Green Industry: The Blueprint for Sustainable Economic Growth
In an era marked by climate change, resource scarcity, and rising environmental awareness, a transformational shift is underway – the rise of the green industry. This model of economic progress prioritizes environmental protection, resource efficiency, and social well-being as its driving forces. From manufacturing and energy to agriculture and construction, green industry principles are reshaping the way we produce, consume, and dispose of goods and services.
A visualization about the green future world (Sawasdee, 2023)
1. What is Green Industry?
At its core, green industry aims to decouple economic growth from environmental degradation. It involves:
- Resource Efficiency: Maximizing the use of water, energy, and raw materials throughout the production process.
- Pollution Prevention: Minimizing emissions, wastewater, and hazardous waste generation.
- Sustainable Product Design: Creating products that are durable, easy to repair, recyclable, or biodegradable.
- Circular Economy: Transforming waste products into valuable resources for new production cycles.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Shifting from fossil fuels to solar, wind, geothermal, and other clean energy sources.
An example of Thailand Ministry of Industry requirements for Green Industry
2. The Drivers of the Green Industry Revolution
The transition towards a green industrial model is fueled by a confluence of factors:
- Environmental Imperatives: The urgent need to combat climate change, air and water pollution, and biodiversity loss demands a new approach to industry.
- Global Sustainability Frameworks: The Paris Agreement, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), and national climate targets provide a roadmap for green transformation.
