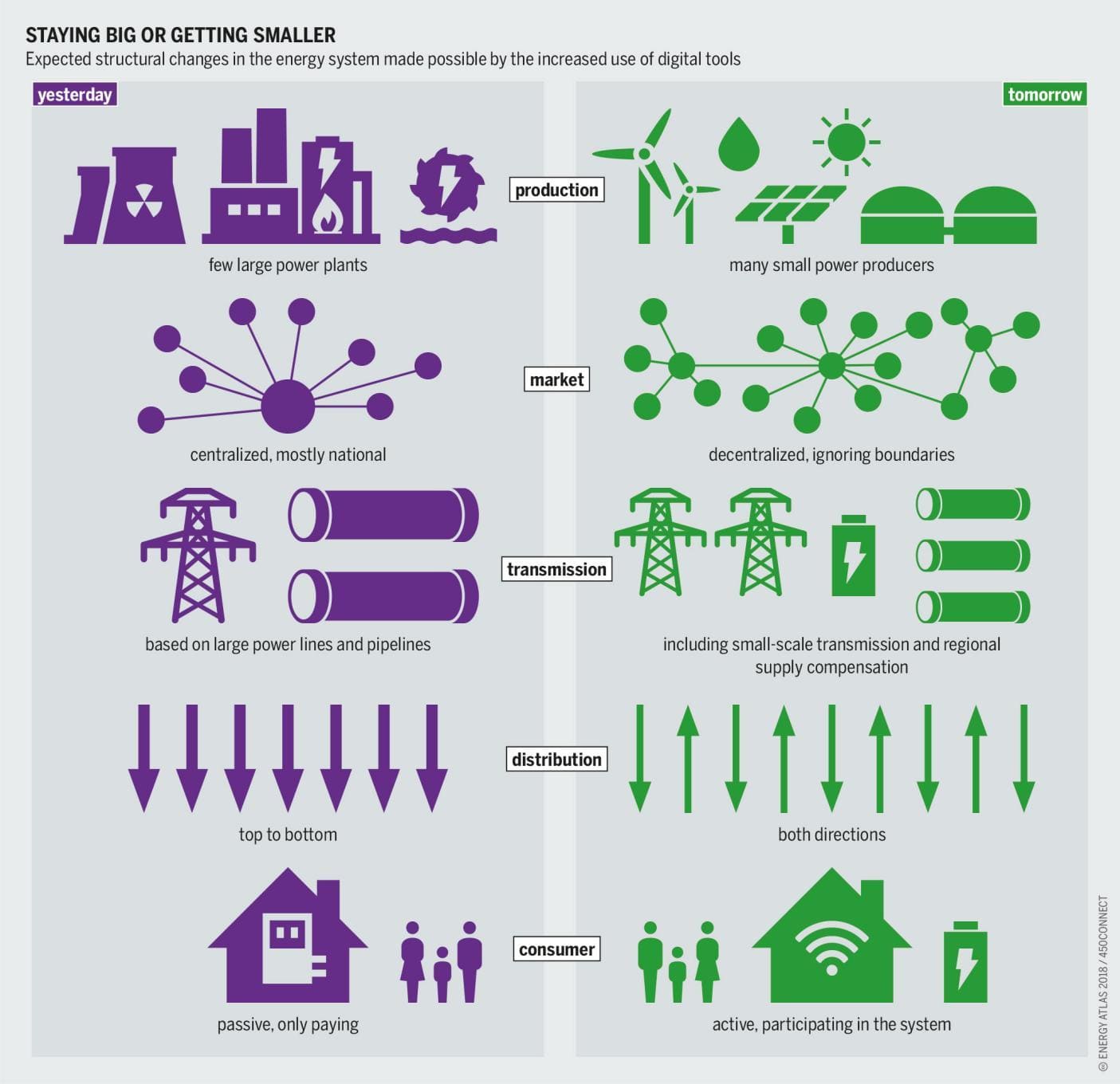
Smart Grids: Optimizing Energy for Efficiency and Resilience Digitalization empowers intelligent power grids that integrate renewable energy seamlessly. AI-based optimization matches energy supply and demand dynamically, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing emissions. This translates to cost savings and a more resilient energy infrastructure.
