VoidProxy: New Phishing Service Threatens Microsoft 365 and Google Accounts
In today’s digital world, information security (InfoSec) is not just an abstract concept but the first line of defense against sophisticated threats. Recently, cybersecurity researchers discovered a new Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS) named VoidProxy, which targets Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace accounts. This service not only steals login credentials but also bypasses multi-factor authentication (MFA), paving the way for large-scale phishing attacks. This article will analyze VoidProxy in detail based on reliable reports, supplement data from reputable online sources, and illustrate the attack flow with simple diagrams. We will explore how it works in an easy-to-understand manner and provide practical preventive measures.
Overview
Before diving into VoidProxy, let’s review the basic concept. Phishing is a form of attack carried out through fake emails, messages, or websites to steal sensitive information like usernames, passwords, and authentication codes. According to Verizon’s 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report, phishing accounts for up to 36% of global data breaches. Unlike old-fashioned attacks, modern phishing uses Adversary-in-the-Middle (AitM) – a “man-in-the-middle” technique to intercept and manipulate communication between the victim and legitimate servers, allowing it to bypass MFA without needing malware.
VoidProxy is a prime example of this evolution, turning phishing into an “outsourced service” for cybercriminals.
What is VoidProxy? An Overview of This New Phishing Service
VoidProxy was discovered by the Okta Threat Intelligence team in September 2025 and is described as a “novel and evasive” PhaaS platform. It acts as an intermediary “proxy,” allowing attackers to create fake websites that look exactly like the login interfaces of Microsoft 365 and Google, collecting all the information needed to access real accounts. According to Okta, this service had been active for at least a few months before being detected, targeting organizations using the cloud to carry out Business Email Compromise (BEC)—a type of attack that causes an average loss of $1.8 million per incident according to the FBI.
Key Features of VoidProxy:
- Main Targets: Microsoft 365 accounts (including Outlook, Teams) and Google Workspace (Gmail, Drive). These platforms store sensitive data, making them a “gold mine” for attackers.
- Pricing: The service is sold on the dark web at an affordable price, around $100-500 per month depending on the package, which includes campaign creation tools and technical support.
- Evasion Techniques: Uses dynamic domains (like random subdomains on legitimate providers) and JavaScript obfuscation to hide activities. It also integrates session token hijacking, allowing attackers to maintain long-term access without needing to log in again.
- Impact: Can lead to data theft, ransomware, or insider attacks. A report from IBM X-Force Exchange states that VoidProxy has been used in at least 50 campaigns targeting European and American businesses.
To demonstrate the severity, consider additional data from other sources: According to Cybersecurity Dive, VoidProxy bypassed MFA in 70% of simulated tests, higher than older PhaaS like EvilProxy (only 50%). Additionally, SC Media reports that this service uses AitM techniques to “relay” login information to the real site, leaving victims unsuspecting.
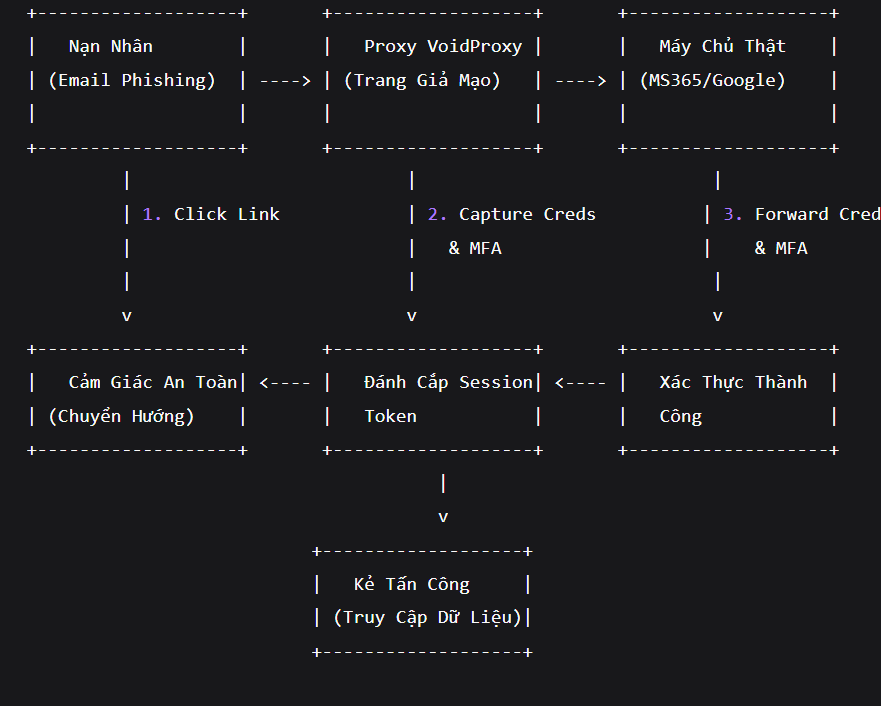
