Thought It Was a Work Appointment, Turns Out It Was a Gateway for North Korean Hackers
Recently, researchers discovered a sophisticated campaign using Telegram to impersonate real employees in target companies and create fake websites resembling Calendly and Picktime to schedule meetings with victims.
This campaign has been attributed to the North Korean cybercrime group Lazarus Group, known for cyberattacks targeting finance, espionage, and stealing cryptocurrency.
About Lazarus Group
Lazarus Group is a notorious hacker group (APT – Advanced Persistent Threat) believed to be closely linked to the North Korean government. This group has been active since the early 2000s and is known for its cyber espionage, sabotage, financial theft, and large-scale cyberattacks worldwide.
Some Notable Campaigns:
- Sony Pictures Hack (2014): Caused leaks of internal data, emails, and unreleased films. It also marked the beginning of Lazarus’s public sabotage attacks.
- Bangladesh Bank Heist (2016): Attacked the central bank of Bangladesh, attempting to transfer nearly 1 billion USD through the SWIFT system. Before being discovered, they successfully stole 81 million USD.
- WannaCry Ransomware Attack (2017): A global ransomware attack that encrypted data and demanded Bitcoin ransom. The campaign caused damage to hundreds of thousands of computers in 150 countries.
- Attacks on Cryptocurrency Exchanges (2017–present): Lazarus increasingly focuses on cryptocurrency to evade international sanctions. The total estimated damage amounts to billions of USD.
Main Impact
- Theft of cryptocurrency wallet keys and login credentials.
- Leak of digital assets worth tens of millions of USD.
- Installation of remote access tools (RAT), leading to loss of system control.
Campaign Details
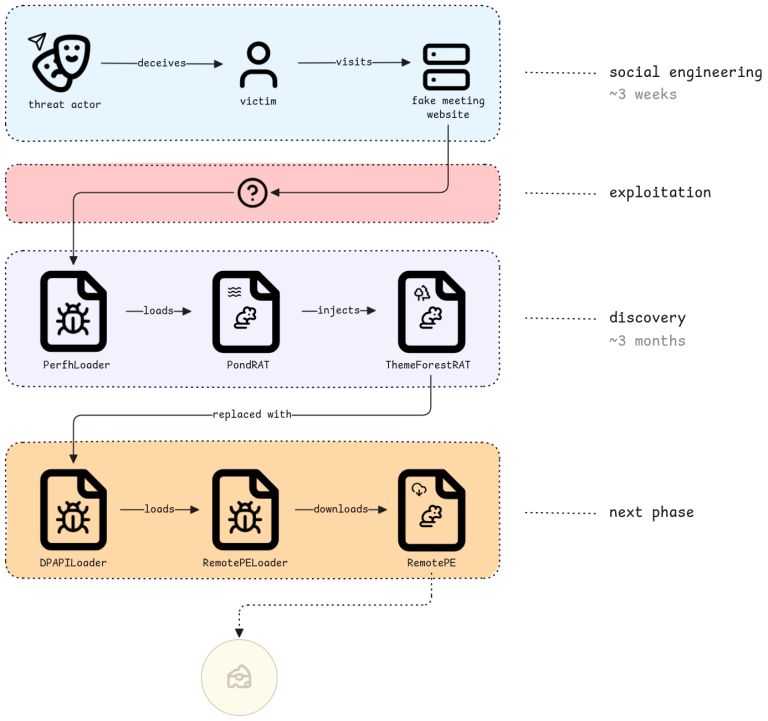
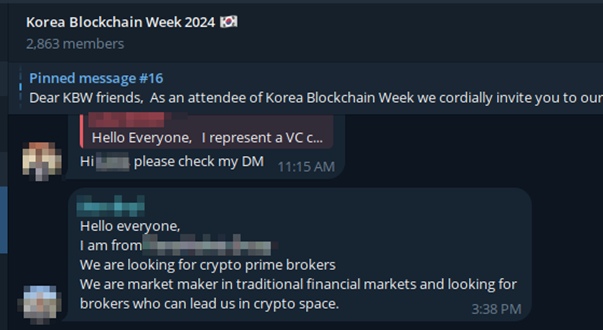
The hacker group Lazarus Group will carry out four main stages in this campaign. Initially, the attackers will conduct phishing through Telegram, where they impersonate employees of a trading company to approach victims. Here, the attacker sets up appointments by leading to fake websites mimicking scheduling services like Calendly or Picktime.