- Government Policies and Incentives: Regulations, subsidies, and tax breaks are incentivizing businesses to adopt environmentally friendly practices.
- Consumer Demand: Increasingly, consumers are seeking out products and services from companies that demonstrate environmental responsibility.
- Investor Pressure: Investors are recognizing the risks of climate change and the opportunities inherent in sustainable businesses, shifting investment towards green industries.
- Technological Innovation: Advancements in clean technologies, renewable energy systems, and resource-efficient processes are making green industry practices more accessible and cost-effective.
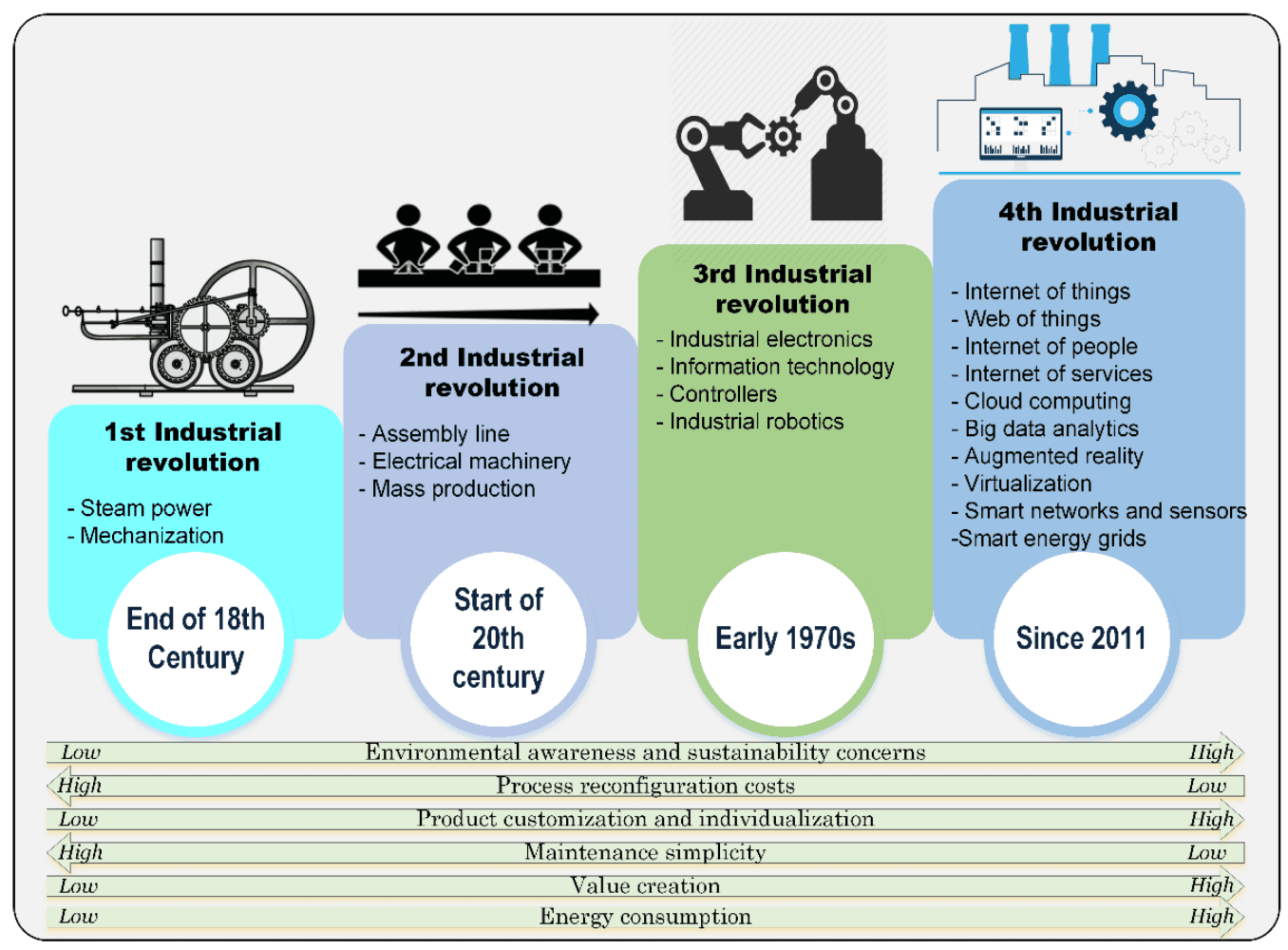
Four industrial revolutions and their links to environmental concerns
3. Benefits of Green Industry
The green industry paradigm offers a multitude of benefits for businesses, society, and the planet:
- Environmental Protection: Reduces greenhouse gas emissions, conserves natural resources, protects ecosystems, and improves air and water quality.
- Economic Growth and Job Creation: Stimulates innovation, creates new markets, and generates employment opportunities in renewable energy, clean technology, and sustainable manufacturing.
- Enhanced Competitiveness: Improves brand image, attracts environmentally conscious consumers, and opens doors to markets with strict environmental standards.
- Cost Savings: Reduces energy and material costs through efficiency improvements and waste minimization.
Improved Public Health: Lessens the health impacts of pollution and promotes healthier communities.
- Resilience to Climate Impacts: Helps businesses and economies adapt to the effects of climate change, ensuring long-term sustainability.