Smart Grids: Next-Generation Power Systems
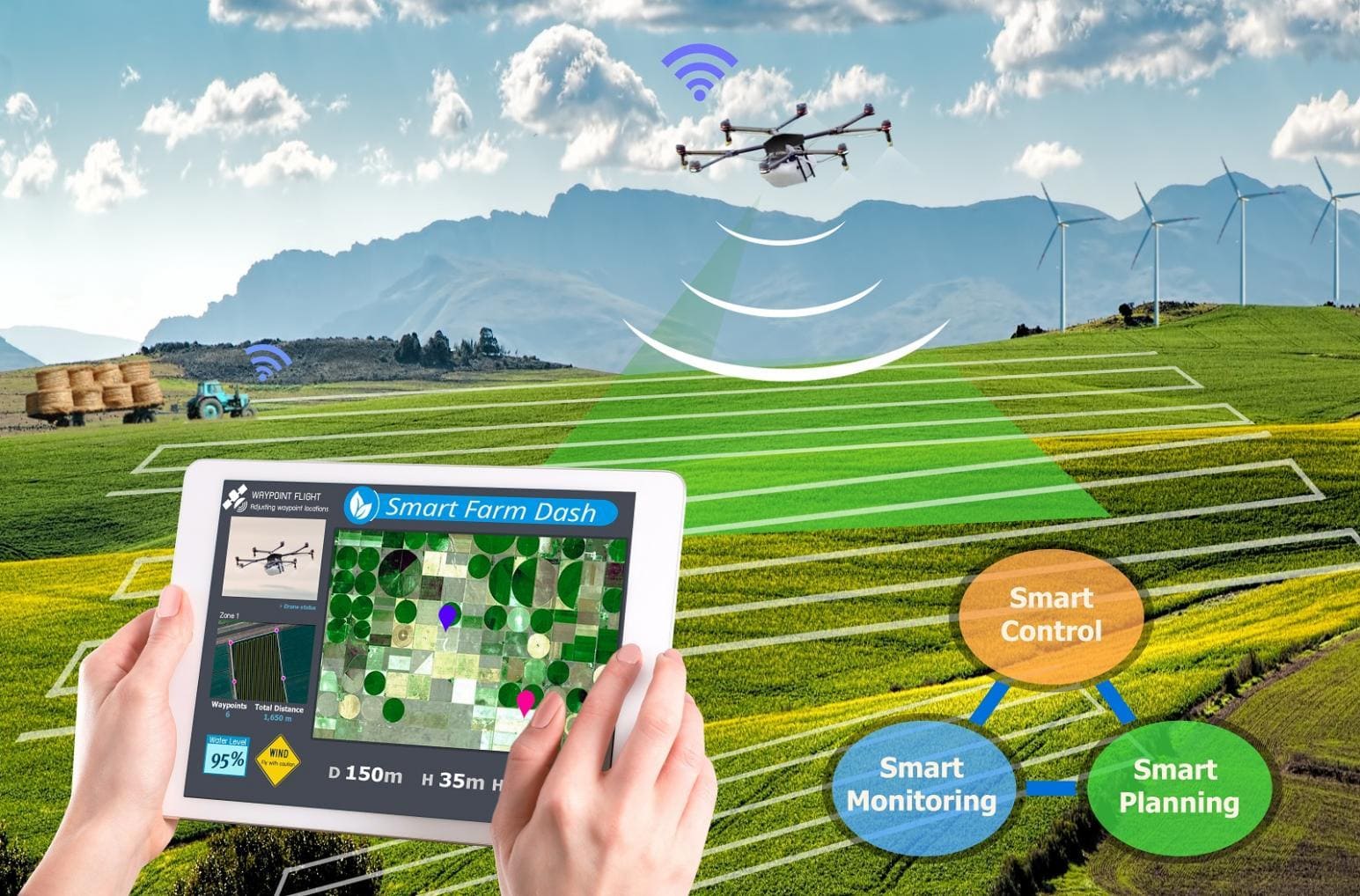
Precision Agriculture: Data-Driven Resource Management In precision agriculture, sensors and drones collect granular field data, enabling targeted use of resources like water and fertilizer. This approach minimizes waste, increases yields, and promotes sustainable farming practices. Businesses in the agricultural sector benefit from reduced operational costs and improved environmental performance.
Precision Agriculture – Smart Farm Use-case.
