The war against ransomware: Attack to stay safe
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts a victim’s data, rendering them inaccessible until the ransomware demand is paid. Attackers often use social engineering tactics, such as phishing emails, and exploitable system vulnerabilities to find a way into the victim’s environment.
Understand the risks
The most common types of ransomware include:
Crypto Ransomware/Encryptors
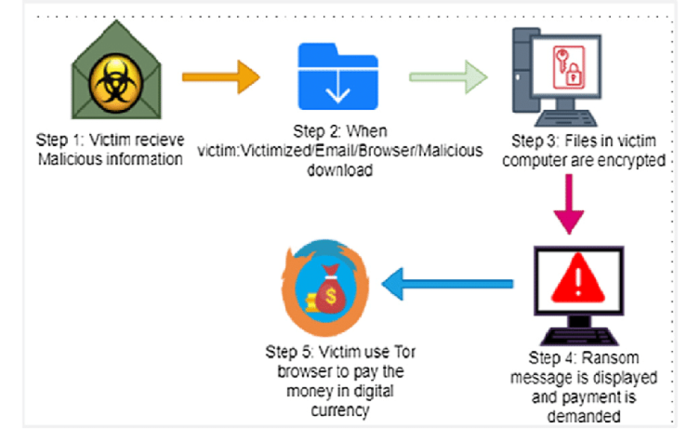
This is one of the most popular and damaging variants. This type encrypts files and data in the system, making them inaccessible, and providing no decryption key.
How Crypto Ransomware Works
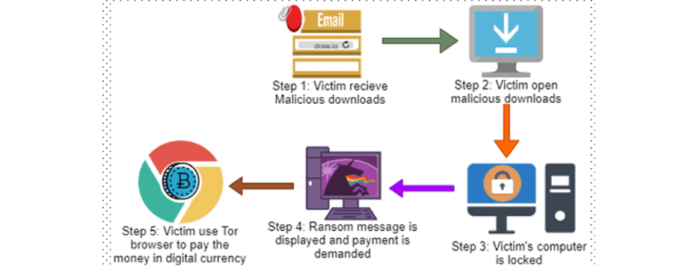
Lockers:Completely isolate (lock) you out of the system, rendering files and applications inaccessible. A lock screen will display a ransom demand, possibly accompanied by a countdown timer to increase urgency and urge victims to take action.
How Locker Works
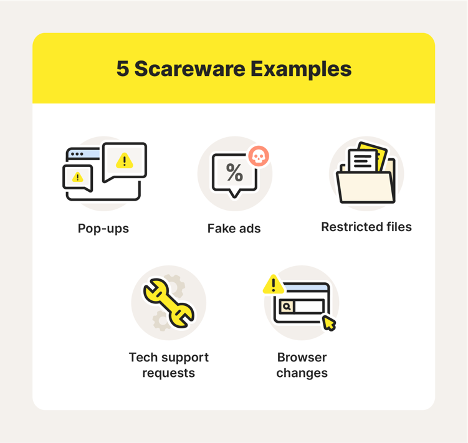
Scareware:Fake software that claims to have detected a virus or other problems on the victim’s computer and tricks them into paying a fee to resolve the problem. Some types of scareware lock the computer, while others simply fill the screen with pop-up warnings without causing actual harm to files.
An example of Scareware
Doxware/Leakware:A variant of ransomware designed to look like police, claiming that an illegal online activity has been discovered by the law enforcement agency, but can be resolved by paying a fine.
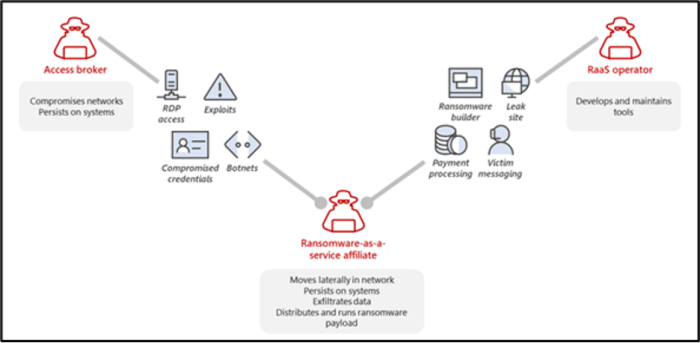
Ransomware as a Service (RaaS):Refers to malware hosted anonymously by a “professional” hacker who handles all aspects of the attack, from ransomware distribution to payment collection and access restoration, in return for a portion of the large sum received.
Ransomware attach vectors
Ransomware can gain access to a victim’s systems in a number of different ways. These pathways exploit vulnerabilities or intrusion techniques to launch attacks: Below are some common attack vectors:
- Phishing
- Malicious websites
- Malicious attachments
- RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) attacks
- Use of software with security vulnerabilities
- USB and portable storage devices
How to protect against ransomware threat vectors
Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is crucial for organizations to mitigate the risks posed by ransomware attack vectors. By adopting best practices and preventive measures, businesses can significantly reduce their attack surface and fortify their defenses against potential ransomware threats.