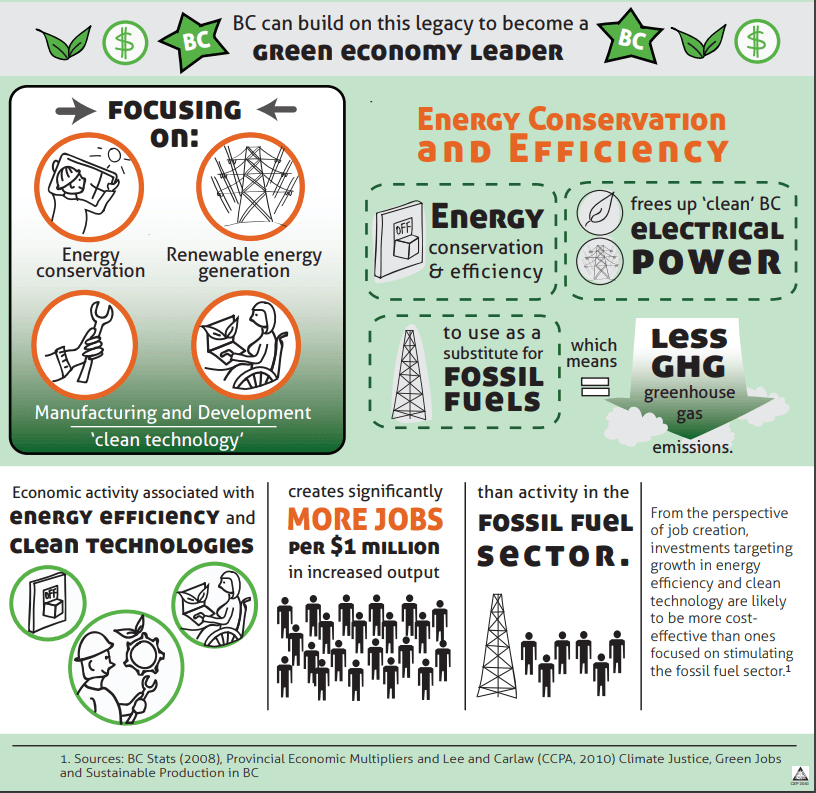
How Energy efficiency and clean technologies create more job opportunities in Energy sector of British Columbia, Canada (Teach Climate Justice, 2023)
4. Key Sectors Within the Green Industry
The green industry revolution is permeating numerous sectors of the economy:
- Renewable Energy: Solar power, wind power, hydropower, geothermal energy, biomass, and other renewable energy sources are replacing fossil fuels.
- Energy Efficiency: Technologies and practices that optimize energy use in buildings, transportation, and industrial processes.
- Green Construction: Sustainable building materials, energy-efficient designs, and water conservation systems.
- Clean Manufacturing: Pollution prevention, resource efficiency, and adoption of circular economy principles in manufacturing processes.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Regenerative farming practices that improve soil health, conserve water, and reduce reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
- Ecotourism: Tourism that minimizes environmental impact, supports local communities, and promotes conservation.
- Waste Management and Recycling: Advanced technologies and systems for sorting, processing, and reusing valuable materials from waste streams.
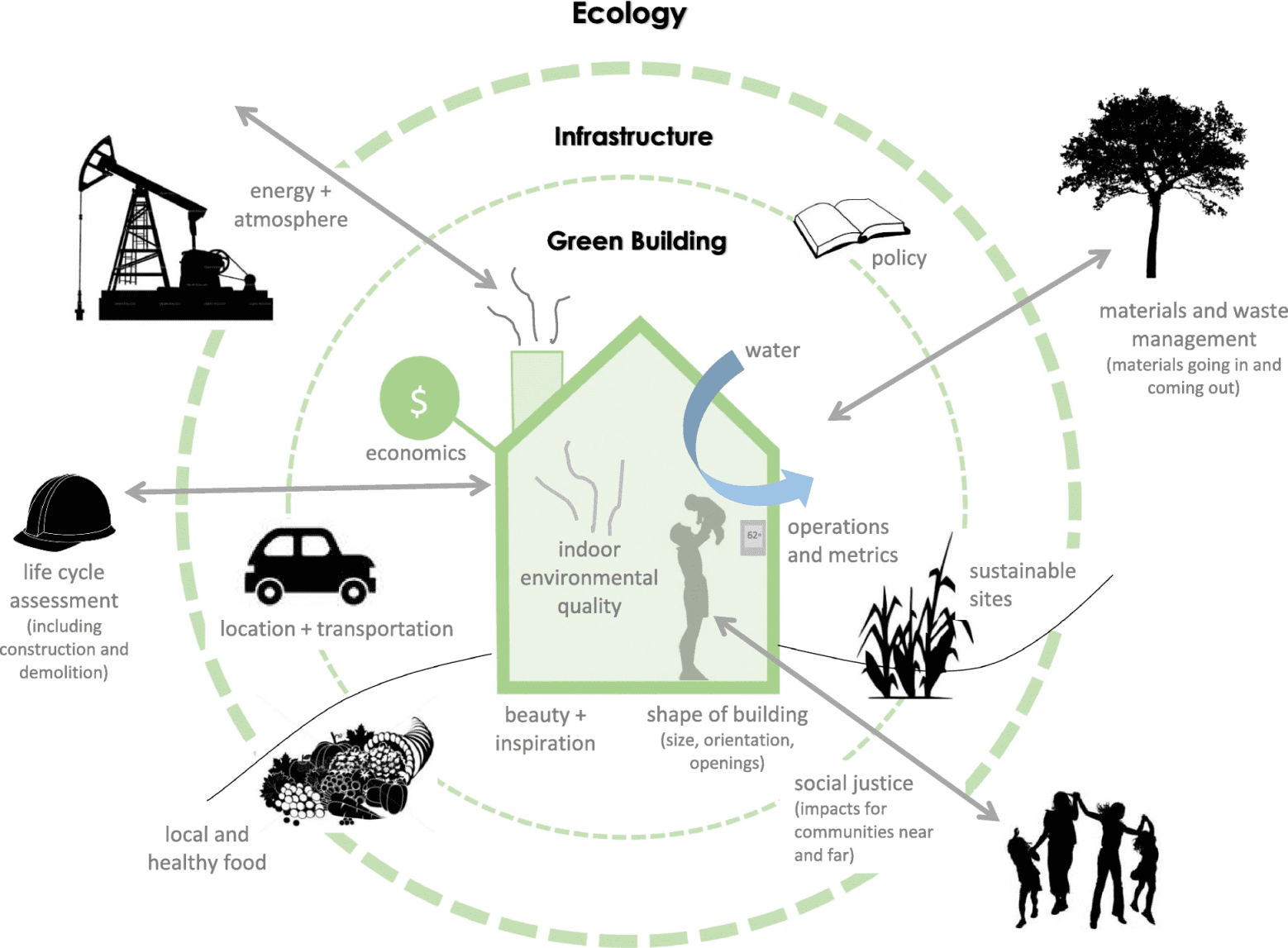
Green Building Factors for Consideration (Cole, 2019)
5. Green Industry Success Stories
Globally, companies across sectors are demonstrating the viability and profitability of green industry practices:
5.1. Tesla:
Tesla’s disruptive vision has revolutionized transportation and energy. The company’s focus on electric vehicles (EVs) and integrated renewable energy solutions underpins a mission to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainability.