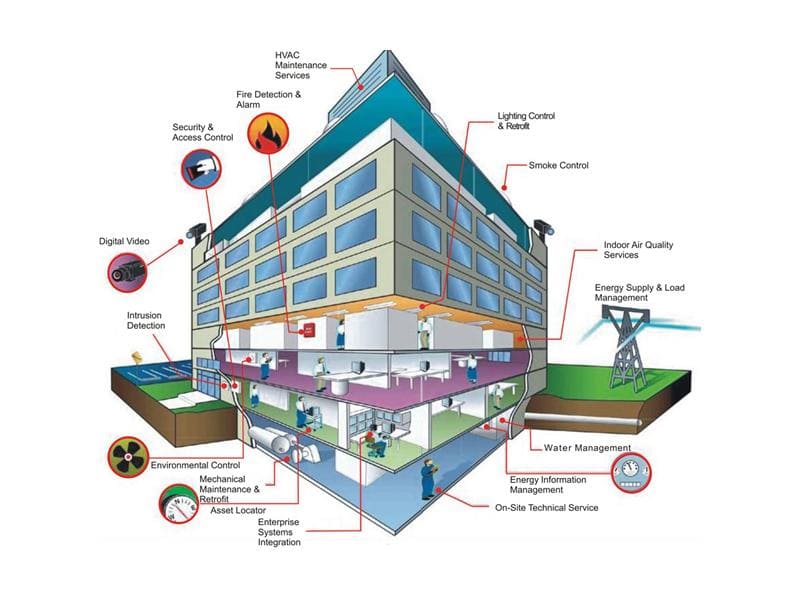
Smart Buildings: Optimizing Energy and Occupant Well-being Integrating digital sensors, automation systems, and AI-based analytics allows for intelligent control of lighting, heating/cooling, and ventilation within commercial buildings. This data-driven approach ensures optimal energy use and comfort levels, reducing both costs and environmental impact. Businesses benefit from efficient buildings that attract tenants focused on sustainability.
Building Energy Management System – Laplace Use-case
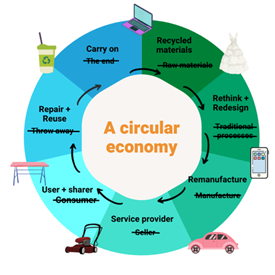
Digital Twins and Circular Economy: Driving Product Lifecycle Optimization Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical products or industrial assets. They allow for modeling, simulation, and testing throughout a product’s lifecycle, maximizing efficiency and enabling circularity. Businesses can design for durability and easier remanufacturing, reducing waste and unlocking new revenue streams.
Example of Circular Economy thanks for Digital Transformation
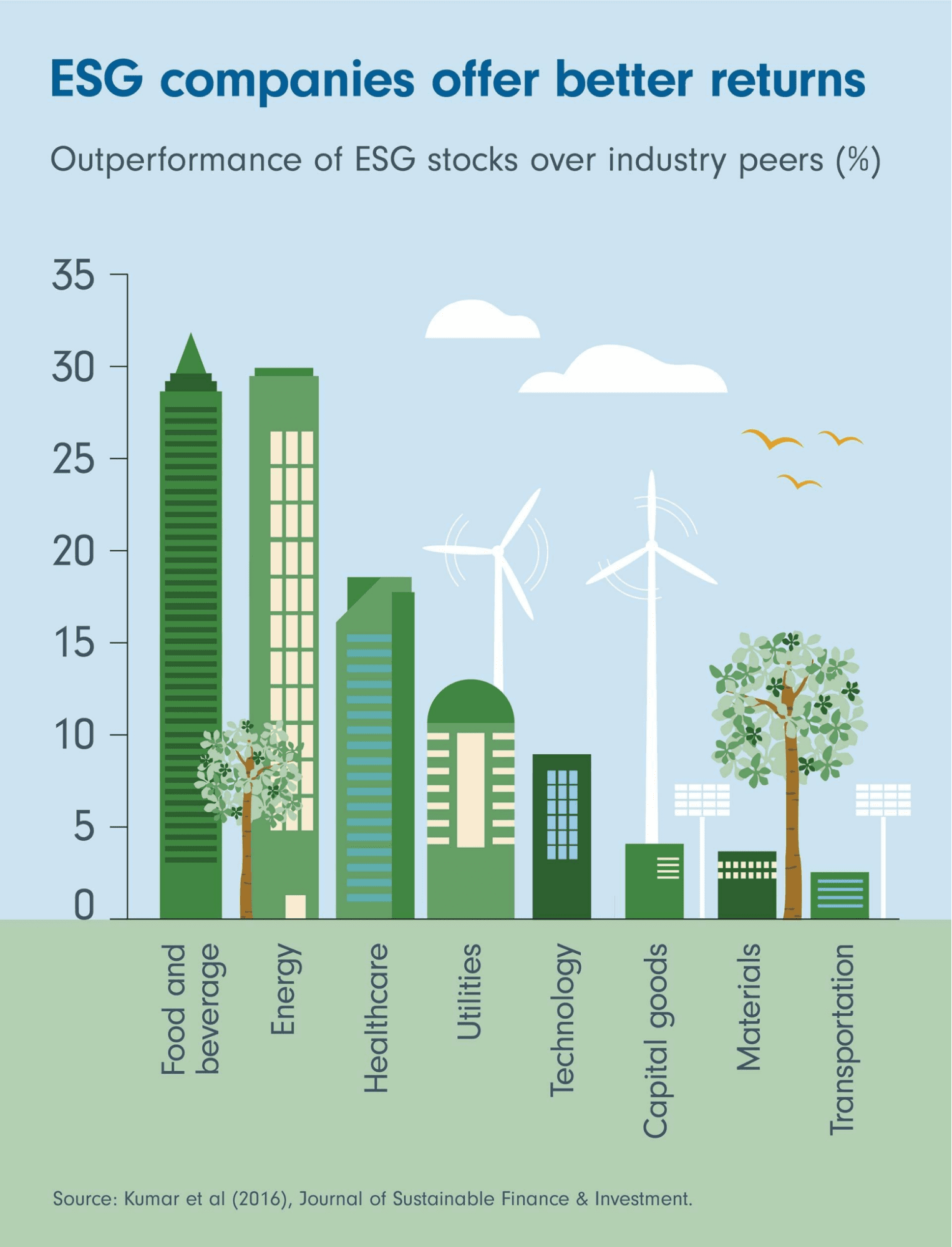
Sustainable Finance: Data and AI for ESG Investing Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors are playing an increasingly important role in investment decisions. AI-powered platforms now analyze vast amounts of sustainability data to inform investment choices, helping channel resources towards green initiatives. Businesses with strong ESG credentials can attract investment and build trust with stakeholders.
Banking Perspective on Green Lending
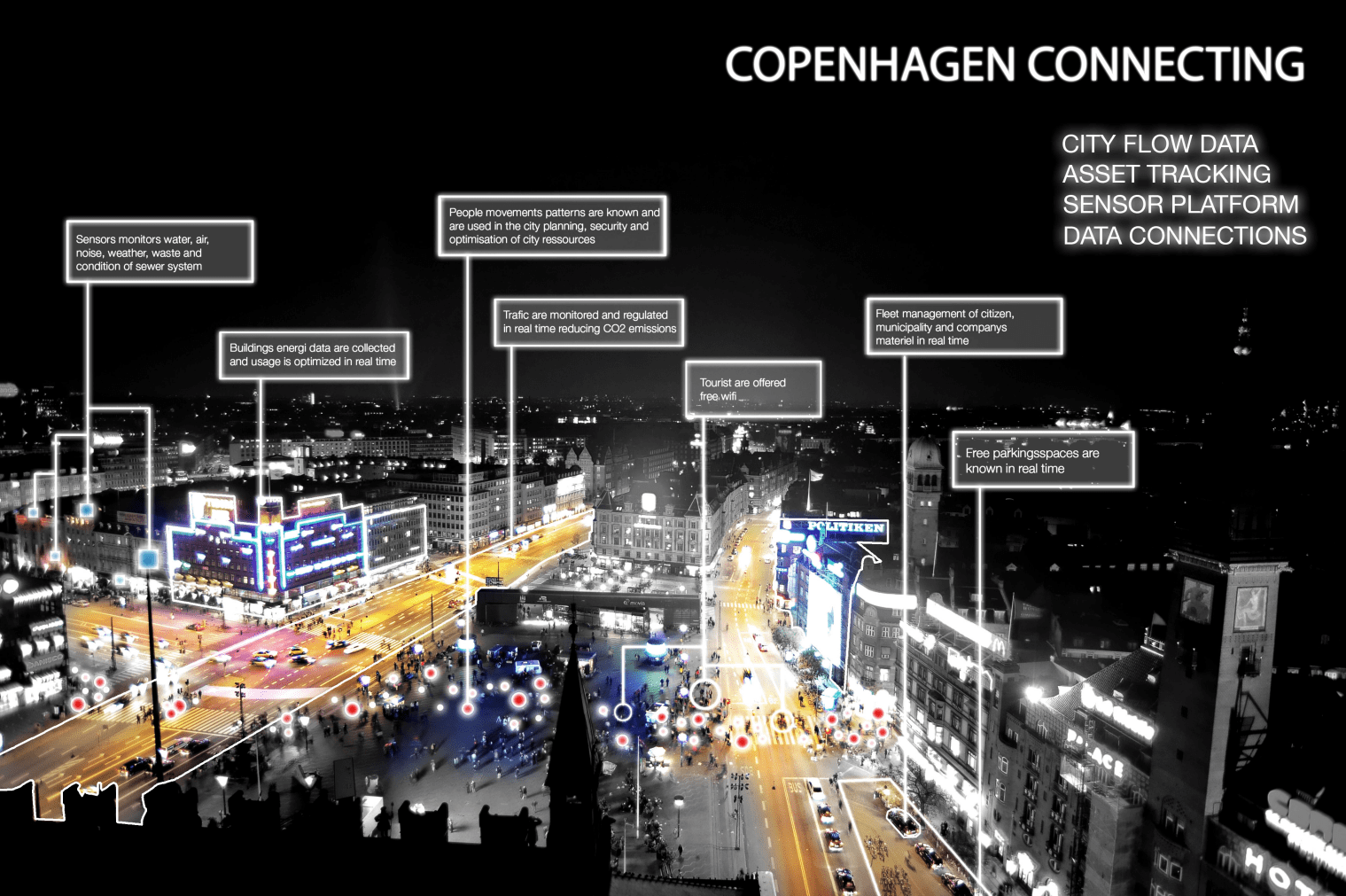
Smart Cities: Optimizing Urban Systems Digital technologies power smart cities, where interconnected sensors, networks, and analytics optimize traffic flow, waste management, water systems, and public services. This enhances livability, attracts businesses and skilled workers, and reduces the overall environmental footprint of urban areas.
