Banking and financial transaction in the era of industry 4.0
People nowadays can open online accounts, obtain debit or credit cards, apply for loans within an hour, transfer money and make payments without a password, and sign electronic contracts with banks within minutes. To facilitate this, the National Assembly, the Government, and Ministries such as the State Bank of Vietnam and the Ministry of Information and Communications have issued decrees and regulations, promoting the application of IT for digital transformation in various sectors, especially finance and banking. Additionally, major technology companies in Vietnam like FPT, Viettel, CMC, and VNPT have developed solutions to enhance customer experiences, thereby accelerating the digital transformation of banks.
1. Legal basis
1.1. Decree no.87/2019/ND-CP:
Banks can choose whether to meet face-to-face with their customers when first establishing a relationship. If they decide not to meet customers directly, they must ensure that adequate measures, forms, and technologies are in place to identify and verify customers.
1.2. Decision no.149/QD-TTg:
The National Comprehensive Financial Strategy, approved by the Prime Minister in January 2020, permits the use of a simple and remote customer identification process with online electronic methods (eKYC) for opening accounts at licensed organizations. This is intended to meet the payment needs of individuals and businesses for small transactions.
1.3. Law on Identification no.26/2023/QH15:
The Research and Application Center for Residents Data (RAR), under the Ministry of Public Security, has officially launched a service for authenticating citizen information in chip-based ID cards. This service applies to various fields, including public services, banking and finance, taxation, social insurance, notary, education and training, transportation and aviation, security services, bailiff services, and more.
1.4. Decree no.130/2018/ND-CP:
The decree provides guidelines for the Law on E-transactions regarding digital signatures and digital signature authentication.
1.5. Decree no.165/2018/ND-CP:
The decree improves the legal framework and promotes e-transactions in the financial sector.
1.6. Circular no.16/2019/TT-BTTTT:
The circular provides a list of mandatory standards to be applied to digital signatures and digital signature authentication services in form of mobile PKI and remote signing.
1.7. Law on E-Transactions no. 51/2005/QH11 supplemented by Law no.20/2023/QH15:
The law defines electronic contracts, recognizes their legality, and outlines the principles for entering into and implementing them. It applies to the following fields:
- Employment contracts
- Service provision contracts
- Freelance contracts
- Loan agreements
- Bank guarantees
- Insurance contracts
- Passenger or cargo transport contracts
- Sales and purchase agreements
- Service and commercial contracts
- Agency contracts
- Purchase orders
- …
2. Technology Solutions
Based on the above legal foundations, corresponding technologies have been developed to apply IT in addressing the challenges posed by the Government.
2.1. eKYC (electronic Know Your Customer)
2.1.1. Overview
eKYC, a method of customer identification and authentication, utilizes various technologies to verify a customer’s identity by comparing collected data, such as images and videos of customer portraits, and identity documents (such as identity cards or passports) with databases.
This process enhances accuracy and reduces time and effort required for customer verification. Technologies employed in eKYC include:
- Video Call: It enables forensics to engage with customers in a manner akin to face-to-face identification and verification processes, making it more dependable than methods such as OTP or PIN codes.
- OCR (Optical Character Recognition): This technology is utilized to identify and extract information from crucial identity documents such as passports and identity cards, accelerating the verification process and reducing the likelihood of human errors.
- Face Matching: This technology analyzes and compares the similarity between portrait photos on identity documents like ID cards, driver’s licenses, passports, etc., with real face photos/videos to accurately identify the document’s owner. It can even discern the customer’s age.
- Liveness detection: This technology is employed to ensure that real individuals are present in real-time interactions, validating the authenticity of identification steps and preventing fraudulent activities.
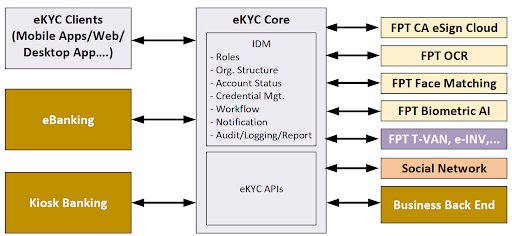
2.1.2.FPT.eKYC solution
Overall architecture of FPT.eKYC solution
Advantages of the solution:
- Verifying phone number via OTP
- Matching ID information with trusted identification data sources
- Comparing photos on ID cards with those uploaded by individuals
- Detecting facial spoofing attempts
- Verifying user-declared information against database records
- Searching for user information on social networks such as Facebook
- Verifying phone numbers, uploaded photos, and user device information
- Integrating FPT’s built-in online digital signature, eliminating the need for a USB token.
