Overcoming Carbon Accounting Roadblocks: A Case Study
1. Carbon Accounting: International Challenges for Companies
The complexity of carbon accounting without life cycle analysis has been identified as a major challenge due to subjectivity, inaccuracy, and complexity (Lackner, 2023). Methodological challenges related to system boundaries, functional units, and allocation in life cycle assessment for sustainability assessment of biofuels and bioproducts also pose obstacles in carbon accounting (Gheewala, 2023).
The challenges in carbon accounting extend to the need for more robust and standardized accounting methods for carbon removal approaches like soil carbon sequestration and enhanced weathering (Buck et al., 2020). Furthermore, the slow implementation of carbon calculation tools in industries like construction poses challenges that need to be addressed (Jackson & Kaesehage, 2020). The integration of carbon emission reduction into core business activities is crucial, highlighting the importance of accounting for divergent stakeholder demands (Winschel, 2021).
2. Company Highlights
- Publicly-listed IT Software company
- More than $1 billion annual turnover
- Active in 28 countries
- 26,000 employees worldwide
- More than 5,000 suppliers
Committed to achieving carbon neutrality, a category-leading IT Software company set ambitious science-based climate action targets to reduce its environmental impact. But how are they planning to reach these goals?
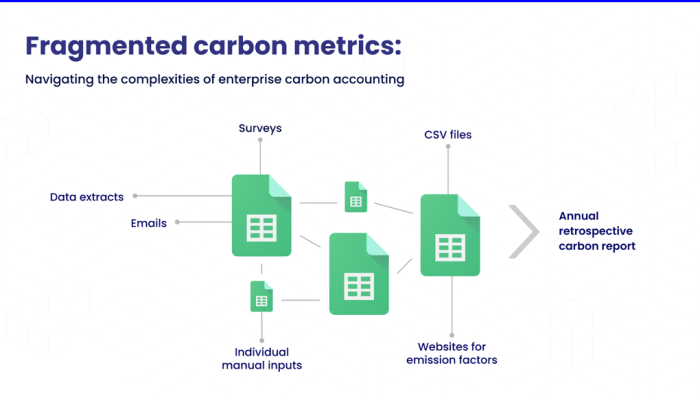
3. Problem: Outsourcing carbon footprinting has limitations for IT Software company companies.
For several years, the company had been using consulting services and spreadsheets to track its carbon footprint. Over time, their sustainability lead realized that this approach was insufficient for accurately measuring progress towards such ambitious targets. The process was disconnected, opaque, heavily dependent on manual data entry, and too slow. With a large workforce, operations in more than 28 active markets, and a large variety of use cases for carbon insights, a standard carbon accounting process would not be able to handle the company’s complexity. They concluded that the most future-proof approach was to bring this process from manual to automation.
“A large company wouldn’t hand over complete control of its finances to an outside consultants with manual processes. The same logic applies to carbon accounting – relying solely on manual processes leaves a company vulnerable and limits its ability to fully understand its environmental impact – Chief of Sustainability Officer”
4. Challenge: Tailored carbon management for data-driven sustainability across a multinational company
Carbon emissions, like financial data, are now a critical business metric for the company. This prioritization aims to empower every team with the insights needed to make emission-reducing decisions, from optimizing logistics routes to evaluating the carbon impact of raw materials.
Fragmented Carbon Metrics
The team prioritized the following in their new carbon management solution:
- Real-time insights: Automated, continuous tracking of carbon emissions across all operations (scope 1-3), providing a real-time picture of the company’s environmental impact.
- Adaptability for growth: A scalable, flexible system that easily integrates new data sources, regions, and sustainability initiatives as the company expands.
- Actionable data: Tailored carbon insights for specific teams (logistics, procurement, etc.), empowering them to make informed, emission-reducing changes.
- Transparency and trust: Calculations based on established scientific standards (like the GHG Protocol), ensuring accuracy and reliability for reporting and disclosure.
- Data security and efficiency: Full control over data governance to protect sensitive information, while streamlining processes and reducing reliance on manual, error-prone calculations.
5. Solution: Integrating carbon data into company-wide decision-making processes
The company is creating a centralized sustainability data hub then use this data hub to integrate with professional carbon accounting software for automation, accuracy and global comliance. This softwae will streamline data collection, integrate carbon insights, and provide teams with the information they need to optimize operations, reduce emissions, and enhance reporting – all without the burden of manual data management.
Project Team: Key Roles
- Sustainability Manager: Provides strategic vision for carbon management initiatives, aligns project goals with company-wide sustainability targets, and champions the project across the organization.
- Data & Analytics Manager: Oversees data strategy, ensures data quality and integrity, develops analytical models for carbon insights, and leads data-driven decision-making.
- Software Engineer: Develops and maintains software applications, tools, and dashboards for carbon tracking, reporting, scenario modeling, and integration into operational processes.
- [Partner] Carbon Accounting Software Expert: Provides specialist knowledge on carbon accounting standards (like GHG Protocol), best practices, software solutions, and ensures accurate and auditable calculations.
- [Partner] Data Analyst: Collects, cleans, and analyzes relevant data for carbon accounting, pinpoints emission hotspots and potential reduction areas, and translates complex data into actionable insights.
- [Partner] Data Engineer: Designs and builds the data infrastructure supporting the sustainability data hub, ensures scalability, data pipeline efficiency, and seamless integration across systems.
- [Partner] Climate Change Expert: Brings deep understanding of climate science, the latest research, and policy developments around climate change. This expertise helps inform targets, strategies, and translates the company’s efforts in the broader context of global climate action.
6. Automating carbon emission calculations
A major challenge in designing the sustainability data hub was the need for accurate carbon emission data. To avoid the pitfalls of manual data management, the team sought a partner with a scalable API solution. The software’s robust, transparent emission data provided the perfect solution, saving time and minimizing potential errors.
“The software provided immediate value with its reliable, well-structured, and transparent emission factor data. This streamlined our processes and ensured confidence in our sustainability reporting.” – Sustainability Manager
7. Lessons Learned: Driving Environmental Impact through Data
Investing in Data-Driven Sustainability: Challenges and Rewards
Creating a robust sustainability data management system demands strategic planning, including team building, scalable architecture, and iterative project execution. This commitment delivers significant returns. Here’s what this company achieved in just a few months:
- Automated Efficiency: Minimized manual work by integrating API for automated carbon emission calculations within a scalable system.
- Tailored Insights: Empowered teams across the organization with self-service access to relevant carbon metrics through a flexible, modular structure.
- Accountability and Trust: Ensured transparency and auditability through calculations aligned with the GHG Protocol and scientifically vetted methods.
- Data Sovereignty: Maintained full control over sensitive data with secure in-house data governance.
- Optimized Resources: Increased cost and time savings by automating tasks, reducing the need for external support, and effortlessly addressing stakeholder requests.
- Key Takeaway: While the initial setup may seem complex, the benefits of a data-driven sustainability strategy quickly become apparent, driving both environmental impact and business efficiency.
8. Take the next step towards data-driven sustainability
Discover how a robust, pre-built software solution like VertZéro can streamline your carbon management, automate emissions calculations, and deliver the transparency you need for strategic decision-making. Contact VertZéro to start your sustainability transformation today – for a greener tomorrow.