Electric Vehicle Revolution:
- Performance Breakthrough: Tesla’s high-performance EVs, like the Model S and Model 3, dispelled myths of slow, limited-range electric cars. This shifted consumer perception and attracted a broader market to EVs.
- Supercharger Network: Addressing range anxiety, Tesla built a global network of Superchargers, facilitating long-distance EV travel and spurring adoption.
- Software-Defined Vehicles: Regular software updates, featuring innovations like Autopilot, maintain Tesla’s technological edge.
Renewable Energy Empowerment:
- Solar Roof and Powerwall: Tesla’s solar roofs and Powerwall home batteries enable consumers to generate and store their own clean energy. This promotes energy independence and reduces reliance on traditional grids.
- Disrupting Energy Models: Tesla’s all-in-one approach (EVs, solar, storage) challenges centralized energy systems, empowering individuals to become active participants in the clean energy transition.
Impact and Future:
- EV Market Catalyst: Tesla accelerated the automotive industry’s shift towards electrification, with major automakers following its lead.
- Mainstreaming Sustainability: Tesla raised consumer awareness of EVs and renewable energy options, fueling broader public interest in sustainable solutions.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Price Parity: Continuously reducing costs remains key to making EVs accessible to a wider market.
- Charging Infrastructure: Further expansion of charging networks is needed to fully address range anxiety.
- Battery Advancements: Improvements in range, charging speed, and cost will further drive EV adoption.