2.2. Digital identity verification
- This technology allows access to information stored on the ID chip, including the name, date of birth, hometown, parental information, facial data, and fingerprints.
- Integrated with the system of C06, a department under the Ministry of Public Security responsible for resident management, and the National Population Database, the technology also facilitates accurate and foolproof verification of personal information with 100% accuracy, effectively combating counterfeit data.
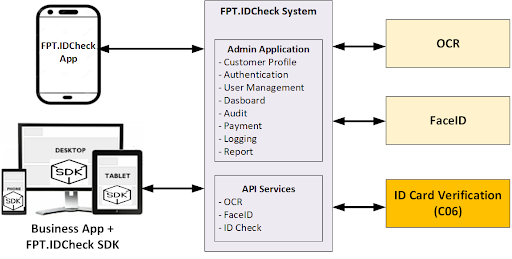
FPT.IDCheck solution
FIS and C06 (Police Department for Administrative Management of Social Order – Ministry of Public Security) have entered into a Partnership Agreement, a Non-Disclosure Agreement, and a Service Supply Cooperation Contract. These legal instruments form the basis for collaboration between the two parties to deploy a digital identity verification solution. This solution enables users to authenticate chip-based ID cards and utilize facial recognition technology with 100% accuracy, leveraging anti-fraud authentication AI technology that conforms to international standards (ISO 30107-3).
Overall architecture of FPT.IDCheck solution
Integration process
Advantages of the solution:
- Extraction of data from ID photos
- Extraction of data from ID chips
- Comparison of the portrait photo on the chip with the customer’s photo
- Comparison of the information on the chip with the data from the ID photo
- Comparison of the portrait image on the chip with the portrait image on the ID card
- Facial authentication utilizing Face Matching and Liveness Detection technologies
2.3. Digital signature
2.3.1. Overview
A digital signature is a type of electronic signature that encryptes information with the sender’s private key and attaches it to the document to ensure that the recipient can verify the correct origin and integrity of the received data.
When using digital signatures, it’s crucial to understand the following notable features:
- Authenticity: Digital signatures leverage digital certificates of individuals, organizations, and businesses to authenticate the identity of the signature owner.
- Security: Digital signatures offer robust security, making it difficult for hackers to steal information. This security is ensured by two layers of keys: a private key and a public key.
- Integrity: Documents bearing digital signatures can only be accessed by the designated recipient, ensuring the absolute integrity of the information in electronic transactions.
- Non-repudiation: Digital signatures prevent the alteration or deletion of signed documents or contracts.
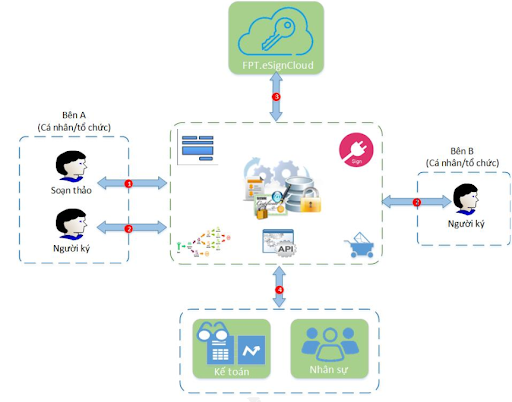
2.3.2. FPT.eSign solution
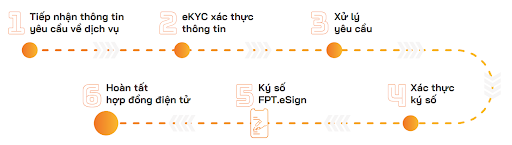
This solution offers digital signing services directly on mobile devices, eliminating the need for USB tokens or SIM cards by leveraging cloud technology. It is ideal for authenticating electronic transactions swiftly, securely, and reliably, enabling an unlimited number of transactions between individuals and organizations.
E-contract signing process
Advantages of the solution:
- Direct digital signing on mobile devices, eliminating the need for USB tokens or SIM cards.
- Compliance with Vietnamese laws and regulations regarding digital certificates and digital signatures, being licensed by the Ministry of Information and Communications.
- Full adherence to eIDAS regulation for digital identity and authentication (ISO 9001:2008, 27001:2013, and 50001:2011).
- Saving 80% of time and 85% of costs
- Capability of processing millions of transactions daily with high-speed connectivity.
- Applicable across various sectors including Banking, Finance, Insurance, Securities, and Business, facilitating the transition to Paperless Offices.
2.4. Electronic contract
2.4.1. Overview
An electronic contract is a contract established in the form of a data message, providing the following benefits:
- Convenience in managing, storing, and retrieving contracts
- Time and cost savings in terms of storage, preservation, and transportation
- Ease of signing contracts
- Ability to integrate with CRM and HR operational systems.
