Carbon Accounting Case Studies of The World’s Learning Value’s based banks
Addressing a Critical Need: Carbon Emissions Reporting in Finance
The Partnership for Carbon Accounting Financials (PCAF) has established itself as a leader in addressing the urgent need for streamlined carbon emissions reporting within the financial sector. Their Global GHG Accounting and Reporting Standard, tailored to various asset classes, provides a framework for financial institutions to track Scope 3, Category 15 emissions – those tied to investments and lending activities. This standard is a crucial step in aligning financial practices with the goals of the Paris Agreement, which emphasizes the importance of redirecting capital towards sustainable, low-carbon solutions.
In its 2020 version, the PCAF standard covers the following asset classes:
- Listed equity and corporate bonds
- Business loans and unlisted equity
- Project finance
- Commercial real estate
- Mortgages
- Motor vehicle loans
We’ve analyzed three independent case studies from values-based banks according to the report of GABV (2022). These studies illuminate the real-world challenges and exciting opportunities that come with implementing the PCAF standard.
Banking participants for completing this studies (GABV, 2022)
Key Takeaways for Your Enterprise
These case studies hold powerful lessons for large businesses interested in carbon reporting, credits, and ESG leadership. By learning from the experiences of early adopters, your enterprise can:
- Anticipate Challenges: Proactively tackle potential roadblocks for smoother implementation.
- Maximize Opportunities: Discover the potential benefits of carbon emissions assessments and disclosure.
- Enhance ESG Performance: Demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and position your enterprise as a positive force in the transition to a low-carbon economy.
1. Why measured financed emissions?
In today’s rapidly shifting business landscape, measuring and reporting your financed emissions isn’t just about environmental responsibility; it’s a strategic decision. Understanding the climate impact of your investments is crucial for setting attainable goals and spearheading the transition to a low-carbon economy.
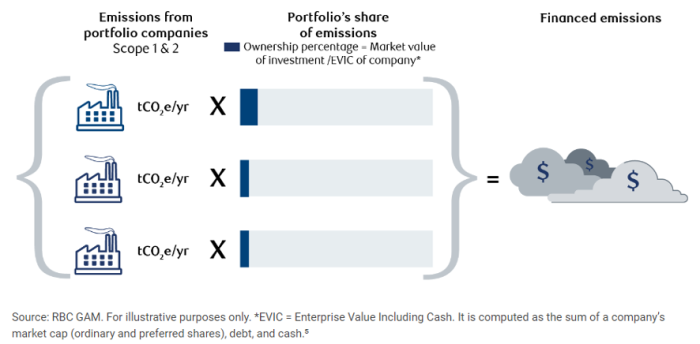
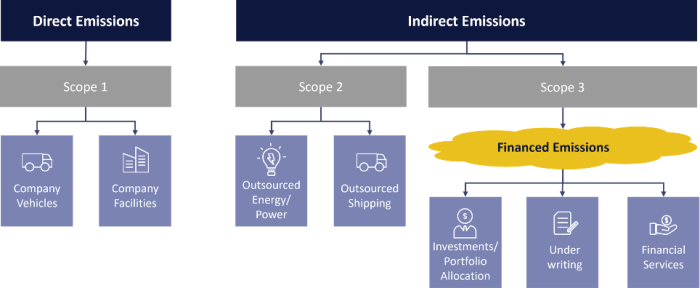
Finance Emissions in Category 15 – Scope 3 (PCAF, 2024)
Finance Emissions Breakdown (Invartis, 2024)
According to Global Alliance for Banking on Values (GABV) studies, there are three key takeways before any banks want to implement PCAF for their carbon emission declaration.
Key Takeaways:
- Essential Data for Informed Action: “Fighting climate change is a top priority for banks. We have a pivotal role in financing environmentally conscious initiatives. The PCAF standard gives us the data we previously lacked – the carbon footprint of our investments. It’s a baseline that allows us to set a clear direction toward a sustainable future.”
- Transparency = Trust: “Understanding our true environmental impact is crucial. We’re working to uncover the carbon emissions associated with our credit portfolio. This transparency is essential for building trust within our client relationships.”
- Sparking Client Dialogue: “Measuring financed emissions isn’t just about metrics; it’s an opportunity. It opens a dialogue with our clients about reducing their carbon footprint. It’s about demonstrating leadership – to clients and stakeholders – that meaningful, comparable action is possible within the financial sector.”