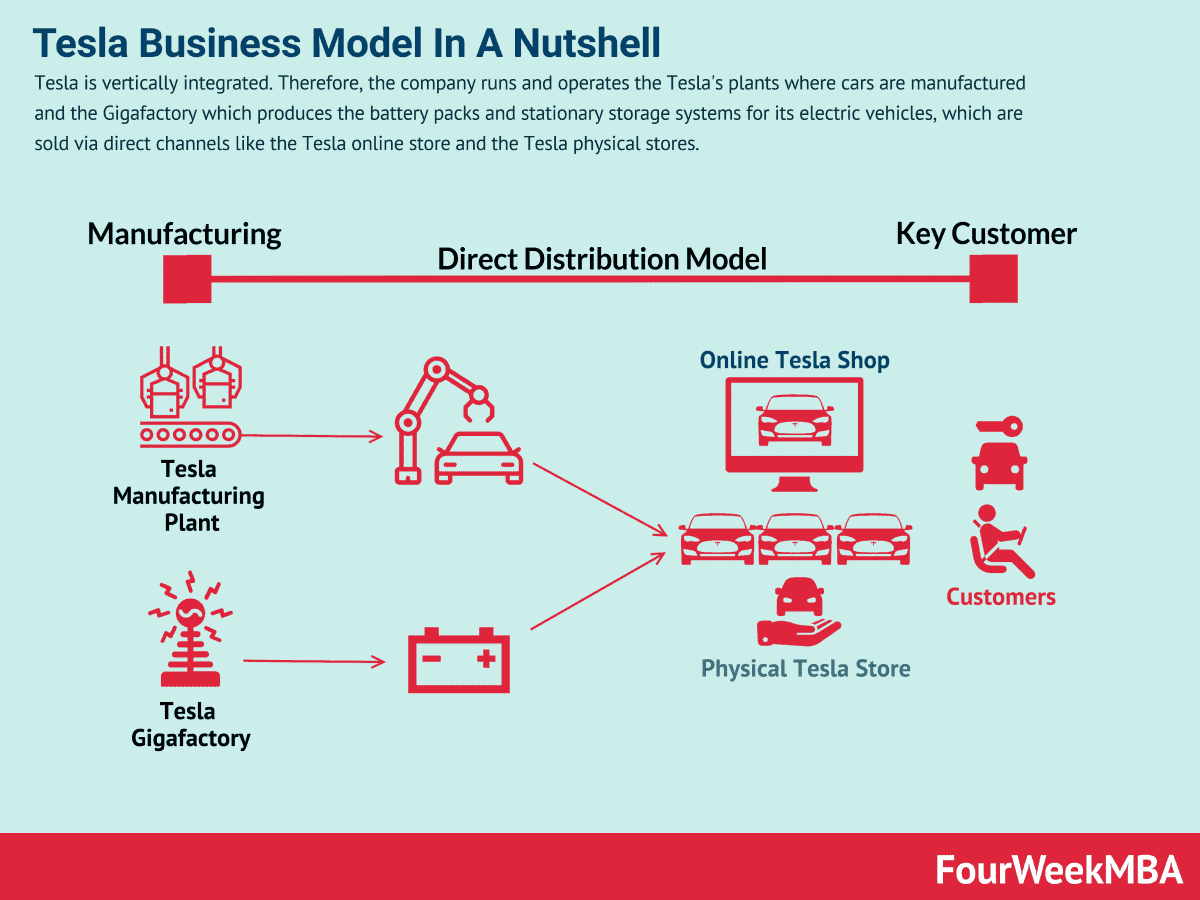
Telsa Sustainable Business Model (Tesla, 2023)
Tesla’s bold approach has transformed how we think about transportation and energy. By making stylish, high-performance EVs and integrated renewable energy solutions, the company is spearheading a more sustainable future. Tesla’s ongoing innovation promises continued progress in both clean energy and the EV market.