Copenhagen (Denmark) wons the World Smart City Award
Remote Work and Green Commuting: The shift to remote and hybrid work, accelerated by the pandemic, has potential environmental benefits. Cloud-based collaboration tools and videoconferencing reduce the need for daily commutes, curbing emissions. Companies can attract top talent with flexible work arrangements and reduce the need for physical office space.
E-waste Management: Digital technologies can help tackle the growing e-waste problem. Platforms that facilitate the repair, resale, and recycling of electronics extend the lifespan of devices and reduce landfill waste. Companies can demonstrate responsible practices and potentially uncover new revenue models in used equipment markets.
4. Benefits for Businesses: Beyond the Bottom Line
The twin forces of Green and Digital Transformation hold immense potential for businesses, offering benefits that extend far beyond compliance. By adopting sustainability initiatives and leveraging digital technologies strategically, companies can gain a competitive edge, enhance their reputation, and build a more resilient future.
Key Dual Transformation Benefits
4.1. Cost Savings: Efficiency as the Profit Driver
One of the most immediate advantages is cost reduction through improved resource efficiency. Smart grids and building automation systems optimize energy use, cutting down on utility expenses. Precision agriculture and streamlined logistics powered by digital tools minimize waste, leading to tangible savings on raw materials and operational costs. The financial gain from ‘greening’ operations has the power to significantly improve a company’s bottom line.
4.2. Innovation: The Gateway to New Opportunities
The Green and Digital Transition acts as a catalyst for innovation. Necessity fuels the development of new products and services tailored to a green economy – from renewable energy technology solutions to sustainable product development. Process improvements, driven by data analytics and automation, pave the way for greater efficiency and new business models that fundamentally change how a company operates.