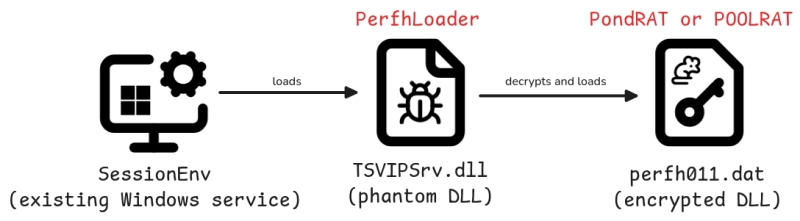
After tricking the victim into visiting the fake websites, the attacker will deploy perfhloader using the phantom DLL loading technique. Notably, it will automatically start when the user restarts their computer by setting the command: “sc config sessionenv start=auto“.
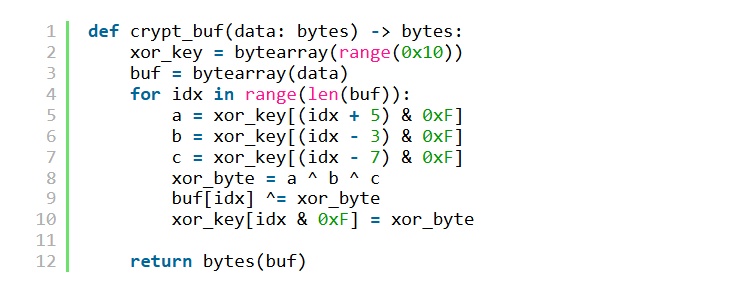
These loaders are responsible for reading an encrypted file (perfh011.dat), decrypting it, and loading the malware into memory. To avoid detection or complicate static analysis, the attacker used an XOR code.
After infiltrating and setting up the loader, the hacker group begins deploying PondRAT along with additional tools for the campaign. PondRAT can be understood as a simple variant of POOLRAT (aka SIMPLESEA) – deployed as a basic RAT to read and write files, launch processes, and execute shellcode.
Supplementary tools are also installed at this stage, such as a keylogger, screenshot utility, cookie or Chrome credential stealer, Mimikatz, and proxies like FRPC, MidProxy, Proxy Mini to support attacks through hidden networks.
Next, ThemeForestRAT will be deployed and run entirely in memory (fileless), through the previously established PondRAT. It can execute up to about 20 commands: manage files, list processes, inject shellcode, timestomp, execute commands, check TCP, download files, spawn processes, hibernate… Additionally, it will continuously communicate with C2 servers.
In the final stage, after operating with PondRAT and ThemeForestRAT, Lazarus will clean up traces of the previous RATs and deploy RemotePE. RemotePE is downloaded from the C2 through RemotePELoader, which is encrypted using Windows DPAPI (Data Protection API) and loaded by DPAPILoader. This enhances security and reduces the likelihood of analysis by security experts.
RemotePE is written in C++ by the attackers, indicating that it is the most sophisticated RAT, used only for high-value targets, with the ability for long-term control and high stealth.
Conclusion
The Lazarus Group’s attack campaign, observed in 2024 and published on September 2, 2025, demonstrated a multi-layered approach—from social engineering, through loaders, to advanced-stage RATs—to deeply infiltrate DeFi financial organizations. The attackers showed the ability to adapt their tactics flexibly depending on the situation and target.
This serves as a continued warning about the sophistication that APT groups like Lazarus can deploy in the high-tech and crypto-financial space.
Recommendations
- Enhance Input Security
- Train employees to recognize phishing techniques on Telegram, LinkedIn, and fake meeting schedules (fake Calendly/Picktime).
- Limit sharing of email addresses or personal contact information publicly.
- Implement an email gateway with sandbox to check attachments and links.
- Alert when employees click on external links.
- Access Management and Monitoring
- Enable mandatory MFA (2FA).
- Remove admin rights from regular users.
- Apply the principle of Least Privilege Access.