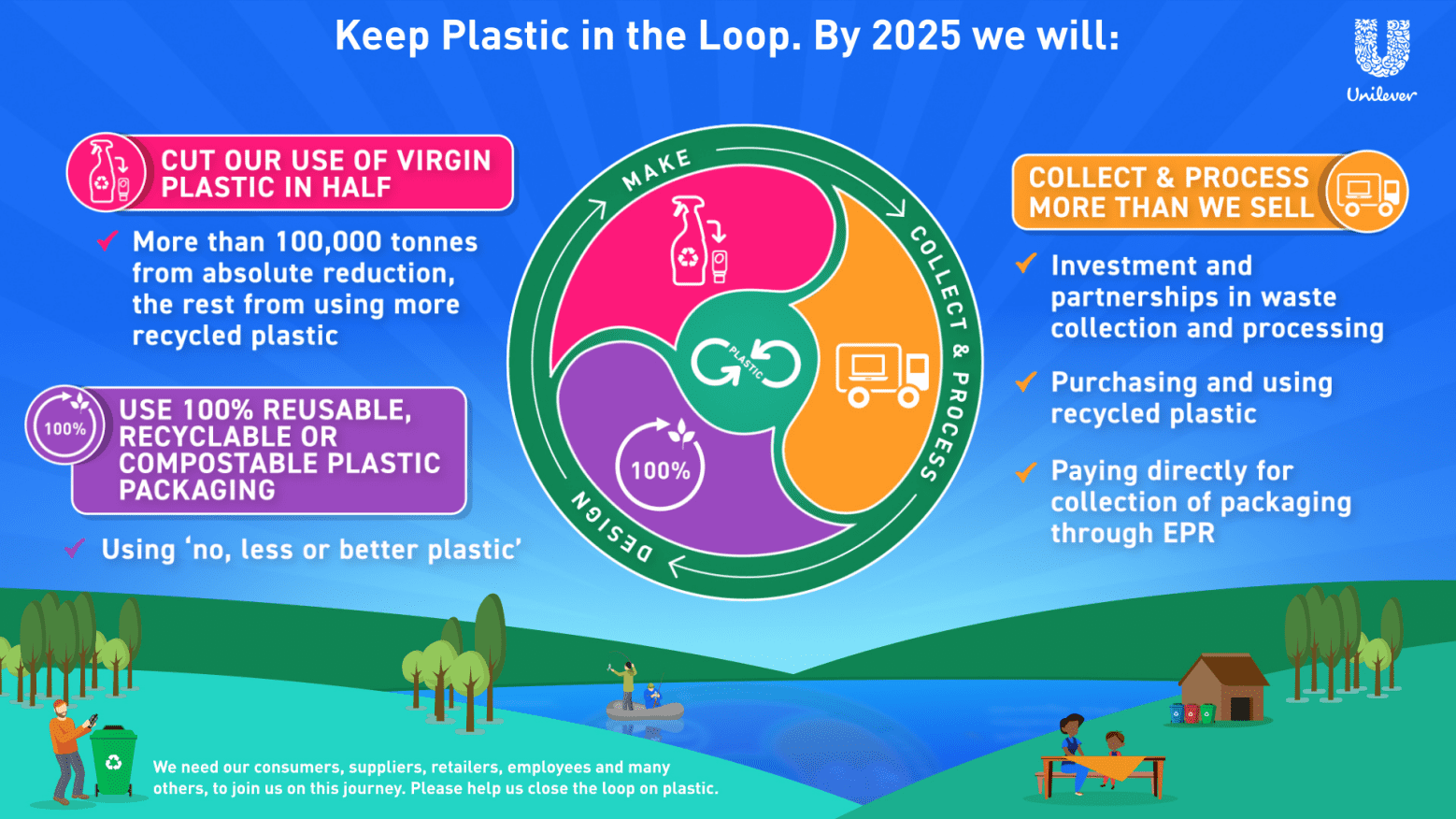
5.2. Unilever:
Unilever, one of the world’s largest consumer goods companies, has undertaken a bold commitment to transform its business model and become a leader in sustainability. This case study explores Unilever’s multi-faceted approach towards achieving ambitious environmental targets.
Unilever’s Sustainable Living Plan (USLP):
- Halving Environmental Footprint: Unilever aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and waste generation across its product lifecycle. This encompasses both manufacturing and consumer use.
- Zero-Waste Operations: The company strives to eliminate non-hazardous waste throughout its facilities and supply chain, seeking circular solutions to minimize landfill contributions.