Here are some of the best ways to mitigate ransomware threat vectors:
- Anti-phishing protection and email security
- Password security and management
- Software updates and patching
- Security awareness training
Attack to defend
Handling and recovery from ransomware attacks can be extremely challenging and costly. Attackers tend to demand additional ransom in most ransomware attacks instead of walking away with the initial “agreed” amount. Therefore, robust ransomware defense must be a top priority for any company or individual. To build the most optimal defense plans, two major things need to be taken into account: Understand your systems and know your attackers.
To gain insight into the systems, organizations need to perform periodic checks and in-depth analysis of network structures, systems, and applications to identify weaknesses and security vulnerabilities, and accordingly taking necessary measures to protect the systems from potential threats.
Acquiring knowledge about attackers is equally important. This helps organizations better understand how these hackers operate, their goals, as well as their attack methods. By familiarizing themselves with potential cyberthreats from hackers, organizations can develop more accurate and effective defense plans.
To cover both of the above aspects, Penetration Testing could be an option. A penetration test (pen test) is a simulated real-world attack performed on a computer system to evaluate its security. Through regular pentests, organizations can detect and remediate security vulnerabilities before they are exploited by attackers. This helps strengthen systems and increase defenses against ransomware attacks and other cyber threats.
The goal of a penetration test is to attempt to get into the systems and discover systems’ security vulnerabilities and weaknesses, enabling businesses and organizations to work out corrective and defensive measures against future attacks.
Pentest: Attack to defend
Pentest is an important step in protecting the information and data of an organization or network. This requires continuous cybersecurity advancement as attackers are constantly looking to take advantage of security vulnerabilities to crash or infiltrate systems.
First, pentests help detect security holes in the system. By simulating external or internal attacks, pentests reveal weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers to infiltrate or steal important information.
Second, pentests provide an overview of the security posture of the system and network environment, thus enabling organizations to evaluate the performance of existing security measures and identify weak areas for improvement.
Third, pentests enable organizations to comply with security regulations and standards. As a number of industries require compliance with specific information security requirements, pentests will be a useful tool to ensure an organization’s satisfaction of these standards.
Fourth, pentests help build trust from customers and partners. Positive pentest results show an organization’s commitment towards information and data protection, creating trust and confidence from its partners and customers.
Finally, defense and attack play mutually reinforcing roles in safeguarding a system. Understanding the system and how to attack it enable you to build a secure one.
1. Pentest: Choose the right time
Before deploying a new system: Before deploying a new system or application, pentests help identify and address security vulnerabilities from the development phase, ensuring that the deployed system is highly secure.
When changing the system structure: Any change in the system’s structure can create new security vulnerabilities. Pentests performed after each structural adjustment will help maintain the system’s security.
On a periodic basis: Carrying out pentests periodically, such as every 6 months or annually, is an important part of a security strategy. This helps identify emerging security vulnerabilities and ensure that the system keeps meeting security requirements.
After an incident or attack: If case of security incident or attack, a pentest reassesses the security posture of the system and detects security vulnerabilities that may have been attacked.
When there is a change in the operating environment: Any change in the operating environment such as the expansion or contraction of IT infrastructure can also affect the security of the system. Performing a pentest helps ensure that the system security requirements are met in the new environment.
2. Pentest service implementation process
3. Preparation phase: Collect customer requirements, determine implementation scope and access boundaries. Set up security regulations to ensure customer systems will not be affected during the pentest implementation process
4. Information gathering phase: An important phase to collect information and search for potential signs and targets in a computer system or network. This process includes the following steps:
- Open information gathering: This is the first step and aims to collect information without penetrating into the system. Open information often includes domain names, contact information, network infrastructure information, etc.
- Use of automated tools: Pentest experts usually use automated tools such as Nmap, Recon-ng, Maltego, or Shodan to automate information collection. These tools can scan the network to identify hosts, open network ports, services running on those ports, and more.
- Data analysis: Once information is gathered, experts will analyze the data to understand how the network operates, where systems are located, what services are running, and what vulnerabilities may exist.
- Specific target information search: This process involves seeking specific information about targets such as usernames, emails, password encryption, etc., normally through public websites, forums, social networks or other information sources.
- Learn about system architecture: Learning about system architecture enables pentest experts to understand how system components connect to each other and how to find potential vulnerabilities in the system.
The information gathering takes place throughout the pentest process.
- Information optimization phase: Identify targets that require protection, attack targets, and produce a separate checklist that suits the system’s circumstances based on the collected information. Set up optimized configurations for pentesting software and tools.
- Foothold establishment phase: Gain a foothold via discovered system loopholes after all possible vulnerabilities have been searched and identified.
- Lateral movement and privilege escalation phase: Re-collect information, attack other targets in the system’s internal network, escalate privileges, and determine the most serious damage that can be done to the system.
- Reporting and defense recommendations phase: Compile a detailed and comprehensive report describing the attack implementation process, and provide practical recommendations to improve the system’s defense system.
| Exclusive article by FPT IS Technology Experts
Pentest Team – FPT IS Cyber Security Center |