Embracing financed emissions reporting positions your business as a climate-conscious leader, unlocking competitive advantages, managing risks, and attracting investors and clients driven by a commitment to sustainability.
2. Why use the PCAF Standard rather than GHG Protocol?
The PCAF Standard offers a globally recognized framework for standardized carbon emissions reporting, providing businesses like yours with several compelling advantages:
- Global Standardization: “In a world of diverse reporting requirements, the PCAF Standard establishes a consistent, globally accepted methodology. This ensures comparability and builds credibility for your sustainability initiatives.”
- Comprehensive Asset Coverage: “Whether you’re dealing with diverse investment portfolios or specialized asset classes, the PCAF Standard’s comprehensive and evolving methodology adapts to your needs. It’s a versatile solution for businesses of all sizes and sectors.”
- Expert Support: “Implementing a new reporting standard can be complex. The PCAF Secretariat and organizations like the VertZero provide invaluable technical assistance, ensuring a smooth transition and maximizing the value of your carbon reporting efforts.
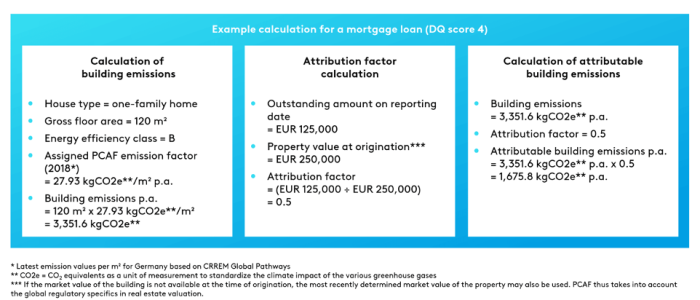
Example calculation for a mortgage loan (DQ score 4) (BankingHub, 2022)
Key Insight from Industry Leaders
Enterprises in developing economies highlight the importance of PCAF as a trusted global benchmark. Additionally, specialized institutions like microfinance banks emphasize the adaptability of the standard across various financial assets.
Universally Compelling Motivations
We’ve observed that banks across diverse business models, sizes, and locations share a common desire to implement PACF and align with the Paris Climate Agreement. These institutions universally recognize that measuring financed emissions is the crucial first step towards climate action. This underscores the widespread appeal of the PCAF standard, which offers a robust framework regardless of an institution’s characteristics.
The PCAF Standard streamlines your emissions reporting, strengthens the credibility of your ESG commitments, and positions you as an industry leader in the transition to a low-carbon future.
3. Navigating the PCAF Standard: Anticipating Challenges for Success
3.1. Understanding the Road Ahead: Anticipating Challenges with PCAF Adoption
The PCAF Standard offers a powerful tool for aligning your financial institution with the Paris Climate Agreement. However, like any significant initiative, its implementation requires careful preparation to address potential challenges. Understanding these challenges will streamline your journey and maximize the impact of your carbon emissions reporting.
3.2. Two Key Areas of Challenge:
Hard Challenges: These stem from the technical complexities of carbon accounting, including:
- Data Gaps: Limited access to reliable emissions data for certain investments.
- Data Quality: Inconsistent or incomplete data.
- Systems Integration: Adapting your institution’s data management to meet PCAF requirements.
- Understanding Complexity: Navigating the detailed methodologies of the PCAF Standard.
Soft Challenges: These relate to organizational and resource management:
- Limited Capacity: Insufficient staff or expertise dedicated to PCAF implementation.
- Process Clarity: The need for step-by-step guidance, especially in the initial stages.
- Language Barriers: Potential difficulties in accessing and interpreting resources.
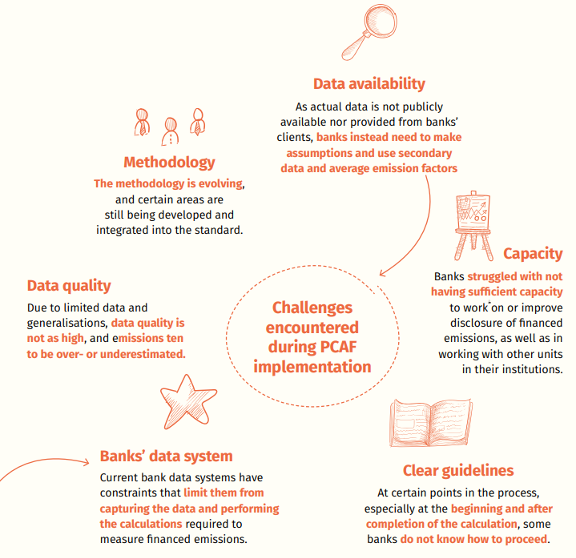
Challenges Encountered During PCAF Implementation (GABV, 2022)
Proactive Strategies from Industry Pioneers
Institutions already utilizing PCAF have successfully navigated these roadblocks. Learning from their best practices such as:
- Prioritize Data Improvement: Start with the best available data and establish systems for continuous improvement.