IOC
- Malicious Domain
- calendly[.]live
- picktime[.]live
- oncehub[.]co
- go.oncehub[.]co
- dpkgrepo[.]com
- pypilibrary[.]com
- pypistorage[.]com
- keondigital[.]com
- arcashop[.]org
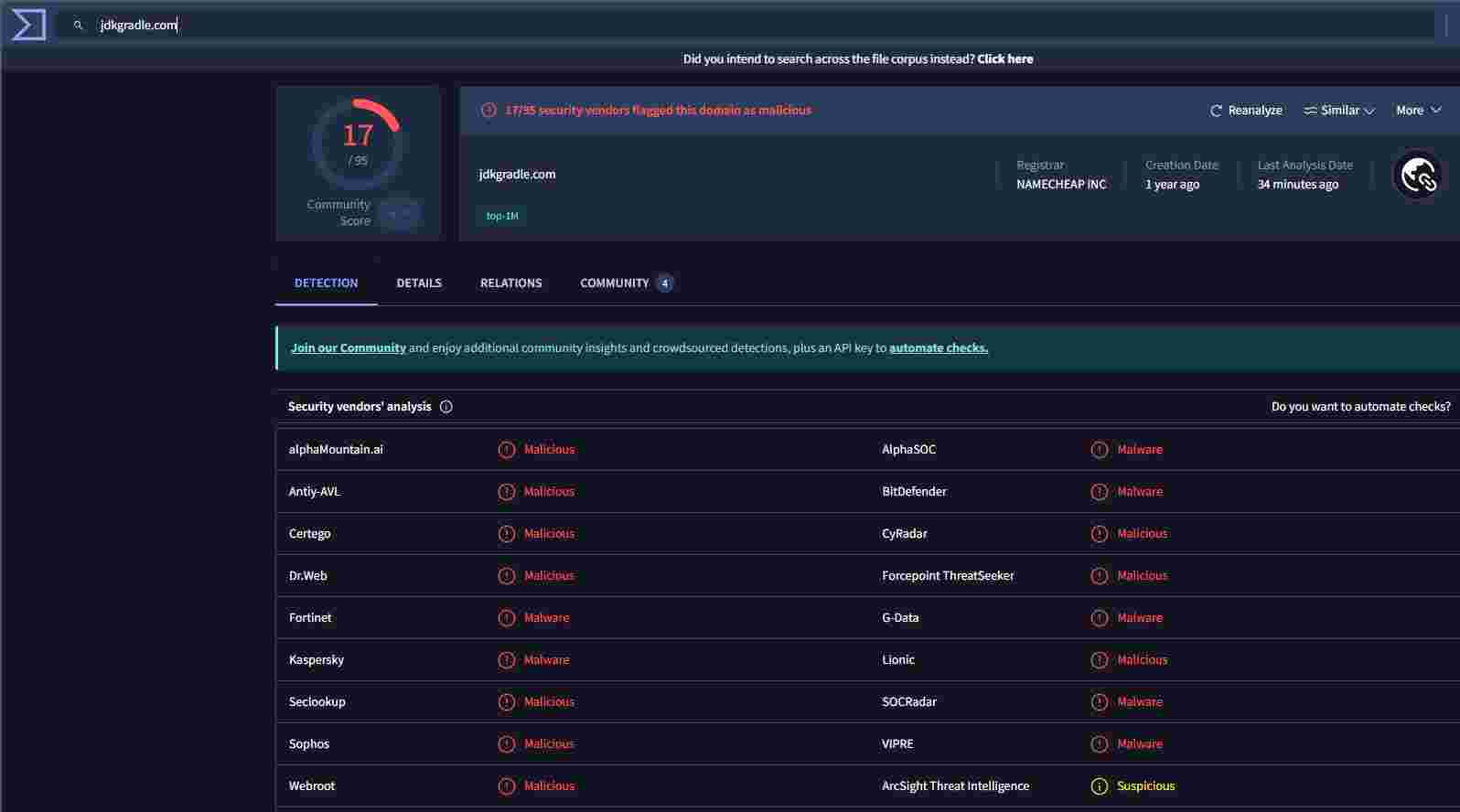
- jdkgradle[.]com
- latamics[.]org
- lmaxtrd[.]com
- paxosfuture[.]com
- www[.]plexisco[.]com
- ftxstock[.]com
- www[.]natefi[.]org
- nansenpro[.]org
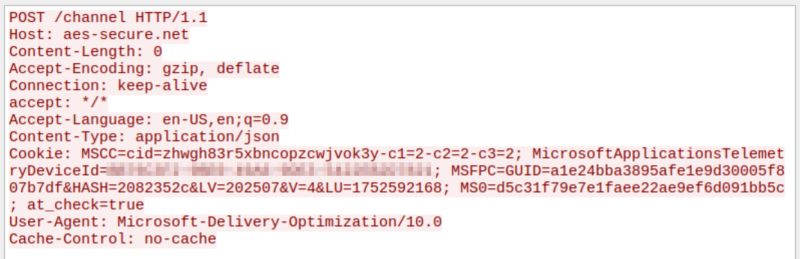
- aes-secure[.]net
- azureglobalaccelerator[.]com
- azuredeploypackages[.]net
- IP Addresss
- 144.172.74[.]120
- 192.52.166[.]253
References
- Lazarus Group Expands Malware Arsenal With PondRAT, ThemeForestRAT, and RemotePE
- Lazarus Hackers Deploying Three RATs on Compromised Systems Possibly Using 0-Day Vulnerability
- Lazarus Hackers Exploit 0-Day to Deploy Three Remote Access Trojans
| Exclusive article by FPT IS Technology Experts
Luu Tuan Anh – FPT IS Cyber Security Center |