- Sustainable Sourcing: Unilever is committed to sourcing 100% of its agricultural materials from sustainable sources, reducing the environmental impact associated with raw material production.
Strategies & Initiatives:
- Science-Based Targets: Unilever grounds its goals in science, collaborating with organizations like the Science-Based Targets initiative (SBTi) to ensure targets are ambitious and align with climate change mitigation goals.
- Renewable Energy Integration: The company invests in renewable energy sources within manufacturing facilities and targets a 100% renewable electricity grid by 2030.
- Product Innovation: Unilever reformulates products to reduce water and energy consumption during use. It also explores solutions that minimize packaging waste and increase recyclability.
- Supplier Collaboration: Unilever partners with suppliers to improve sustainability practices throughout its vast supply chain.
Impact and Future Outlook:
- Demonstrated Progress: Unilever has made significant strides in reducing its environmental footprint, demonstrating the feasibility of sustainable practices even within a global conglomerate.
- Influencing the Industry: Unilever’s position as a major player sets a precedent for sustainable business, encouraging competitors and suppliers to adopt similar practices.
- Transformative Potential: Unilever’s commitment to zero waste and sustainable sourcing could drive systemic change within the consumer goods industry.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Complexity of a Global Supply Chain: Managing environmental impacts across a vast, multi-tier supply chain remains a complex challenge.
- Consumer Behavior: Inspiring behavioral shifts towards more sustainable product choices and waste reduction is an ongoing task.
- Policy Landscape: Policies on carbon emissions, waste management, and sustainable agriculture vary across markets, impacting implementation strategies.
Unilever’s program towards circular economy
6. Challenges and Opportunities for Green Industry
The path towards a fully realized green economy isn’t without its obstacles:
- Upfront Costs: Transitioning to green technologies and practices can often involve initial investments, potentially creating a barrier for some businesses.
- Policy Uncertainty: Inconsistent or inadequate government policies and regulations can hinder the long-term planning and investments needed for green industry development.
- Limited Infrastructure: Insufficient infrastructure for renewable energy grids, recycling facilities, or electric vehicle charging stations can slow down adoption.
- Consumer Awareness and Behavior: While consumer demand for sustainable products is growing, lack of awareness or greenwashing can impede progress.
- Global Cooperation: International collaboration is essential in addressing transboundary pollution issues, technology sharing, and setting global standards.
7. Overcoming Challenges, Seizing the Opportunities
Despite these hurdles, the potential rewards of the green industry far outweigh the risks. Here’s how we can accelerate progress:
- Finance and Investment: Mobilizing capital through green bonds, impact investing, and public-private partnerships is critical to scaling up green solutions.
- Government Leadership: Clear policies, emissions targets, financial incentives, and research funding can provide a stable framework for businesses to innovate and transition.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Cross-sector collaboration between businesses, research institutions, and governments can foster innovation and knowledge exchange.
- Consumer Engagement: Building consumer awareness of the benefits of green products and services can drive market demand.
- Capacity Building and Training: Developing a skilled workforce in renewable energy technologies, sustainable design, and circular economy principles is essential.