- Outsource Strategically: Engage consultants for specialized technical expertise and to streamline processes.
- Utilize Carbon Emission Software: Integrate all data touch-points and updated emission factors for financial activities from the software allow the banks to focus on bridging data gaps and improving data quality.
- Increase Internal Capacity: Dedicate sufficient resources and consider hiring specialists.
- Seek Guidance: Tap into the support resources offered by the PCAF Secretariat and industry organizations.
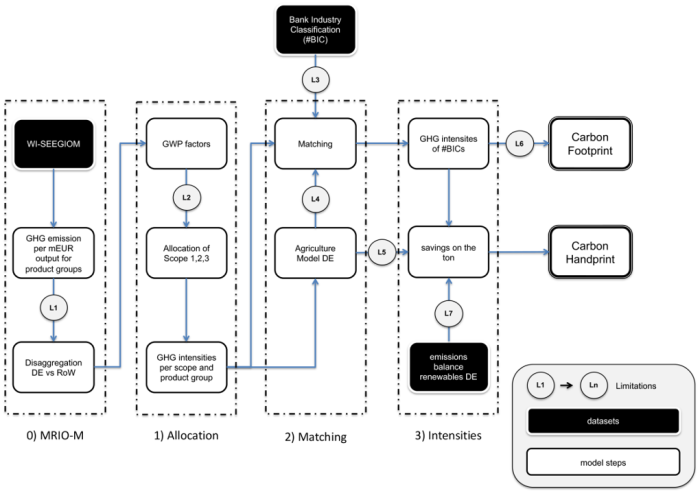
VertZero Model framework and model steps for Banking Data
Overall, anticipating these challenges is the first step toward success. By proactively addressing them, your institution will reap the full benefits of PCAF adoption, cementing its reputation as a responsible investor committed to climate action.
3.3. Data availability challenges & solution
Tackling Data Gaps in PCAF Implementation: A Common Challenge
Data availability is a key hurdle when calculating financed emissions using the PCAF Standard. Financial institutions frequently face a lack of accurate client-level emissions data and reliable public data sources, especially for specialized sectors or asset classes.
Key Issues:
- Missing Client Emissions Data: Often, the necessary details on clients’ direct emissions are simply not collected during the lending process.
- Limited Attribution Factors: Calculating the portion of a loan attributable to your institution can be complex, especially in microfinance contexts.
- Incomplete Industry Databases: Standard industry classifications (e.g., NAICS) may lack emissions factors for specific sectors or offer only generic data.
- Outdated Systems: Banking systems aren’t designed to capture the detailed data needed for PCAF emissions reporting.
- Adaptability Issues: Modifying systems, especially for smaller banks, can be time-consuming and costly.
- Manual Workarounds: Reliance on spreadsheets and manual data collection is inefficient and prone to errors.
- Incompatible Systems: Data stored in disconnected systems makes it hard to gain a comprehensive picture of emissions.
Solution 1: Addressing Data Challenges
- Simplified Data Collection: VertZero and similar platforms offer streamlined workflows to collect client emissions data. This may include customizable questionnaires, data templates, and integrations with existing client management systems.
- Access to Emissions Factors: Platforms often maintain extensive emissions factor databases, covering diverse industries and asset classes. These readily available factors simplify calculations and mitigate reliance on incomplete or unreliable external sources.
- Collaboration Features: Platform facilitate secure data sharing between financial institutions and their clients. This enhances transparency and fosters a collaborative approach to improving the accuracy of emissions data over time.
Solution 2: Overcoming Technical Hurdles
- Automated Calculations: Platforms automate complex PCAF calculations, reducing the need for in-house expertise in carbon accounting methodologies. This helps ensure accuracy and saves time.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Intuitive dashboards and reporting tools make it easier for non-specialists to interpret results and extract insights from emissions data. This supports decision-making and engagement across the organization.