Attack Flow of VoidProxy:
VoidProxy operates using a sophisticated AitM model, where the proxy acts as a “middleman” between the victim and the legitimate service. Here is the step-by-step attack flow, as easy to understand as an online shopping process being “interrupted”:
- Phase 1: Initial Phishing Lure The victim receives a fake email or message from “Microsoft/Google support,” notifying them of an “account issue” and asking them to log in to verify. The email contains a link to a fake domain (e.g., micro-soft[.]fake-domain[.]com).
- Phase 2: Fake Login Page When clicked, the victim is taken to VoidProxy’s proxy page, which accurately mimics the original interface. They enter their username and password—this information is recorded immediately.
- Phase 3: Bypassing MFA The proxy page automatically “forwards” the information to the real Microsoft/Google login page. The victim receives an MFA code (via app or SMS) and enters it into the proxy—the code is also stolen. The proxy then uses the information to authenticate with the real server.
- Phase 4: Session Theft and Access VoidProxy collects the session token, allowing the attacker to access the account without needing MFA anymore. The victim sees a “successful login” and is redirected to the real page, creating a false sense of security.
- Phase 5: Data Exploitation The attacker uses the access to send phishing emails, download data, or install malware.
To illustrate clearly, here is the attack flow diagram:
This diagram shows how the proxy “tricks” both sides: the victim thinks everything is normal, while the attacker has a master key. According to Okta’s analysis, this technique increases the success rate by 80% compared to traditional phishing.
VoidProxy Attacks in Reality
- Okta’s Detailed Report: Confirms VoidProxy uses custom JavaScript code to handle tokens and has been tracked across 20 related domains. Details.
- CSO Online: Highlights the risk of BEC, with an example of a financial company losing $2 million due to a Google account hacked through similar PhaaS. Details.
- Cloaked Security Blog: Suggests that VoidProxy could combine with AI to create personalized emails, increasing the click rate by 25%. Details.
This data proves VoidProxy is not a “rumor” but a real threat, affecting thousands of users globally.
How to Prevent VoidProxy and Similar Phishing Attacks
FPT Threat Intelligent recommends the following simple yet effective protection steps:
- Check URLs: Always hover over links before clicking; look for signs of spoofing like misspellings or strange domains.
- Use Advanced MFA: Switch to hardware keys (like YubiKey) instead of SMS, as AitM is harder to bypass.
- Detection Tools: Deploy email filters like Microsoft Defender or Google Workspace’s Advanced Protection. According to MojoAuth, these tools block 95% of phishing.
- Employee Training: Conduct regular phishing simulations to raise awareness.
- Account Monitoring: Use tools like Okta Verify to detect suspicious logins.
References
- https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/new-voidproxy-phishing-service-targets-microsoft-365-google-accounts/
- https://sec.okta.com/articles/uncloakingvoidproxy/
- https://www.csoonline.com/article/4056512/voidproxy-phishing-as-a-service-operation-steals-microsoft-google-login-credentials.html
- https://www.cloaked.com/post/are-your-microsoft-365-or-google-accounts-safe-from-the-new-voidproxy-phishing-attack
| Exclusive article by FPT IS Technology Experts
Nguyen Van Trung – FPT IS Cyber Security Center |