2.4.2. FPT.eContract solution
Overall architecture of FPT.eContract
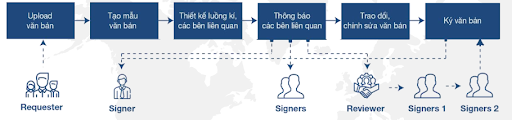
E-contract signing process:
- Document upload: The contract or document to be signed is uploaded to FPT.eContract.
- Identification of reviewer/signer 1/signer 2: The contract/document signing flow is created.
- Determination of fields to be filled: Signing positions and any additional information required from partners are defined.
- Email for notification: Relevant parties receive an email for signing the contract/document.
- Contract/document signing: Relevant parties sign or refuse to sign the contract or document.
Advantages of the solution:
- Management by distributed models at multiple levels
- Design of contract templates tailored to each type of contract.
- Enable management and signing of multiple documents simultaneously.
- Utilization of various digital signing functions, including signing with photos, USB tokens, or using CA.eSign Cloud
- No FPT.eContract account required for signing participants, including those outside the organization
3. Technology application to solve banking problems
Below is a digital transformation story of TPBank,
the first bank in Vietnam to implement the VTM (Video Teller Machine) system known as LiveBank. This innovative technology enables customers to perform various banking activities such as depositing money, transferring funds, opening savings accounts, and obtaining cards without needing to visit a traditional bank counter.
LiveBank’s system is fully automated and incorporates numerous advanced technologies, including biometrics, OCR handwriting recognition, digital signatures, and electronic contracts. The system is equipped with biometric identification devices and dual cameras to authenticate living entities and record transaction scenes. Each month, LiveBank facilitates the opening of tens of thousands of new accounts and the issuance of cards through this channel.
3.1. Online account opening
Technologies such as eKYC and digital identity verification are set to be implemented for opening online bank accounts.
This method offers convenience and speed in creating a bank account through online means. Below are the basic steps involved in opening an online account or online card at a bank:
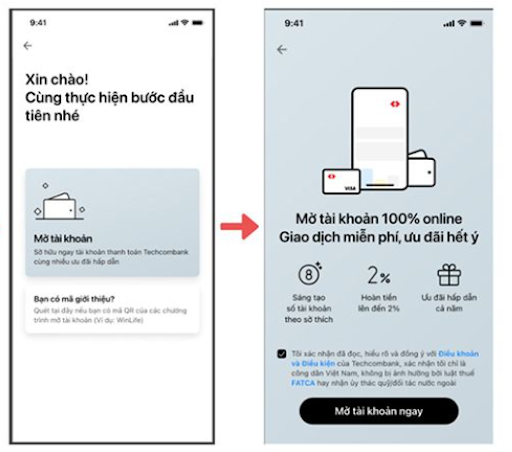
Step 1: Download the Mobile Banking app via CH Play or AppStore > Select New to Techcombank > Select Bank account > Select Register now.
Download the Bank’s Mobile App and choose to open an account.
Step 2: Enter and confirm personal details
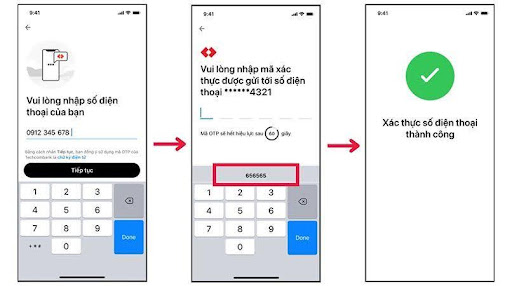
Enter the phone number and get OTP for verification: Enter the phone number > Confirm use of electronic signature > Enter OTP sent to the phone > Phone number successfully verified.
Enter the phone number and get OTP for verification.
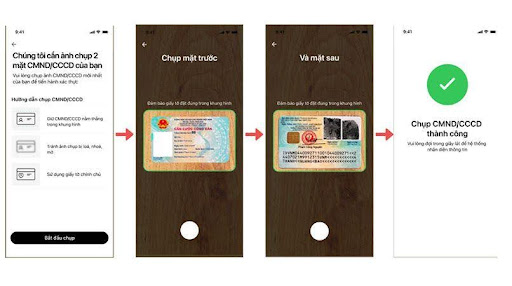
Step 3: Take photos of the ID card
Select Take ID card photos > Take photos of both sides of the ID Card.