- Educational Resources and Support: VertZero offer training guides, webinars, and dedicated support to help users understand the PCAF Standard and navigate the technical aspects of reporting.
Solution 3: Streamlining Organizational Processes
- Centralized Data Management: Platforms provide a centralized repository for emissions data, eliminating the need for disparate spreadsheets and manual data aggregation. This improves data quality, consistency, and accessibility.
- Reporting Templates and Automation: Customizable reporting templates align with PCAF and other sustainability standards, making it easier to generate reports for stakeholders, regulators, and potential investors.
- Scalability: Cloud-based platforms are designed to handle increasing volumes of data and support the growth of your institution’s carbon accounting program over time
Key Considerations
While platforms like VertZero significantly reduce the barriers to PCAF adoption, it’s important to remember:
- Data Quality: Even with streamlined processes, the accuracy of your emissions reporting ultimately depends on the quality of input data. Continuous improvement of client data collection is crucial.
- Customization: Choose a platform that offers flexibility to adapt to your institution’s specific needs and existing systems.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Thoroughly evaluate the costs associated with a platform against the potential benefits in terms of time savings, accuracy, and enhanced reporting capabilities.
3.4. Data quality challenges & solution
The Impact of Data Quality on Emissions Reporting
Limited data availability poses a significant challenge to the accuracy of financed emissions calculations. Financial institutions, like those within the GABV, frequently face situations where they must rely on assumptions and industry averages. This creates the risk of over- or underestimating your institution’s true environmental impact.
Key Issues and Limitations:
- Client-Specific Gaps: Vital details on client emissions, particularly those demonstrating strong environmental performance, are often missing. This forces the use of generic industry data.
- System Constraints: Core banking systems may not capture essential data points (e.g., property size for mortgages), hindering precise calculations.
- Tracking Progress: Overreliance on rough estimates makes it difficult to measure emissions reductions over time and inform strategic decision-making.
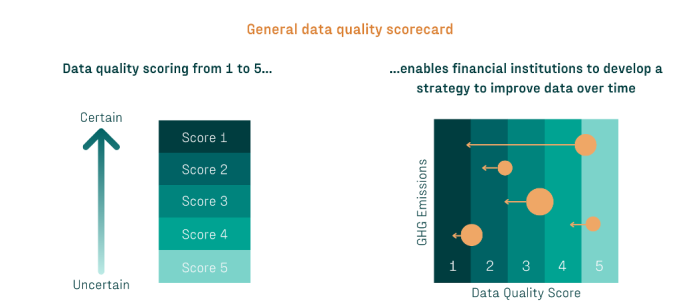
General data quality scorecard (PCAF, 2022)
Solution 1: Streamlining Data Collection and Management
- Client-Facing Tools: VertZero provide customizable questionnaires, templates, or integrations with existing client portals to gather more granular emissions data directly from the source. This can minimize reliance on generic industry averages and better reflect the environmental performance of your clients.
- Centralized Data Repository: The platform acts as a secure, centralized hub for emissions data. This eliminates manual data handling, improves consistency, and facilitates tracking of quality improvements over time.
- Data Validation: Platforms can incorporate built-in data checks and validation rules to identify potential inconsistencies or errors before calculations are performed.
- Access to Emissions Factors: VertZero often maintains an extensive database of emissions factors. This allows banks to replace generic industry averages with more sector-specific or even company-specific data, improving reporting accuracy.
- Collaboration Features: Some platforms may offer data-sharing tools that facilitate secure exchange with clients. This can foster an ongoing dialogue to improve the detail and accuracy of the data your institution has access to.
- Supporting the PCAF Data Quality Score: VertZero may have built-in features that align with the PCAF Data Quality Score framework. This helps banks transparently assess data quality and identify areas for targeted improvement.
- Integration Capabilities: The platform can seamlessly integrate with your existing banking systems to streamline workflows and minimize manual data entry.
- Continuous Improvement: Data quality requires ongoing effort and collaboration with clients.
Solution 2: Enhancing Decision-Making
- Visualizations and Analytics: Intuitive dashboards and reporting tools help visualize emissions data, allowing banks to pinpoint areas where data quality needs attention. This informs decisions on where to focus data collection efforts and client engagement.
- Tracking Improvements Over Time: Platforms can track historical data quality scores and improvements. This allows your institution to demonstrate a commitment to data transparency and track progress in its carbon accounting practices.
Let’s explore how VertZero’s specific features and data access can address your institution’s data quality challenges and drive more accurate emissions reporting.