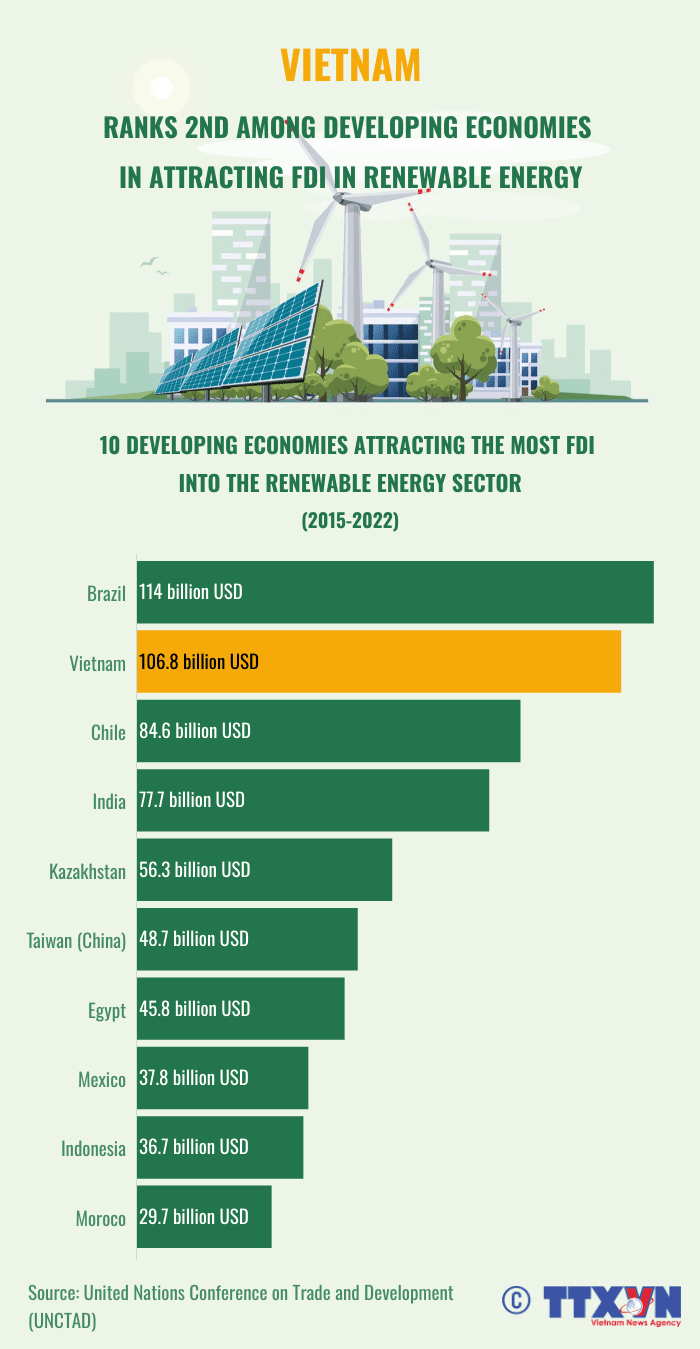
8. Green Industry as a Springboard for Developing Economies
For developing countries such as Vietnam, the green industrial revolution presents a unique opportunity to leapfrog traditional, polluting industries and build a sustainable economic foundation. By embracing renewable energy sources, resource-efficient manufacturing, and sustainable agriculture practices, these nations can attract foreign investment, create jobs, and improve the well-being of their populations.
Vietnam Ranks 2nd Among Developing Economies In Attracting Fdi In Renewable Energy (TTXVN, 2023)
9. The Role of Technology and Innovation
Technological advancements are continuously unlocking new possibilities for the green industry:
- Energy Storage: Breakthroughs in battery technologies and other energy storage solutions are crucial for making renewable energy sources more reliable and competitive.
- Smart Grids: Intelligent power grids optimize energy distribution, integrate renewable energy, and empower consumers to manage their energy use.
- Materials Science: Development of bio-based materials, compostable plastics, and innovative recycling techniques are revolutionizing product design and reducing waste.
- Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence: AI-powered systems can enhance energy efficiency, optimize resource management, and predict environmental risks.
10. The Future of Green Industry: A Roadmap to Sustainability
The green industry is not simply a trend; it’s an economic, environmental, and social imperative. As the global community strives to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals and create a truly carbon-neutral world, green industry principles will be at the forefront of this transformation.
Businesses that embrace sustainability will be the leaders of tomorrow, driving innovation, attracting customers and investors, and building resilience in a changing world. Governments that create conducive policy environments will foster green economic growth, create jobs, and improve their citizens’ quality of life.
The green industrial revolution is a defining challenge and opportunity of our time. By working collaboratively, embracing innovation, and investing in a sustainable future, we can create a thriving economy in harmony with our planet.
| Exclusive article by FPT IS expertAuthor Pham Tuan – Director of VertZero product |