Take photos of both sides of the ID Card
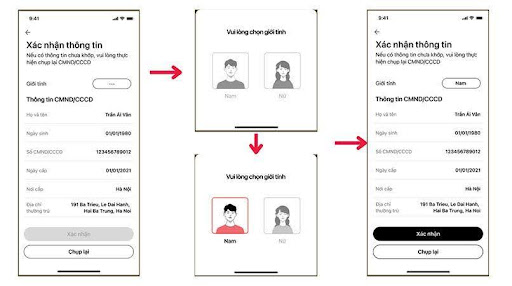
Confirm personal details: Confirm personal details > Select Confirm if they are correct or Retake if they are not correct > Select gender Male/Female > Confirm.
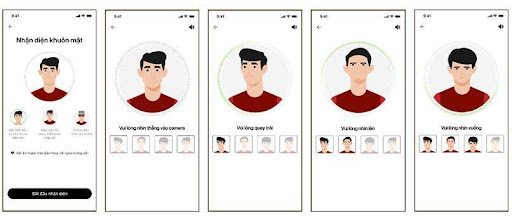
Step 4: Facial recognition: Select Start selfie verification > Look into the camera and follow facial movement instructions.
Verify your real face in every angle
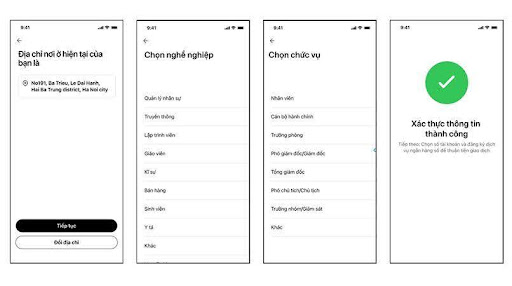
Confirm current residential address or change address if necessary > Select occupation and job position > Information successfully confirmed.
Confirm residential address, occupation and position.
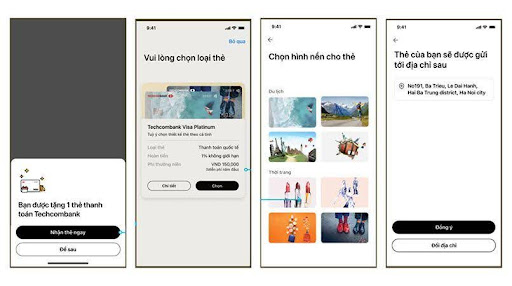
Step 5: Selection of card type and confirmation of physical card
Select Yes, send me one or Maybe later if you don’t need to use the card yet > Select card type > Press Select this card > Select card design > Reconfirm and select Agree > Confirm card delivery address and select Agree.
Confirm the card, choose the card type and your favored card design.
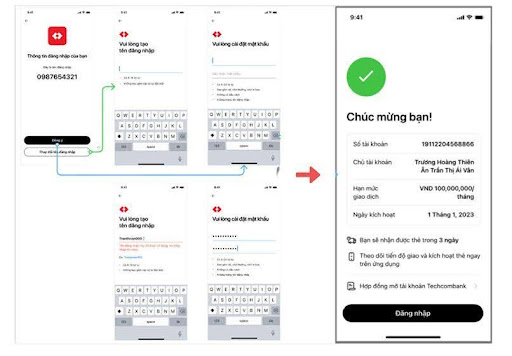
Step 6: Login setup: Enter login name > Set the password > Account successfully registered.
Create login details (phone number as username) and password.
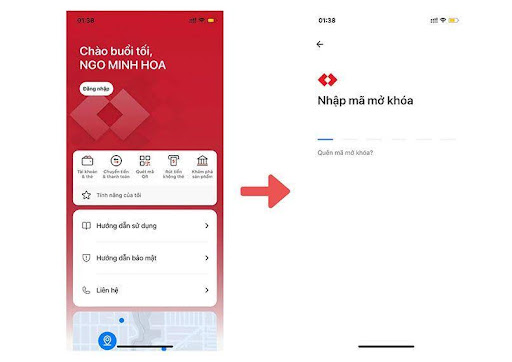
Step 7: Log in
Go to Techcombank Mobile > Select Log in > Enter the passcode or use Touch ID /Face ID to log in.
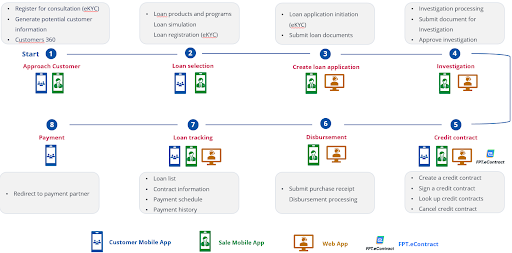
3.2. Online loan
Technologies such as eKYC, digital identity verification, electronic contracts and digital signatures will be also utilized in online loan application.
Below is an online loan process:
|