4.3. Reputation: Building Trust and Attracting Value-Driven Stakeholders
Consumers and talented employees are increasingly prioritizing companies with a demonstrated commitment to sustainability. Proactive engagement in the twin transition signals to customers a responsible approach to business, leading to increased brand loyalty and trust. A strong reputation in environmental and social responsibility can attract socially-conscious investors and give companies an edge in a competitive talent market.
4.4. Resilience: Preparing for an Uncertain Future
Climate change and supply chain disruptions pose significant risks to businesses. Digital tools such as predictive analytics and real-time supply chain visibility help companies build resilience, anticipating and mitigating supply shocks. Diversifying energy sources and investing in circular practices reduces dependence on resources that may become volatile in the future. Businesses that proactively embrace the twin transitions are better positioned to navigate a world of growing uncertainty and adapt to future challenges.
Unlocking the Power of Purposeful Transformation
While the initial adoption of green and digital technologies may require investment, the long-term benefits far outweigh the costs. The savings generated through efficiency, the potential for innovation, and the enhanced brand value make a strong business case. Moreover, companies taking the lead in these transformations position themselves as forward-thinking and responsible corporate citizens.
The Green and Digital Transition is not just a necessity; it’s a strategic opportunity. Businesses that grasp the interconnected nature of these transformations and align their actions accordingly, are setting themselves up for success in the 21st century and beyond.
|